Insuetifurca xiae, Li, Xiaochen, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.187234 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5627402 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038ED76E-FF9F-F04E-25C7-FDDEFC2E2A7C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Insuetifurca xiae |
| status |
comb. nov. |
Insuetifurca xiae View in CoL comb. nov. ( Li, Su & Yu, 2004)
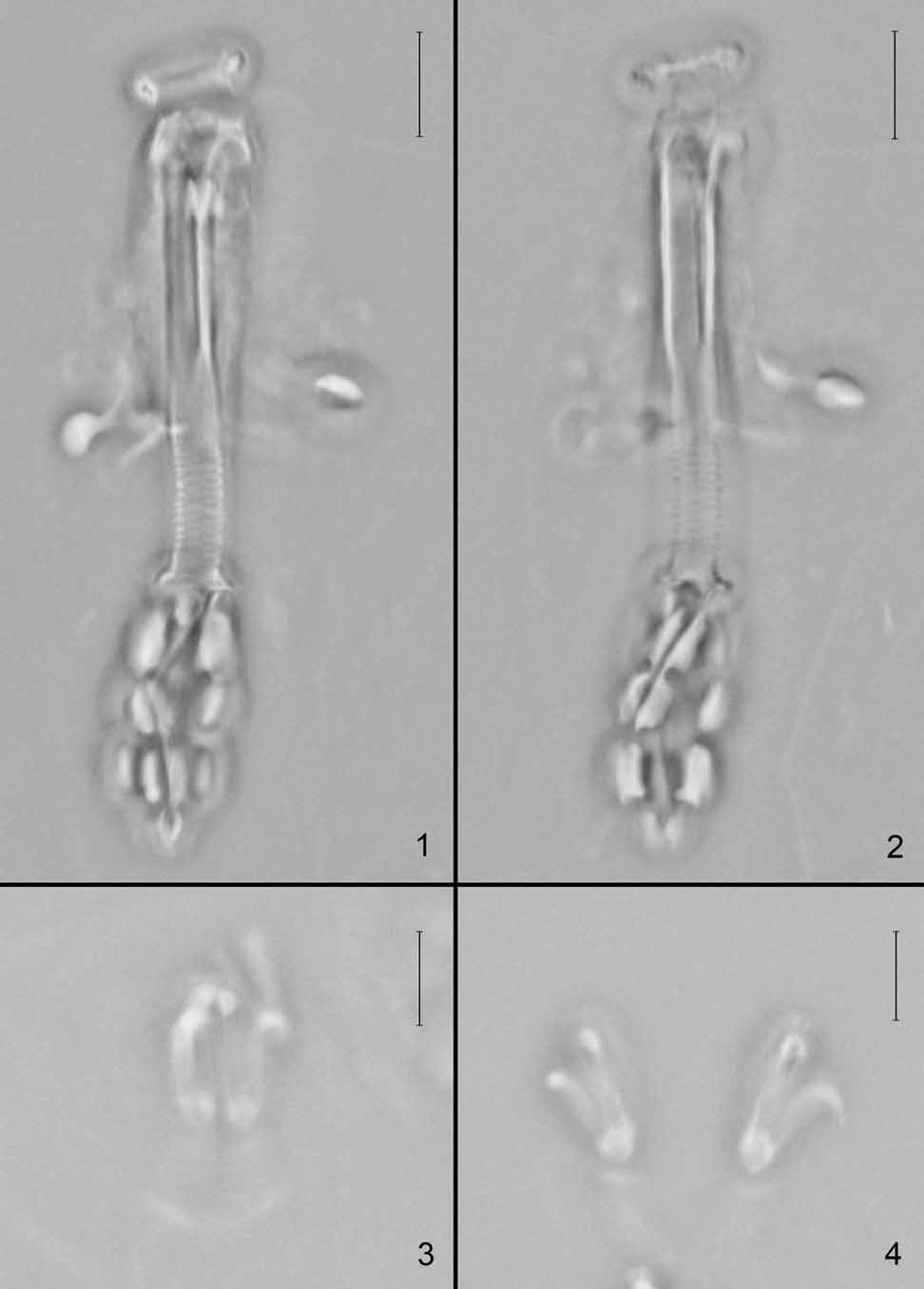
Figs. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 4 –7, Table 1 View TABLE 1
Material examined: Holotype (Slide number 04/02/002) from Zhaobaoshan, Zhenhai County, Zhejiang Province, China. Additional material: three adults (Slide numbers Hi0704021, Hi0704023, Hi0704024) from the Five-Finger Mt. (18°52.920΄N, 109°39.698΄E) at 1200 m above sea level, Hainan Province, China ( Li et al., 2008). All specimens were mounted in Hoyer’s medium and deposited at the College of Life Sciences, Shaanxi Normal University.
Description: Colorless, eyespots not visible (possibly dissolved after fixation), cuticle smooth without pores. Mouth antero-ventral with ten small peribuccal lamellae. Oral cavity armature well developed and composed of two bands of teeth in the posterior part of the cavity. First band of teeth is a row of small ridges parallel to the main axis of the buccal tube, slightly longer in the medial portion and just anterior to second band of teeth; second band of teeth consists of three transverse crests/ridges, divided into ventral and dorsal series. Buccopharyngeal tube consisting of a rigid anterior portion and a posterior flexible portion with spiral thickenings on the wall ( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 5). Thin walled, buccal tube (rigid portion of bucco-phayngeal tube) with ventral lamina; buccal tube much longer than the pharyngeal tube. Pharyngeal tube with spiral thickenings, with screw threads disconnected. Stylet supports inserted close to the junction of buccal and pharyngeal tube. Stylet furcae well developed with the posterior processes arched and converging backwards. Pharyngeal bulb elliptical, with apophyses, three short-rod shaped macroplacoids and a microplacoid. Three macroplacoids equal in length, sometimes the second slightly shorter. The third macroplacoid with inward-projecting enlargement at the posterior end. Apophyses and microplacoid well developed.
Claws of a slightly modified Macrobiotus type with the basal portion subdivided into a very short stalk and a large distal portion less sclerified than the common tract. Lunules thin and smooth. Accessory points well developed on the primary branches of all claws. Crescent-shaped cuticular bar present at the base of claws I–III ( Figs. 3–4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 , 6–7). Claw sequence 2-1-1-2. Claws increasing in size from I to IV.
Remarks: Measurements of all available specimens are given in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . The specimens from Hainan are smaller than the holotype in body size.
Differential diagnosis: Insuetifurca xiae was originally assigned to the genus Biserovus ( Li, Su & Yu, 2004) . Insuetifurca differs from Biserovus by having lunules and by the peculiar shape of the stylet furcae, with the posterior process arched and converging backwards. The characters of the claws and the stylet furcae in I. xiae were misinterpreted in the original description ( Li, Su & Yu, 2004). The erroneous assignment resulted from the poor quality of the microscope used.
Up to now the genus Insuetifurca contained only two species, I. arrowsmithi ( Kathman & Nelson, 1989) and I. fujiense ( Ito, 1997) ( Guidetti & Pilato, 2003) . I. xiae comb. nov. differs from I. arrowsmithi by having a much lower pt of the phayngeal tube and by the presence of crescent-shaped cuticular bars below claws I–III; I. xiae comb. nov. differs from I. fujiense by having the macroplacoids equal in length or the second as the shortest instead of the macroplacoids increasing in length from the first to the third and by the presence of crescent-shaped cuticular bars below claws I–III.
FIGURES 5–7. Insuetifurca xiae comb. nov. ( Li, Su & Yu, 2004) (holotype): 5, buccal apparatus; 6, claws on the second pair of legs; 7, claws on the hind legs. Figure 5: scale bar = 10µm; figures. 6–7: scale bar = 5µm.
Character Holotype Additional specimens (Hainan Province)
(Zhejiang Province)
to be continued.
Character Holotype Additional specimens (Hainan Province)
(Zhejiang Province)
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30770254). I sincerely thank Dr. Sandra Claxton for the English revision of the paper.
TABLE 1. Measurements of Insuetifurca xiae comb. nov. (Li, Su & Yu, 2004). Abbreviations: PBL = primary branch length; SBL = secondary branch length.
| 04/02/002 μm pt | Hi0704021 μm pt | Hi0704023 μm pt | Hi0704024 μm pt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body length Buccal tube length | 368.6 31.3 | 202.8 26.0 | 208.0 23.4 | 221.0 24.7 |
| Buccal tube width | 4.7 15.02 | 3.9 15.0 | 3.6 15.56 | 3.6 14.57 |
| Phayngeal tube length Bucco-pharyngeal tube length | 10.4 33.23 41.8 | 10.4 40.0 36.4 | 10.4 44.44 33.8 | 9.1 36.84 33.8 |
| Stylet support insertion point | 28.7 91.69 | 23.4 90.0 | 20.8 88.89 | 22.1 89.47 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |