Panorpa zhuohengi, Wang & Suzuki, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2022.794.1651 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7C993859-23E0-4380-B9CF-2C1E20EE5898 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6310637 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D216769D-9C58-4725-8856-E6C4D0D10516 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:D216769D-9C58-4725-8856-E6C4D0D10516 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Panorpa zhuohengi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Panorpa zhuohengi View in CoL sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
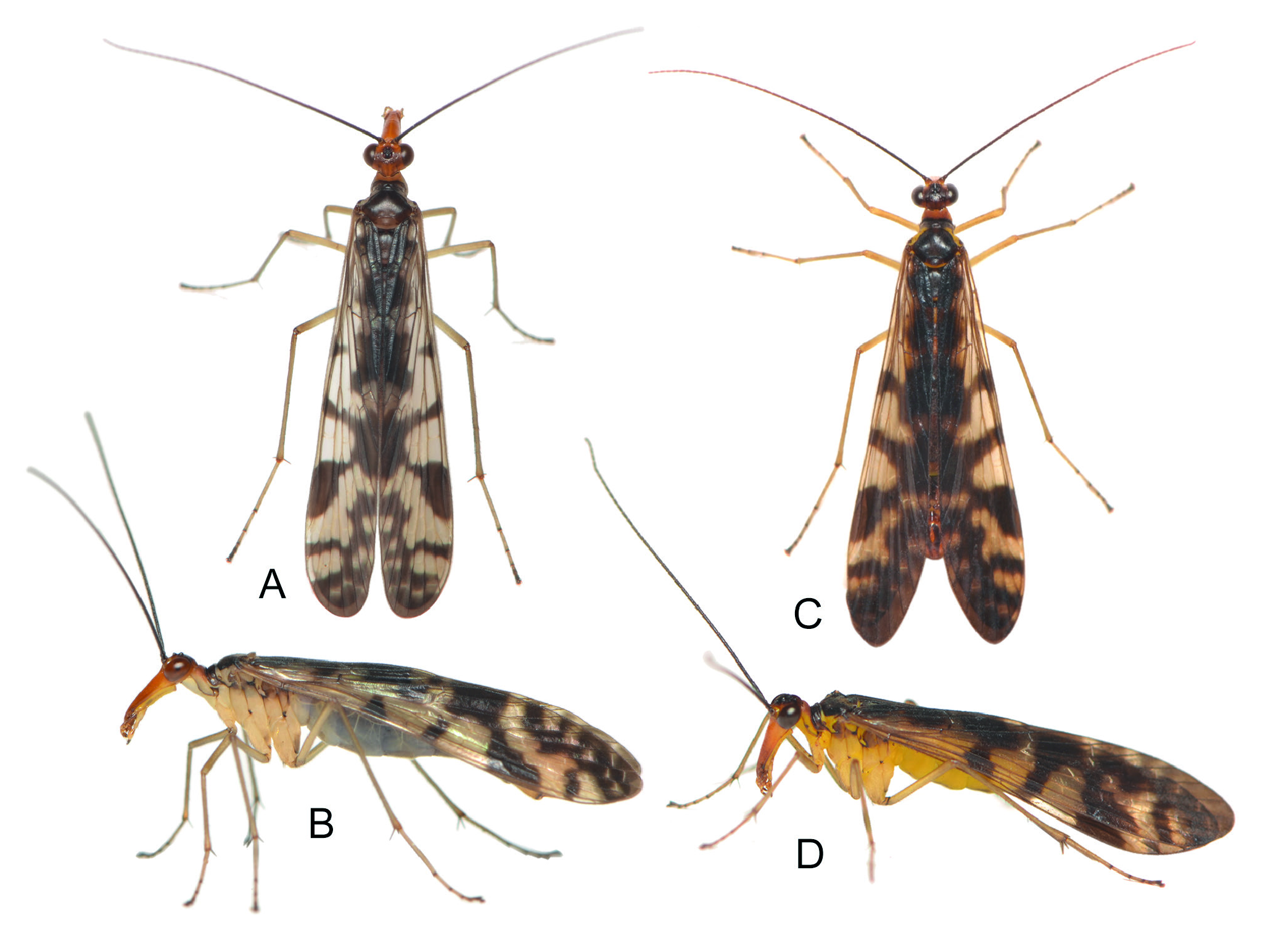
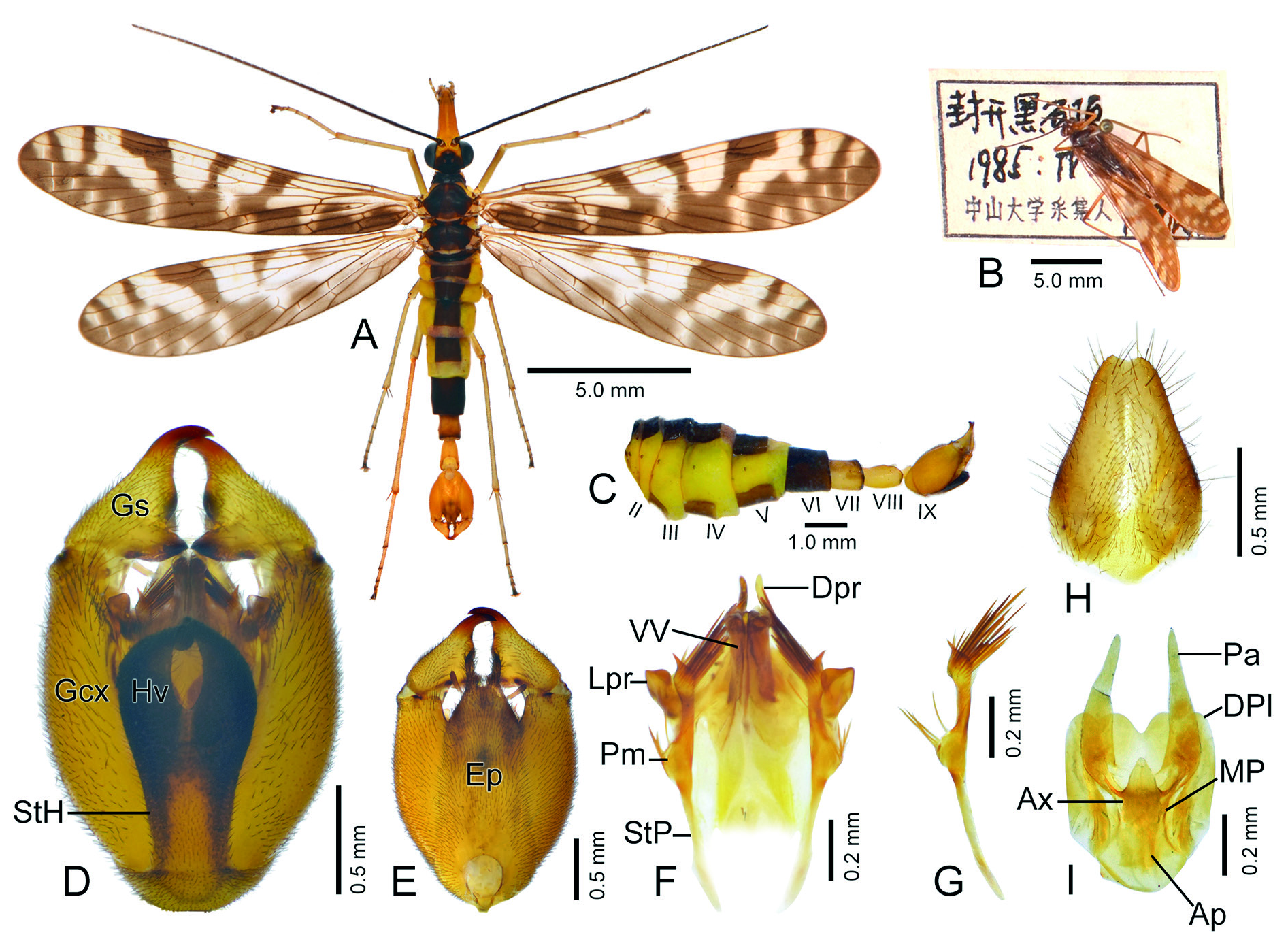
Figs 4C–D View Fig , 5–6 View Fig View Fig
Diagnosis
This species is superficially similar to Panorpa gressitti Byers, 1970 , but can be readily differentiated from the latter by the following characters: in the living insects, 1) body sides light yellow and wing markings dark (cf. body sides greyish and wing markings lighter); in males, 2) gonostylus with basal process stout with a pointed apex (cf. bifurcated); 3) parameres enlarged and bearing long bristles subapically (cf. slender and bearing short bristles); and in females, 4) medigynium with distinct apodemes (cf. lacking). It is also similar to Panorpa obliqua Carpenter, 1945 , but can be readily differentiated by the structure of the male parameres.
