Uca (Paraleptuca) splendida ( Stimpson, 1858 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4083.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FC132216-6CFB-4E3F-B166-6F9BE3C50588 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6069882 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038B87E0-2E7C-5D7E-FF6A-3A3F83196146 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Uca (Paraleptuca) splendida ( Stimpson, 1858 ) |
| status |
|
Uca (Paraleptuca) splendida ( Stimpson, 1858) View in CoL
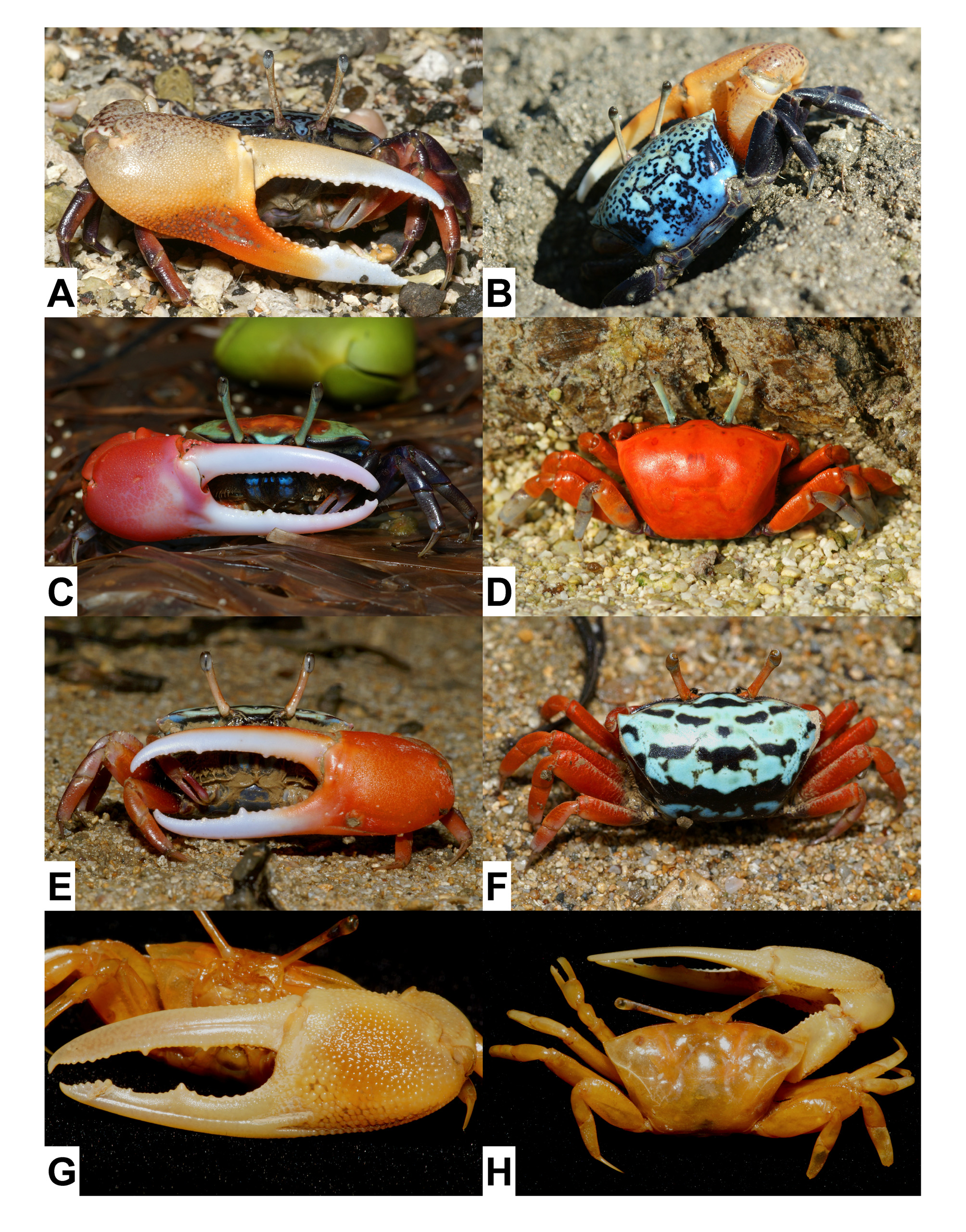
( Fig. 4E, F View FIGURE 4 )
Gelasimus splendidus Stimpson, 1858: 99 [type locality: Hong Kong]; 1907: 106, pl. 14(2) (see Shih et al. 2012 for list of citation of synonyms).
Uca crassipes View in CoL — Aoki & Wada 2013: 791 (not Gelasimus crassipes White, 1847 View in CoL ). Uca (Paraleptuca) splendida View in CoL —Shih et al. 2012: 34, figs. 2, 3, 4, 6, 7C. Uca splendida View in CoL — Shih 2012b: 68, figs. 97, 98.
Material examined. See Shih et al. (2012) for specimens from Taiwan (including Penghu and Dongsha).
Distribution. Ryukyus (Iriomote), Taiwan (including Penghu, Kinmen, Dongsha), China (including Hainan and Hong Kong), and Vietnam.
Remarks. Based on the molecular analyses and morphological comparison, Shih et al. (2012) resurrected Uca splendida , which was synonymized with U. crassipes by Crane (1975). It is easy to distinguish the two species by the morphologies of the carapace. The coloration is also useful for species identification, but juveniles sometimes show similar color patterns (Shih et al. 2012: figs. 4, 5). Whereas U. crassipes is widely distributed from the eastern Indian Ocean to the western Pacific, U. splendida is restricted to the continental coast, including Taiwan, southeastern China, and Vietnam.
The record of Uca splendida from Xiamen (Fujian, China) ( Cano 1889: 92, 234) has been discussed by Shih et al. (2012: 43). An individual of this species from the adjacent islet, Lieyu (= Lesser Kinmen), has been observed and photographed (P.-Y. Hsu, personal communication), which supports the finding from Xiamen. It is possible that the northernmost limit of this species in the continental East Asia is the region of Xiamen and Kinmen.
In spite of the close proximity, no specimens of U. splendida have been reported from the Ryukyus. However, in the phylogeographic study of U. crassipes , using 504-bp mitochondrial control region sequences, Aoki & Wada (2013: appendix table 2) found specimens from Vietnam and Iriomote, with haplotypes (H75, H76 and H77) that are very different from those of other specimens. These haplotypes have been aligned and compared with sequences of U. splendida in Shih et al. (2012) that clearly support the occurrence of U. splendida in Iriomote , the Ryukyus (unpublished data). Nevertheless, it is likely that U. splendida is rare in Iriomote, as only three specimens were collected, compared with 19 specimens of U. crassipes from this island ( Aoki & Wada 2013: table 1).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Paraleptuca |
Uca (Paraleptuca) splendida ( Stimpson, 1858 )
| Shih, Hsi-Te, Lee, Jung-Hsiang, Ho, Ping-Ho, Liu, Hung-Chang, Wang, Chia-Hsiang, Suzuki, Hiroshi & Teng, Shao-Jyun 2016 |
Gelasimus crassipes
| White 1847 |