Lepus sinensis, Gray, 1832
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6625539 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6625498 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03822308-B76E-FFD0-FF6B-FB07F8A1F099 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Lepus sinensis |
| status |
|
63. View On
Chinese Hare
French: Lievre de Chine / German: China-Hase / Spanish: Liebre de China
Taxonomy. Lepus sinensis Gray, 1832 View in CoL ,
“China.” Restricted by G. M. Allen in 1938 to “more orless in the region of Canton,” Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China.
It has been placed in the genus Caprolagus and allied with L. hainanus and L. brachywrus. Formerly, L. sinensisincluded L. coreanus as a subspecies. All these relationships have not been supported by genetic analysis. As taxonomists are still trying to clarify the species differentiation in Lepus , the subspecific taxonomy is not elaborated yet. The original descriptions of the subspecies are often not very helpful as they are mostly based on a few exterior characteristics and on a small numbers of individuals. It has been shown that the variability is clinal in more careful investigations. Hence, the distinction in subspecies might be arbitrary and unreasonable. Three subspecies recognized.
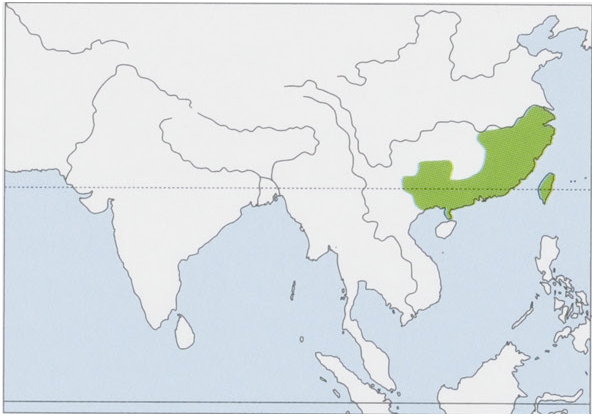
Subspecies and Distribution.
L.s.sinensisGray,1832—SEChinaSoftheYangtzeRiver.
L.s.formosusThomas,1908—Taiwan.
L. s. Province (yuenshanensis China). Shih, 1930 — Hunan
Taxonomic status of the Chinese Hare in NE Vietnam has to be determined. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 350-450 mm, tail 40-57 mm, ear 60-80 mm, hindfoot 81-111 mm; weight 1.1-9 kg.
The Chinese Hare is small, with short ears and short, straight, and coarse hair. Its general appearance is rather uniform butrich in color. Dorsal, head, and chest furis chestnut and rufous. Ventral pelage is paler, and tail is brown. Ears have black triangular tips. Pelage color varies seasonally, with yellowish tone in winter.
Habitat. Edges of grassland habitats and scrubby vegetation in hills but not in rice fields. In Taiwan, Chinese Hares are a minor pest of forestry, and they occur in bamboo habitats up to elevations of 4000-5000 m.
Food and Feeding. Diet of the Chinese Hare consists ofleafy vegetation, green shoots, and twigs.
Breeding. Reproductive season of the Chinese Hare occurs in April-August. Females give birth in burrows. Young are precocial, and littersize averages three young.
Activity patterns. The Chinese Hare is nocturnal but can also be active during the day.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. The Chinese Hares use burrows made by other animals, and they piles fecal pellets outside entrances.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List. The Chinese Hare is also listed as least concern on the Chinese Red List. It is widespread and occurs in protected areas; however, more data are needed to determine population status and current distribution. It is hunted locally for subsistence and sold in markets. Increasing agriculture may isolate populations of Chinese Hares. Populations in Vietnam are thought to be very small, with last confirmed records from the 1990s. Recent surveys did not find Chinese Hares in Vietnam. Major threats to Chinese Hares in Vietnam are habitat loss and hunting.
Bibliography. Allen (1938), Angermann (2016), Corbet (1978), Dao Van Tien (1978), Ellerman & Morrison-Scott (1951), Flux & Angermann (1990), Hoffmann & Smith (2005), Lissovsky (2016), Smith (2008c), Smith & Johnston (20080), Wu Chunhua et al. (2005).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.