Etymology
The new species is named after my friend Mr Zhuo-Heng Jiang, who collected the type specimens. Noun in the genitive case.
Material examined
Holotype CHINA • ♂; Guangdong, Fengkai, Heishiding (Dark Rock Peak); alt. 200 m; 15 Apr. 2019; Zhuo-Heng Jiang leg.; DALU.
Paratypes CHINA • 3 ♂♂; same collection data as for holotype; DALU • 1 ♂; same locality as for preceding; 17–18 Apr. 2004; Chun-Tian Zhang leg.; SYSU • 2 ♀; same locality as for preceding; 10 Apr. 1985; Zhen-Yao Chen leg.; SYSU .
Description
Male HEAD ( Fig. 5A View Fig ). Vertex black medially and yellowish brown near compound eyes and antennal sockets. Ocellar triangle black. Rostrum yellowish brown, long and stout. Scape yellowish brown basally and
dark brown distally, pedicel dark brown, flagellum black with approximately 38 flagellomeres.
THORAX ( Fig. 5A View Fig ). Pronotum black, bearing 6–8 stout setae along anterior margin. Meso- and metanotum black, each with yellowish, gourd-shaped mesal stripe. Pleura light yellow. Legs yellowish brown with distal tarsomeres blackish.
WINGS ( Fig. 5A View Fig ). Membrane hyaline, slightly tinged with yellowish brown. Markings dense and dark brown. In forewing, apical band broad and usually with series of hyaline spots along apical cross-veins; pterostigmal band oblique, with an intact basal branch and detached apical branch; apical branch fused with posterior portion of apical band; marginal spot elongated posteriorly and fused with pterostigmal band and forming V-shaped pattern; basal band broad; basal spot fused with basal band along hind margin with few hyaline spots along basal cross-veins; Sc extending approximately at middle of anterior margin; Rs five-branched; 1A ending far beyond origin of Rs. In hindwing, markings similar but more reduced than those of forewing.
ABDOMEN ( Fig. 5A, C View Fig ). T1–T5 dark brown, S1–S5 brown, pleural membrane yellow. Notal organ on posterior margin of T3 slightly protruded, semicircular and bearing dense setae posteriorly; postnotal organ on anterior portion of T4 acute and curved dorso-cephalad. A6 black, cylindrical and slightly longer than T5. A7 yellowish brown and blackish on apical margin, approximately half as long as A6, cylindrical and slightly beveled apically; A8 similar but slightly longer, thinner, and greatly beveled apically.
GENITALIA ( Fig. 5D–G View Fig ). Genital bulb yellowish brown, oval. Epandrium long trapezoidal, greatly constricted in distal portion, with deep terminal emargination and a pair of finger-like processes laterally. Cercus long clavate and blackish. Hypandrium with long and broad basal stalk, and distally split into a pair of hypovalves; hypovalves slightly shorter than basal stalk of hypandrium, widely divergent basally and slightly convergent distally, and not reaching lateral processes of aedeagus. Gonocoxites beveled apically; gonostylus approximately half as long as gonocoxites, and bearing an obtuse triangular median tooth and stout basal process. Parameres each with slender basal stalk, and greatly enlarged basally and subapically; four long stout bristles on outer margin of basally enlarged portion; and dozens of longer bristles on inner side of subapically enlarged portion; apex of paramere pointed and slightly curving laterad. Aedeagus with ventral valves sclerotized and columnar; dorsal valves very short and inconspicuous; dorsal processes longer and finger-like; lateral processes slightly elongated, stout and nearly truncated with an indistinct terminal emargination.
Female
Similar to males in general appearance, but with slightly denser wing markings ( Fig. 5B View Fig ).
GENITALIA ( Fig. 5H–I View Fig ). Subgenital plate subtriangular with shallow terminal emargination, and bearing sparse long setae marginally. Medigynium with broad dorsal plate emarginated in V-shape terminally; posterior arms slightly arcuate and tapering distally; axis shorter than posterior arms with short and stout apodemes proximally; decorated area of axis greatly elongated posteriorly, subtranslucent and subtriangular.
