Neapion (Neotropion) marquesae, Sousa & Ribeiro-Costa, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4402.3.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:33A988BB-3AB4-4AE7-88C7-6A563FA91D74 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5989620 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039A87E6-FFF9-FF95-FF02-8DEFFED1FCA0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Neapion (Neotropion) marquesae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Neapion (Neotropion) marquesae sp. n.
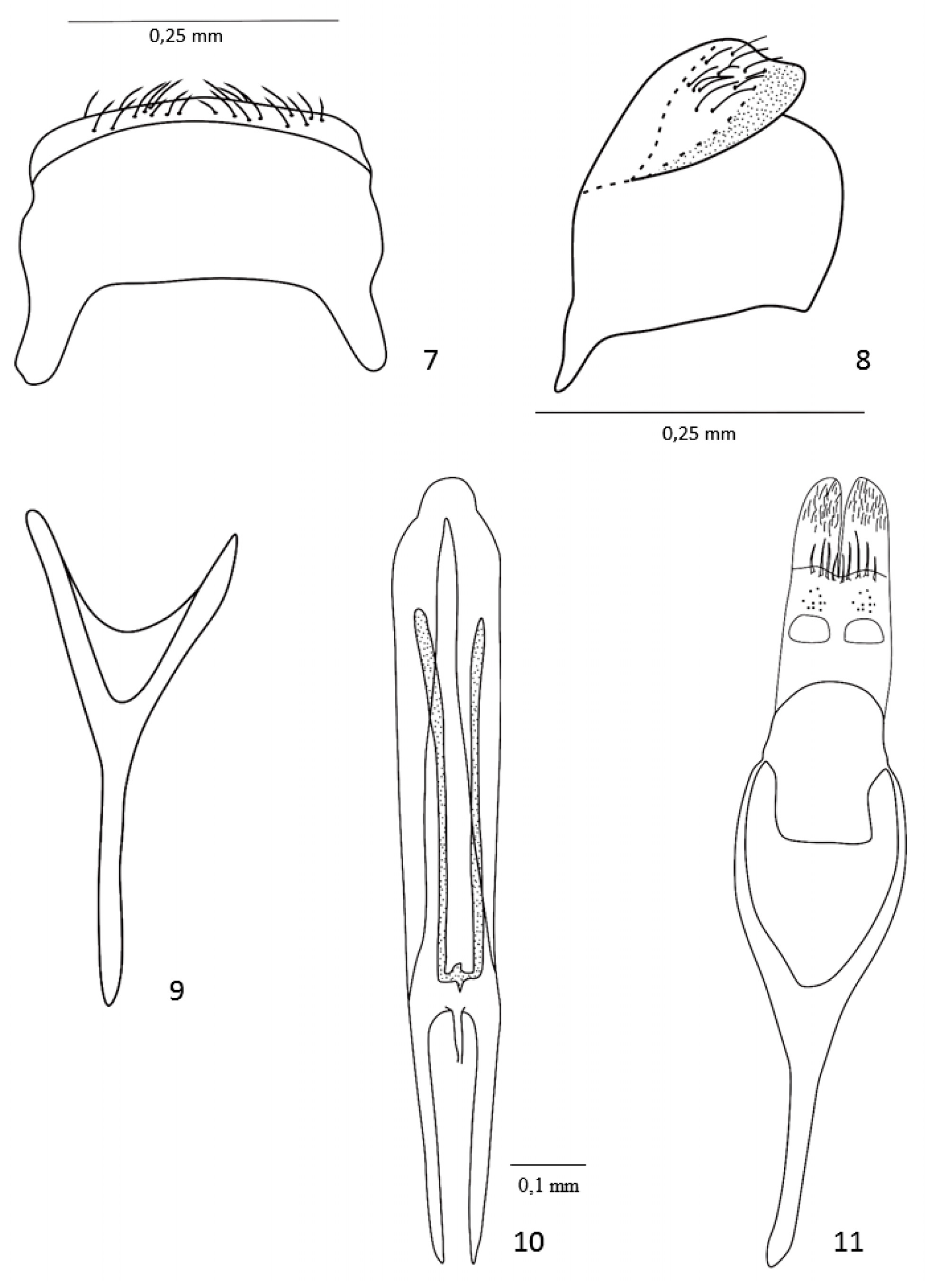
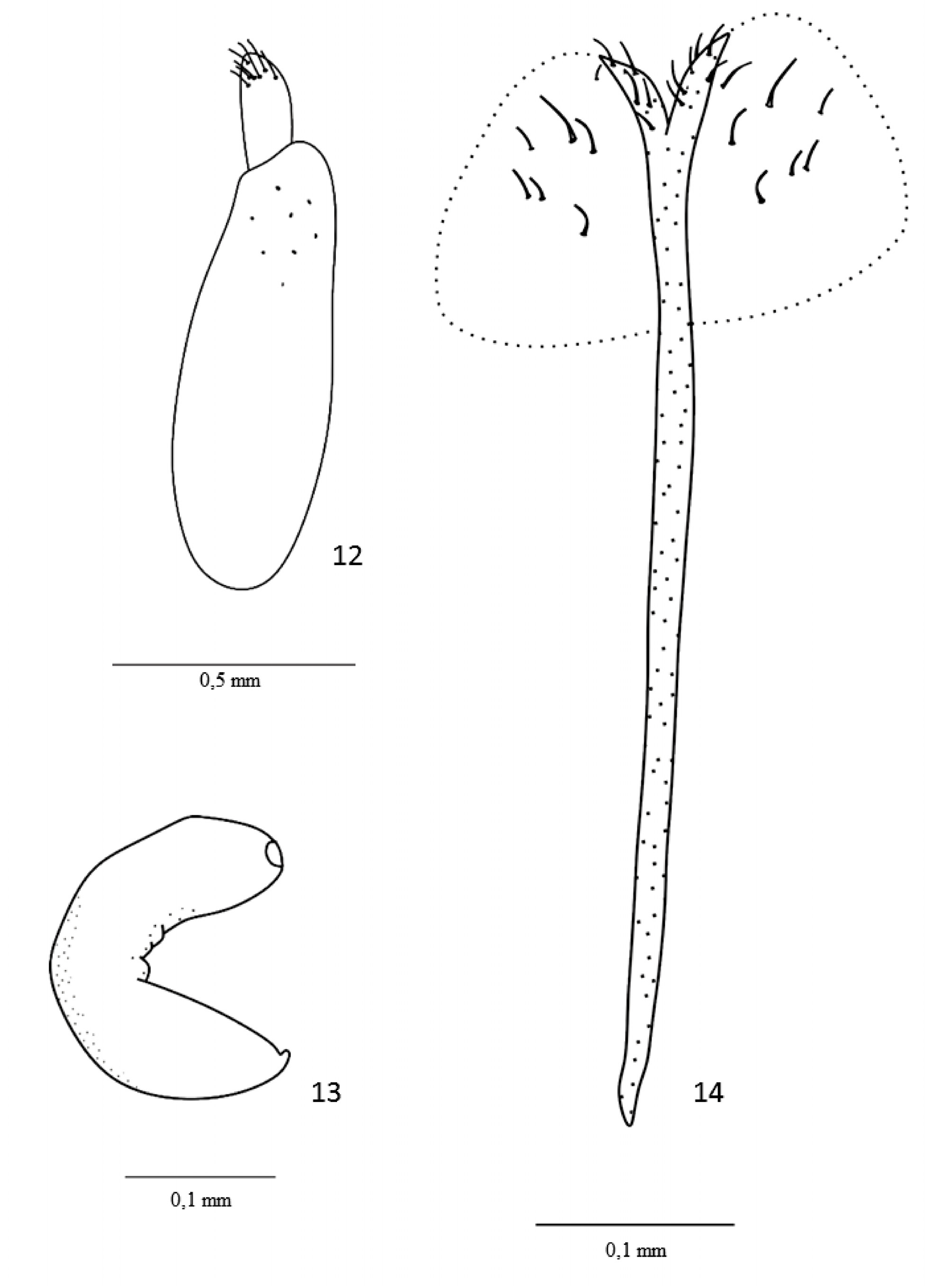
( Figs. 1–14 View FIGURES 1–6 View FIGURES7–11 View FIGURES 12–14 )
Diagnosis. This new species is distinguished from the other N. ( Neotropion ) species by the elytra with Vestiture of dense, thin, off-white to dark brown scales ( Figs. 1–3 View FIGURES 1–6 ), denser and thicker in the lateral regions of the pronotum, mesanepisternum, mesepimeron and metanepisternum ( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURES 1–6 ); with eight raised areas in each elytron, two in the interVal 2 (the largest submedian and the smaller in the posterior half), four in interVal 4 (three in the anterior half and one in the posterior half) and one in each posterior third of interVals 5 and 6 ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 ).
Description. Measurements: male holotype (in mm): length 2.96; rostrum length 0.80; maximum width 0.36; pronotum length 0.88 and maximum width 0.96; elytra length 2.20 and maximum width 1.20.
Integument dark brown, antennae ferrugineous, legs light brown, abdomen black.
Vestiture in general conspicuous, scales dense, heterogeneous, off-white to dark brown; meta- and mesorostrum scales more sparsely distributed, absent on the prorostrum apex; head and pronotal disc scales sparse, on pronotum centripetal pattern; elytra basal half with tan to light brown scales and two oblique dark macules from interVal 1 to 2; Ventral region with off-white scales ( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURES 1–6 ), uniform abdominal Ventrites.
