Devenilia corearia (Leech, 1891)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.25221/fee.420.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F8FBF14B-6855-47F5-A997-C2EF7933CF45 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039F87CE-FFAA-0D6F-DCCB-FA282F2EFBCC |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Devenilia corearia (Leech, 1891) |
| status |
|
Devenilia corearia (Leech, 1891) View in CoL
Figs 1, 2 View Figs 1, 2
Devenilia corearia: Beljaev, 1998: 438 View in CoL , fig. 1
MATERIAL. Russia: Primorskii krai: Pogranichnyi distr., Barabash-Levada,
44°45' N, 131°25' E, 19, 28.VII 1989, 2♂, E.A. Beljaev leg; 20 km SE Ussuriisk GoogleMaps ,
Gornotayozhnoe, 43°42′ N, 132°09′ E, 8.VII 1990, 2♂, E.A. Beljaev leg.
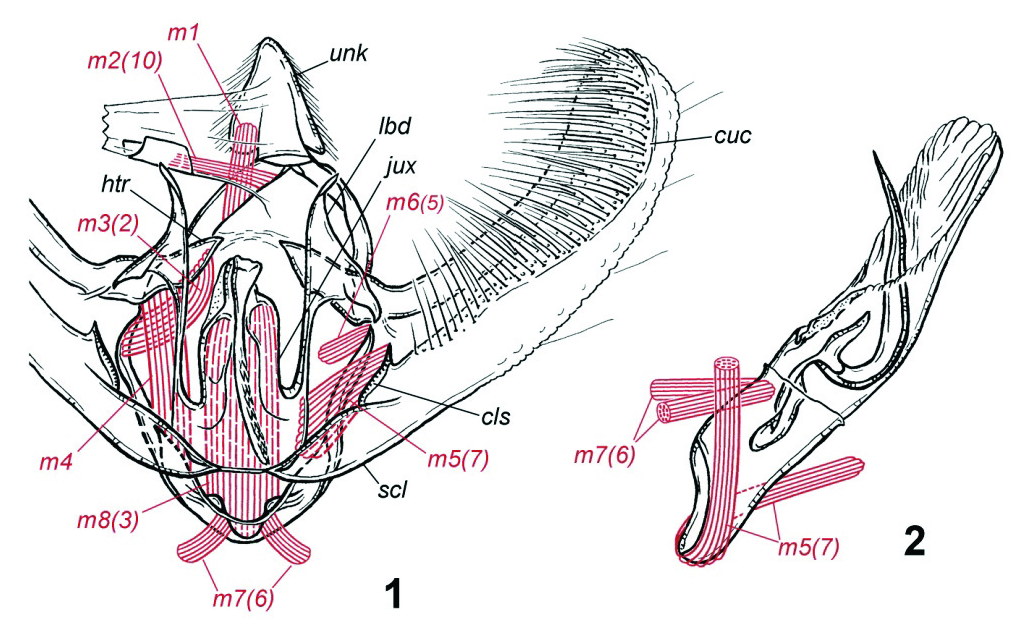
male genitalia, ventroposterior view, muscles m1, m2(10), m3(2), m4 are not shown on the right, and muscles m5(7), m6(5) are not shown on the left; 2 – phallus, lateral view.
Abbreviations: b.pr.v – basal process of valvae, cl – cuiller, clp – clasper, crs – cristae, cst –
costa, cuc – cucculus, d.p.unс – distal process of uncus, gn – gnathos, htr – hemitranstilla, jux –
juxta, lbd – labidum, m.d.cst – medial dilation of costa, m1 – depressors of uncus, m2(10) –
retractors of anal tube, m3(2) – abductors of valvae, m4 – adductors of valvae, m5(7),
m5a(7a), m5b(7b) – flexors of valvae, m6(5) – retractors of phallus, m7(6) – protractors of phallus, m8(3) – ventral adductors of valvae, scl – sacculus, teg – tegumen, tr – transtilla, unc –
uncus, vnc – vinculum.
MALE GENITALIA ( Figs 1, 2 View Figs 1, 2 ). The skeleton. Genital segment (annulus) is clearly divided on tegumen and vinculum by thin narrowing. Lateral lobes of tegumen are narrow, ribbon-like, dorsally connected to each other by very small,
almost point-like, bridge. Vinculum is wide, strongly sclerotized, lateroventrally with a pair of deep notches. Uncus is wide, triangular, weakly sclerotized dorsally,
completely membranous ventrally. Gnathos is lacking. Valvae are long, narrow,
with large cucullus, densely covered with long hair-like bristles. Costa is wide, well sclerotized, medially protruded into wide bar-like hemitranstilla angled to apex;
apexes of right and left hemitranstillae are widely separated. Valvula proximally is bordered by firm oblique rib – clasper (sensu Beljaev, 2008). Sacculus is relatively short, well sclerotized. Juxta very large, wide, long, distally somewhat asymmetric and extending into a long, thin process movably articulated with the juxta and covered with spines on the dorsal side. Pair of very large triangular lateral processes of anellus (labides sensu Beljaev, 2008) are connected medioventrally to laterobasal sides of juxta, and laterally loosely articulated with base of costa. Aedeagus is large,
cylindrical, moderately sclerotized, vesica with a single very large subulate cornutus, hook-like at the base.
The musculature. Depressors of the uncus, m1, are thin, weak, extending from the middle part of the anterior edge of the tegumen, distally attached to the lateral corners of the uncus. Anal cone retractors, m2(10), are extending from most dorsal portion of anterior rib of lateral lobes of tegumen. Dorsal abductors of valvae,
m3(2), are relatively wide, extending from the most dorsal portion of the vinculum,
and are attached in distal half of the hemitranstilla to small round dilation of its ventral margin.
Adductors of valvae, m4, are wide, long, extending from a small extension on the ventral part of lateral branches of the vinculum to the ventral edge of the basal half of the hemitranstilla. Flexors of valvae, m5(7), are short, moderately wide,
proximally attached partly to medial wall of the sacculus, partly to lateral edge of the ventral half of the juxta, distally attached to clasper. Ventral extensor of valva,
m8(3), is unpaired, extremely powerful, long and wide, extending proximally from ventral part of the vinculum between its paired notches, distally extending to the articulation of juxta and its distal process, without attaching to the latter. Protractors of phallus, m6(5), are paired, relatively thin, extending from dorsal corners of vinculum and distally attached to anterior deletion of aedeagus (saccus), but directed differently: right muscle is oriented topologically posterioventrad from saccus, and left muscle is oriented posteriodorsad from saccus. Retractors of the phallus, m7(6),
paired, relatively thin, extending from most ventral posterior edge of vinculum and distally attached to topologically dorsal wall of aedeagus. These unusual features of the muscles attachment are connected with unusual position of the phallus "lying on the side", i.e. turned 90 degree right from common phallus position in ennomines.
Retractor of vesica, m21, is present, but not shown.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Devenilia corearia (Leech, 1891)
| Beljaev, E. A. 2020 |
Devenilia corearia:
| Beljaev 1998: 438 |