Austrokatanga, Weirauch, Christiane, Rabitsch, Wolfgang & Redei, David, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.187595 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6219692 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03889007-9B62-FFF7-FF0B-1FDCFDD3F87C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Austrokatanga |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Austrokatanga View in CoL , new genus
( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 –8)
Etymology: Named for its similarity with species in the genus Katanga , together with the prefix indicating its distribution in the southern continent Australia. The gender is feminine.
Type species: Austrokatanga monteithi , new species
Diagnosis: Recognized by the moderately stout body (males longer and stouter than females), mostly dull brown coloration, elongate, almost cylindrical head, pigments of ocelli present, but lens absent, straight and relatively slender labium with second and fourth segment short, third segment long, cylindrical, antennal setation similar in males and females, legs moderately stout, with strong spine ventromedially on distal third of fore and, to a lesser degree, on middle femora, males longer and stouter than females with fore and middle legs stouter and armature more pronounced. The only known species is apterous in both sexes. Similar to Katanga and Cimbus with respect to general body shape, elongate head, straight labium with third segment about 5 times longer than second segment, lack of fossula spongiosa on fore and middle tibiae, and presence of a subapical spine on ventral surface of fore tibia. Distinguished from both genera by the cylindrical head shape, the slightly greater diameter of the labium, the armature of fore and middle femora, shape of the hind leg, armature of pregenital abdomen, and the pygophore with process on inner margin triangular (narrow triangular in Cimbus , truncate in Katanga , Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ).
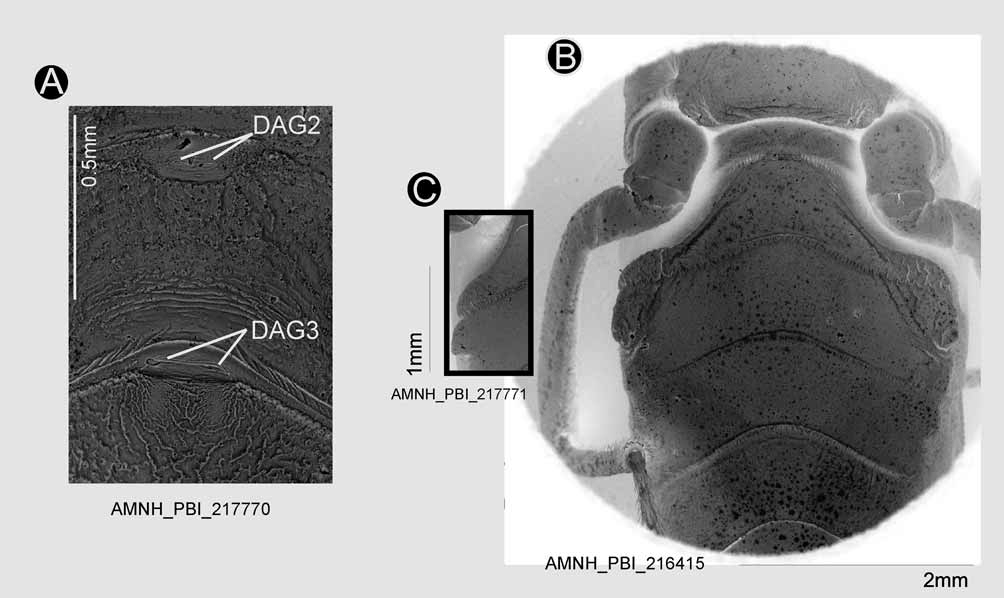
Description: Apterous male: elongate ovoid, of moderate size, head almost cylindrical, thorax stout, abdomen ovoid ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Vestiture: Head, thorax, and abdomen glabrous, with simple and relatively sparse adpressed and suberect setation on antennae and legs ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 ). Coloration ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ): General coloration dull brown with yellowish spots. Structure: Head: almost cylindrical, anteocular area about 1.5 times as long as postocular, postocular region ranging from almost globular to ovoid in dorsal view ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 A–B, 5), mandibular plate small with distinct median depression, maxillary plate of moderate size with rounded apex, genal region distinct anterior to maxillary plate, clypeus slender and slightly raised, labrum subdivided, antennifer pronounced, laterally situated on head at midpoint between anterior margin of eye and apex of clypeus, ocellar lens absent, but pigments of ocelli present on weakly raised area posterior to posterior margin of eye ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C); Eyes: small, half as high as head, globular; Antenna: scapus slender, reaching apex of clypeus, pedicellus about twice length of scapus, distal two-thirds with relatively sparse and short setation, distalmost trichobothrium situated at about three-fourths and with distinct oval membrane ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 D–E, 5A–B), preflagelloid distinct, basiflagellomere divided into two pseudosegments, intraflagelloid present, distiflagellomere divided into four pseudosegments, antenna thus divided into 8 subdivisions; Labium: relatively slender, almost straight; second segment (first visible) short and stout, third segment about 5 times longer than second, straight, fourth segment about as long as second, gently tapering towards apex. Thorax: Pronotum with anterior and posterior lobes at most weakly developed, collar indistinct, laterally with strong, anteriad directed, acute spines; mesonotum with small wing pads, scutellum represented by weak subparallel, longitudinal elevations; prosternum with stridulatory bearing process long and slender, apex rounded ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C); opening of metathoracic gland small ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 D), meshwork-like cuticle of evaporatory area ( Weirauch, 2006) restricted to shallow depression adjacent to metacetabulum. Legs: moderately slender to relatively stout ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 A), coxae globular, trochanters slender and short; fore femur weakly or moderately bent subbasally, armed with ventral, medial process at about apical third ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 E), fore tibia straight with more or less pronounced small tubercles ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 E) and subapical spine on ventral surface ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 F); middle and hind legs more slender than fore leg, femora and tibiae unarmed; fossula spongiosa absent on fore and middle leg ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 F–G); pretarsus with moderately stout claws ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 H). Abdomen: suture between fifth and sixth tergites curved anteriad medially, dorsal abdominal gland (DAG) 1 absent, DAG 2 (tergites 4/5) with close-set paired openings, paired openings of DAG 3 (tergites 5/6) wider apart than those of DAG 2 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A); sternites fused, lines of fusion distinct ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 B), median area of third to sixth sternites raised and flat, with distinct, keel-like rim on third sternite, keel-like rim extending to fourth sternite in large specimens, distinct tubercles present at posterior margin of third sternite and anterior margin of fourth sternite in moderately seized and large specimens ( Figs 4 View FIGURE 4 B–C, 6). Genitalia: Pygophore: ovoid, posterior inner margin with median triangular process ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 B); Parameres: relatively stout and angular, with distinct subapical tooth on anteromedial surface ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 A); Aedeagus: in semi-extended condition elongate ovoid with membranous apical lobe and subapical lateral lobes, basal plates relatively small and rounded, basal plate extension short, basal plate struts high and narrow, dorsal phallothecal sclerite distinct only in distal portion, squarish with rounded edges ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E).
Apterous female: Similar to male, but slightly smaller and more slender ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ) than male, spines on pronotal collar less distinct, legs and especially fore femur more slender ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 A), femoral spine smaller, tibia unarmed, abdominal sternites sloping in cross section, without distinct raised median area and without a keellike rim or lateral tubercles ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 B). External genitalia: short and plate-like, as in Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 F. Internal genitalia: as in Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 G, with large lateral membranous pouch on bursa copulatrix; vermiform gland with both, section 2 (muscle attachment portion) and section 3 (glandular portion) elongate and slender; lateral spermathecae with slightly widened duct and ovoid pouch.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Ectrichodiinae |