Rostrum curVed, robust, in side View conVex dorsally and Ventrally at mesorostral leVel ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 ), apex more or less acutely subulate; in dorsal View about 2.2 times longer than maximum width; 0.90 times pronotum length along midline; mesorostrum matte, laterally dilated ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ), about 1.9 times larger than apex of prorostrum; apical 4/5 polished and finely punctuated.
Head with frons slightly depressed with scales smaller than those around the eyes; subocular keel well deVeloped, extending beyond the posterior margin of the eyes; area between subocular keels microreticulate and impunctate. Eyes oblong-oVal, conVex ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–6 ). Antennae inserted at basal 0.25 of rostrum length; scape 0.55 times mesorostral width, 1,75 times as long as wide, as long as club, 0.7 times club width; pedicel as long as wide, as long as desmomeres 1+2, desmomere 1-5 as long as wide, desmomere 6 as long as wide, subconical; club oblong, compact, 2 times as long as wide, as long as the last 5.5 desmomeres, sutures marked.
Thorax. Pronotum conical in dorsal View, slightly constricted before apex, about 0.91 as long as wide, base 1.5 times apex width, bisinuate with moderate median rounded projection toward scutellum; outline in lateral View slightly depressed anteriorly; pronotal disc with surface irregular, slightly depressed longitudinally and on both sides of midline, with sub-basal foVea; punctures coVered by scales. Scutellum length about 1.4 times maximum width, grades posteriorly into slender, awl-shaped basal angles with apex curVing slightly upwards in lateral View. Elytral length 1.83 times width, gibbose in profile; humeri salient; interstriae conVex, with eight raised areas of different lengths and heights ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–6 ), as described in the diagnosis; striae Visible along the length, strongly punctate apically. Mesocoxae separated by about 0.3 times the mesocoxal diameter. Metasternal rim absent. Median foVea near posterior margin of metasternum.
Abdomen. Abdominal Ventrites with midline length ratios: 40–25–6–8 –17; Ventrite 5 apically truncate; pygidium of incomplete apionine type ( Fig. 7, 8 View FIGURES7–11 ), semicircular, 0.5 times longer than wide, with distinct, deep, transVerse preapical sulcus incomplete laterally, not reaching side margins of pygidium, profile distinctly interrupted by sulcus.
Male terminalia and genitalia. Ninth sternite (spiculum gastrale) Y-shaped, manubrium ca. 1.85 times arm length ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES7–11 ). Penis ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES7–11 ) depressed, curVed, pedon with apical plate straight in side View, rounded and slightly constricted apically in dorsal View; tectum slender and with clear margins; temones length about 0.47 times pedon length; internal sac with two long (520 µm) and parallel sclerites, transVersely joined, forming a ‘tuningfork’ shaped structure. Tegmen ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES7–11 ) with tegminal plate fused to free ring; parameroid lobes slightly notched in the membranous area, microsetose apically, sclerotized area of each side with 5 macrochaetae and sensilla in front of each fenestra; fenestrae width 1.3 times length, separated about 0.4 times fenestral width; linea arquata Visible; prostegium protruding medially in square shape. Manubrium as long as basal piece, with apex rounded.
Female. In general, with the same external characteristics of the male, slight Variations in relation to the length and width of the body; rostrum weakly thinner, more slender, with a less squamous and brighter metarostrum in the female. The dark macula on basal half of elytra is conspicuous, as an inVerted “V”, from interVal 1 to 2 ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–6 ).
Measurements: female paratypes (mean in mm): length 3.00; rostrum length 0.82; maximum width 0.36; pronotum length 0.80 and maximum width 1.00; elytra length 2.26 and maximum width 1.40.
Female genitalia. OVipositor ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 12–14 ): Coxite length about 2.9 times width, with microchaetae. Styli subcylindrical, length about 1.2 times width, with 7 macrochaetae. Spermatheca ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 12–14 ) C-shaped, no nodulus or ramus; cornu as broad as the corpus, with a small apical protuberance. Spiculum Ventrale ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 12–14 ) elongate, straight, apical plate membranous and setiferous.
Type material. Holotype male dissected [red border printed label] (DZUP), glued on paper triangle, with genitalia in a separate microVial. Brasil, Poconé-MT ( Canopy ), 25/10/2012, Bonatti, J., seca, Cord. 0 4, Funil 50, Quadrante F 2. Paratype [white printed label]: 1 female dissected ( DZUP), glued on paper triangle, with genitalia in a separate microVial, same holotype information except Cord. 3, Funil 44 , 1 female (LETA), glued on paper triangle, same holotype information except 05/09/2013, Funil 36.
Etymology. This species is named in honor of Dr. Marinêz Isaac Marques, UniVersidade Federal de Mato Grosso, who encouraged the first author in his studies of weeVils, and who, for more than 20 years, contributed to ecological studies of the Curculionoidea in the Pantanal of Mato Grosso, Brazil. The specific epithet is a noun in the genitiVe case.
| DZUP |
Universidade Federal do Parana, Colecao de Entomologia Pe. Jesus Santiago Moure |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |