Stenodynerus rufescens Giordani Soika, 1977
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5418.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:75E9BBD2-A2E7-4CD3-8296-EDE0C72FA1A1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10718261 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039987A7-FFDA-AF03-96F7-E6C6FC20FB40 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stenodynerus rufescens Giordani Soika, 1977 |
| status |
stat. nov. |
Stenodynerus rufescens Giordani Soika, 1977 stat. nov.
( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 )
Stenodynerus fastidiosissimus rufescens Giordani Soika 1977: 168 , ♀—“ Cirenaica : Wadi Kut ” (holotype female NHMUK).
Diagnosis. Similar to S. fastidiosissimus , but differing in the following characters: black with ferruginous-red markings, apical bands on T1–T2 only, female clypeus with apical emargination 0.25× as deep as wide, male clypeus as long as wide with apical emargination 0.55× as deep as wide.
Material examined. LIBYA: Cyrenaica , Cirene, 1.V.1924, leg. C. Krüger, 1♂ ( MSNVE, OR292164 ) ; Cyrenaica , Wadi Kuf, 4–10.IV.1958, leg. K.M. Guichard, 1♀ ( MSNVE, paratype, OR292163 ) .
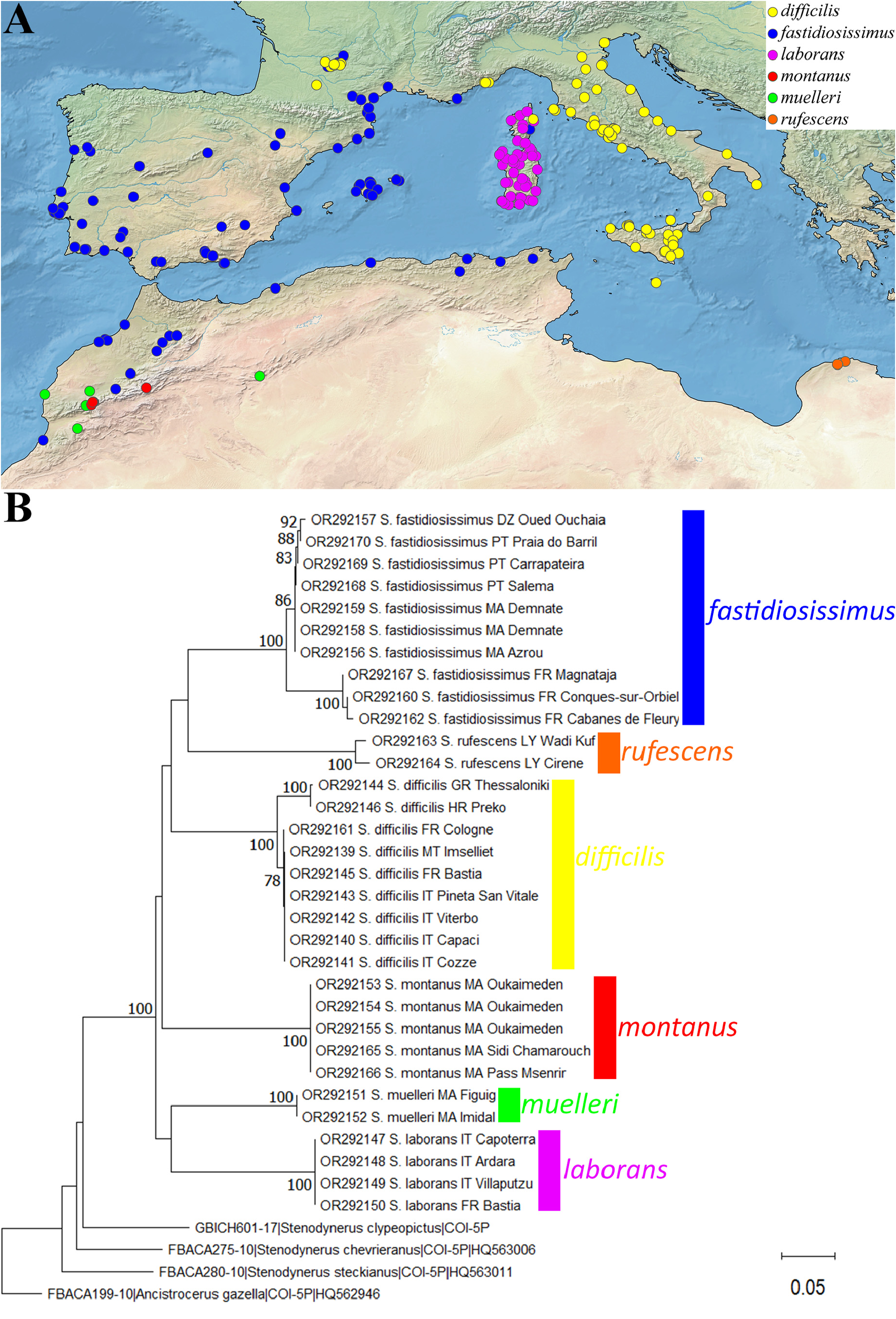
Distribution. Libya ( Giordani Soika 1977) ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6 ).
DNA barcoding. COI-5P gene sequences were obtained from two specimens, including a topotypical paratype. The intraspecific sequence divergence of S. rufescens is 2.39%. The species is clearly separated from the other taxa considered in this study and supported by a bootstrap value of 100 ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ). The lowest interspecific genetic distance exists between S. rufescens and S. fastidiosissimus , with a minimum of 26.56% (mean 28.19%).
Notes. Giordani Soika (1977) described this taxon as a subspecies of Stenodynerus fastidiosissimus (auct. non de Saussure, 1855), based on two females from Wadi al-Kuf. Examination of one paratype and of a male specimen from Cyrene, about 30 km NE of the type locality, showed that this taxon is closer to the true S. fastidiosissimus , sharing the same dense sculpture of S2 and similar shape of ventral lobe of aedeagus. We consider it a distinct species, due to the ferruginous-red markings, apical bands on T1–T2 only and the longer male clypeus with deeper apical emargination (0.55× as deep and wide) and longer and sharper lateral teeth. Genetic data support this treatment, with a genetic distance from S. fastidiosissimus of 26.56–32.05% (mean 28.19%).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Stenodynerus rufescens Giordani Soika, 1977
| Selis, Marco, Cilia, Giovanni, Wood, Thomas J. & Soon, Villu 2024 |
Stenodynerus fastidiosissimus rufescens
| Giordani Soika, A. 1977: 168 |