Krumbachia subterranea Reisinger, 1933
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2022.798.1671 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F136E044-62C8-4FB3-8160-7DAE663D9600 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6323873 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038A87DA-A76D-FF8C-0406-FEC0FD6E0E4C |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Krumbachia subterranea Reisinger, 1933 |
| status |
|
Krumbachia subterranea Reisinger, 1933 View in CoL
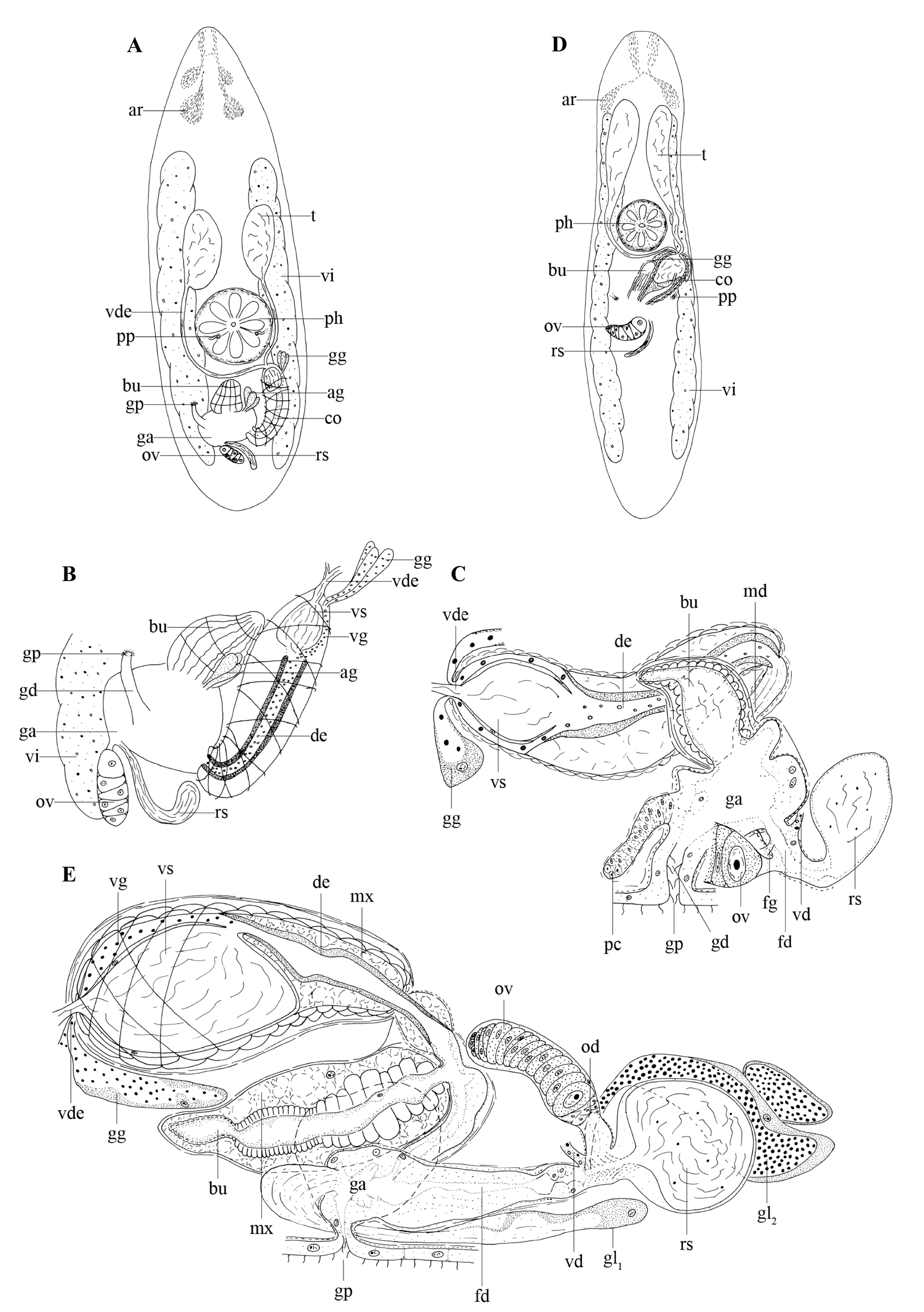
Fig. 8A–C View Fig
Material examined
Neotype GERMANY • 1 spec., studied alive and sagittally sectioned; Hessen; 50°46′30″ N, 09°30′18″ E; 9 Aug. 2011; A.M. Houben and W. Proesmans leg.; submersed meadow at the banks of the Breitenbach creek; neotype no. 823 ; HU. GoogleMaps
Reference material
GERMANY • 1 spec., live observations; same collection data as for neotype GoogleMaps .
Description
The examined specimens are around 2.5 mm long. The body is slender with a somewhat pointy anterior end and rounded posteriorly (see Fig. 8A View Fig ). Adenal rhabdite glands occur just behind the brain ( Fig. 8A View Fig : ar). Paired protonephridiopores (pp) are positioned ventrally, very near to the mouth ( Fig. 8A View Fig : pp). A rosulate pharynx ( Fig. 8A View Fig : ph) is situated just behind the centre of the body.
The gonopore ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig : gp) is located at ±75% of the body and connected to the gonoduct ( Fig. 8B– C View Fig : gd). The gonoduct is surrounded by an inner circular and outer longitudinal muscle layer, and lined with a ciliated, nuclear epithelium resembling the epidermis. The genital atrium ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig : ga) is surrounded by a similar musculature and lined with a high, nucleated epithelium. On both lateral sides of the genital atrium, a group of proliferating cells ( Fig. 8C View Fig : pc) is found. A large group of eosinophilic glands is situated posterior to the genital atrium and probably enters this atrium anteriorly (not drawn on the reconstruction).
The large, egg-shaped testes ( Fig. 8A View Fig : t) lie anterior to the pharynx and ventral to the vitellaria ( Fig. 8A– B View Fig : vi). Paired vasa deferentia unite to form a single vas deferens ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig : vde) just before entering the copulatory bulbus ( Fig. 8A View Fig : co). Two layers of spiral muscles surround the long, curved copulatory organ, which bends up to 80° towards its distal end. The copulatory organ bears an intracapsular seminal vesicle ( Fig. 8B–C View Fig : vs) and a strongly sclerotised ejaculatory duct ( Fig. 8B–C View Fig : de). Several coarsegrained, extracapsular eosinophilic glands ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig : gg) enter the copulatory organ at the proximal end. Their secretion is lightly basophilic when entering the copulatory organ, however, it becomes strongly eosinophilic in the ejaculatory duct. A cone-shaped bursa ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig : bu), surrounded by strong inner circular and outer longitudinal muscles, lies next to the copulatory organ and opens into the genital atrium.
The vitellaria extend from the region of the rhabdite glands to the posterior end ( Fig. 8A View Fig : vi). The vitelloducts ( Fig. 8C View Fig : vd) fuse just before opening into the female duct ( Fig. 8C View Fig : fd). Furthermore, this duct is surrounded by a layer of circular muscles and receives the oviduct, a seminal receptacle ( Fig. 8A–C View Fig : rs), and the female glands ( Fig. 8C View Fig : fg). The seminal receptacle is provided with a short stalk, which also is surrounded by circular muscles.
Discussion
See the general discussion on the genus Krumbachia Reisinger, 1924 .
Previously known distribution
Ruhr, Germany ( Reisinger 1933), riparian forest near Schlitz, Germany ( Schwank 1981). Common species in Europe ( Lanfranchi & Papi 1978).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |