Chaetonotus retiformis, Suzuki, Takahito G. & Furuya, Hidetaka, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.206050 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5684745 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039A8780-4628-FFE0-FF42-FAF0FC9CFC77 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chaetonotus retiformis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chaetonotus retiformis View in CoL n. sp.
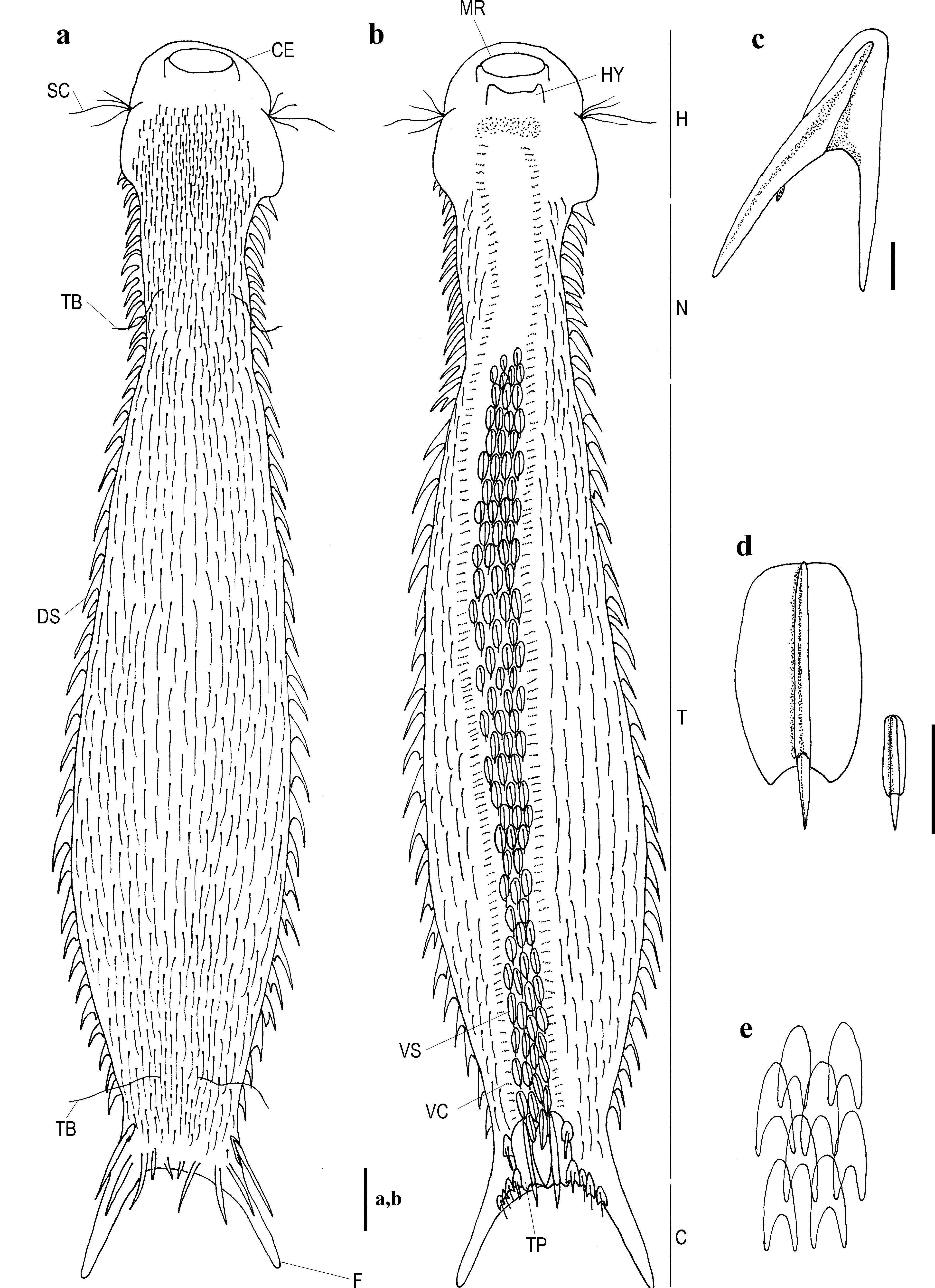
[New Japanese name: Amime-itachimushi] ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Type locality. Japan, Honshu, Osaka Prefecture, Toyonaka, Machikane Pond (34°80′N, 135°45′E).
Type specimens. Holotype (OUM-GA-00001) and paratype (OUM-GA-00002) deposited in Osaka University Museum ( OUM). Other specimens in the first author’s collection.
Etymology. From the Greek in reference to the characteristic net-like pattern on the dorsal surface caused by arrangement of the scales.
Diagnosis. A medium-sized Chaetonotus of total length 180 μm including furca of 10 μm beginning at 93 U; pharyngeo-intestinal junction (PhIJ) at 41 U; head slightly three-lobed, with cephalion, hypostomion, and a pair of sensory cilia. Eye-spots absent. Body enveloped by small arrowhead-shaped, scales with a short spine in 22 longitudinal alternating rows, 38 in each. Four long spines on the base of each member of the furca at 92 U. Ventral scales between two columns of ventral cilia, keeled, oval scales with a short spine, in 2-4 longitudinal alternating rows. A pair of terminal plates covering posterior end of ventral scales is the largest in ventral scales. Juvenile length is about 60% of adult length, but head length is the same.
Description. Based on an adult specimen, 180 μm in total length. Body medium-sized tenpin-like shape with distinct head, neck, and trunk region. Widths of head / neck / trunk / caudal base are 30 / 21 / 41 / 21 μm at 0 8 U / 23 U / 65 U / 88 U, respectively. Length of distal furca 10 μm. Pharynx 58 μm in length, from posterior edge of mouth to junction with intestine; pharyngeo-intestinal junction (PhIJ) at 41 U. Head slightly three-lobed, with cephalion and linear hypostomion posterior of mouth. Hypostomion with forward protrusions on each side.
Sensory organs: Seven or more isolated cephalic sensory cilia on either side of head, length around 11–12 μm. Eye-spots absent. Tactile bristles 12–15 μm in length are at 21 U on neck and 84 U caudally.
Cuticular armature: Body coverd with spined scales in alternating lines (22 longitudinal alternating rows, 38 in each), except for cephalion and furca regions. Dorsal scale arrowhead-shaped, width 3 μm, length 6 μm. Scales and spines relatively small and overlapping. Shape of all dorsal scales identical, but scales of posterior region are larger. Scales on neck region about half the size of those of trunk region. Length of spines on trunk scale 4 μm; 8 spines beneath base of each furca limb, each 8 μm at 92 U. Ventral scales covering region between two columns of ventral cilia are keeled, oval with a short spine, scale width 2 μm, length 6 μm and spine length 2 μm. Terminal plates form a pair covering posterior end of ventral scales width 6.5 μm, length 8 μm and spine length 2.5 μm; larger than other ventral scales.
Ventral ciliation: Densely packed field of cilia at posterior edge of hypostomion (0.5 U) splits into two parallel bands over most of trunk region, ending at 88 U.
Digestive tract: Mouth opening 8 μm in breadth, 6 μm in depth. Pharynx with swelling at both ends; the anterior being less obvious (11 μm) than the posterior (12 μm); central portion of fairly constant width (9.5 μm). Intestine straight, slightly wider anteriorly (21 μm) narrowing gradually over its length (to 3 μm width). Anus ventral, at 87 U.
Remarks. Chaetonotus retiformis is similar to nine species in having the arrowhead-shaped dorsal scales and long spines at the base of the furca: cf. C. christianus Schwank ; C. linguaeformis Voigt ; C. maximus Ehrenberg ; C. microchaetus Preobrajenskaja ; C. multispinosus Günspan ; C. pawlowskii Kisielewski ; C. polyspinosus Greuter ; C. pseudopolyspinosus Kisielewski ; and C. ventrochaetus Kisielewski. However , C. retiformis is easily distinguished from all but C. linguaeformis and C. christianus in having a three lobed head ( Schwank, 1990).
Chaetonotus linguaeformis View in CoL is recorded from Europe and Northern Asia except China ( Voigt, 1902, 1904; Schwank, 1990). Chaetonotus retiformis View in CoL differs from C. linguaeformis View in CoL in the body length (170–190 μm vs. 310– 370?μm), head shape (round-shaped vs. tongue-shaped and obviously three lobed vs. barely three lobed), and the absence of eye-spot-like structures near the mouth ring: none vs. 2( Voigt, 1902, 1904; Schwank, 1990).
Chaetonotus christianus View in CoL is recorded from Europe and Northern Asia, except China ( Schwank, 1990). Chaetonotus retiformis View in CoL differs from C. christianus ( Schwank, 1990) View in CoL in the number of lines of ventral scales (2–4 vs. 12), type of terminal plate (square-shaped with keel and spine vs. slender oval-shaped with keel but no spine) and body shape (ten-pin like vs. cylindrical).
| OUM |
Oxford University Museum of Natural History |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Chaetonotus retiformis
| Suzuki, Takahito G. & Furuya, Hidetaka 2011 |
C. christianus (
| Schwank 1990 |