Distribution
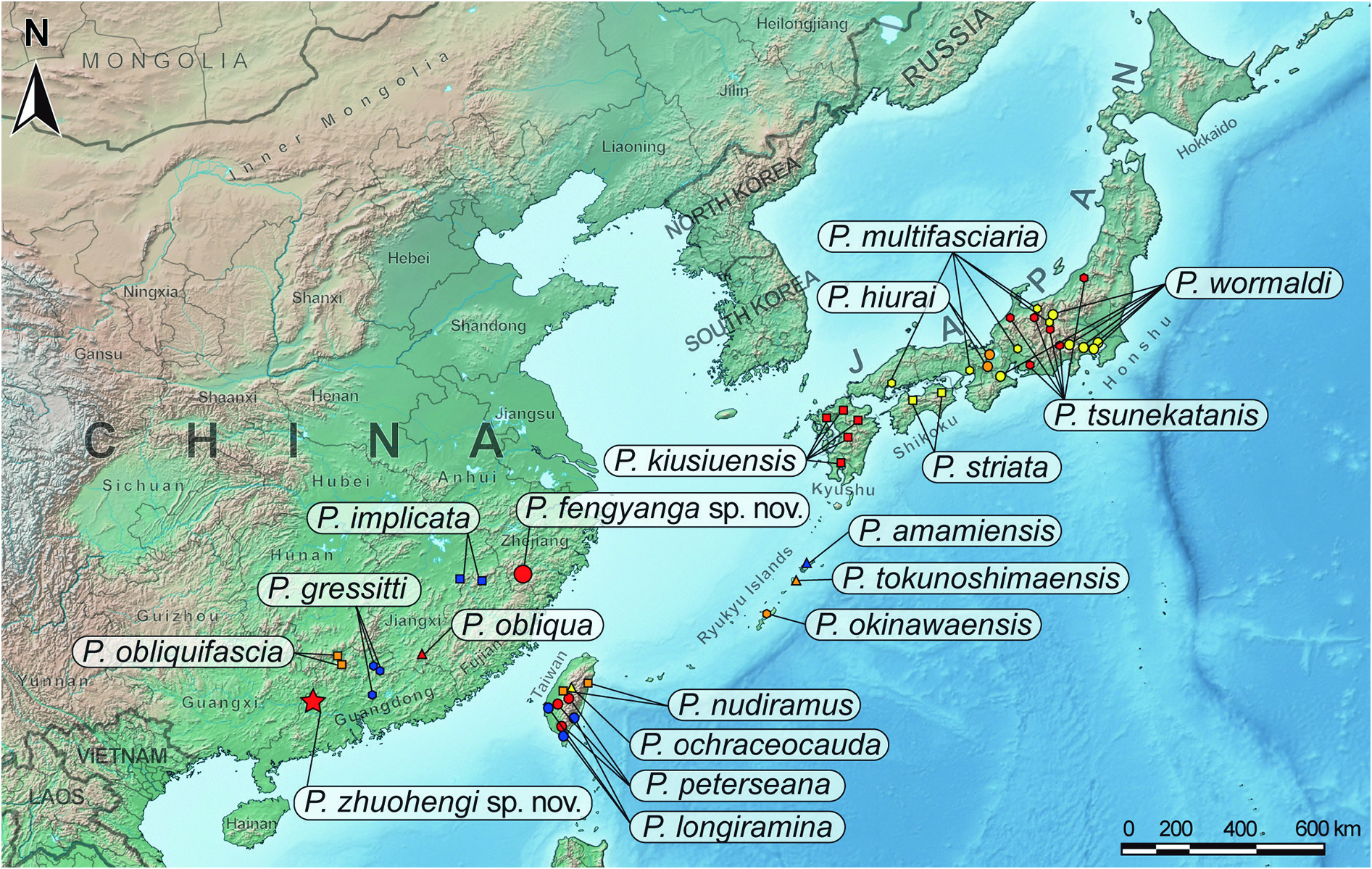
China: Guangdong: Fengkai ( Fig. 6 View Fig ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Pistillifera |
|
SuperFamily |
Panorpoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Panorpinae |
|
Genus |