Bradysia loudoni, Mohrig & Kauschke & Broadley, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4450.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:624934AE-AEF3-4366-81B2-0997054B3DBD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5989672 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A487A5-FFEC-FF8F-FF74-FF67FD3BFC89 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bradysia loudoni |
| status |
sp. nov. |
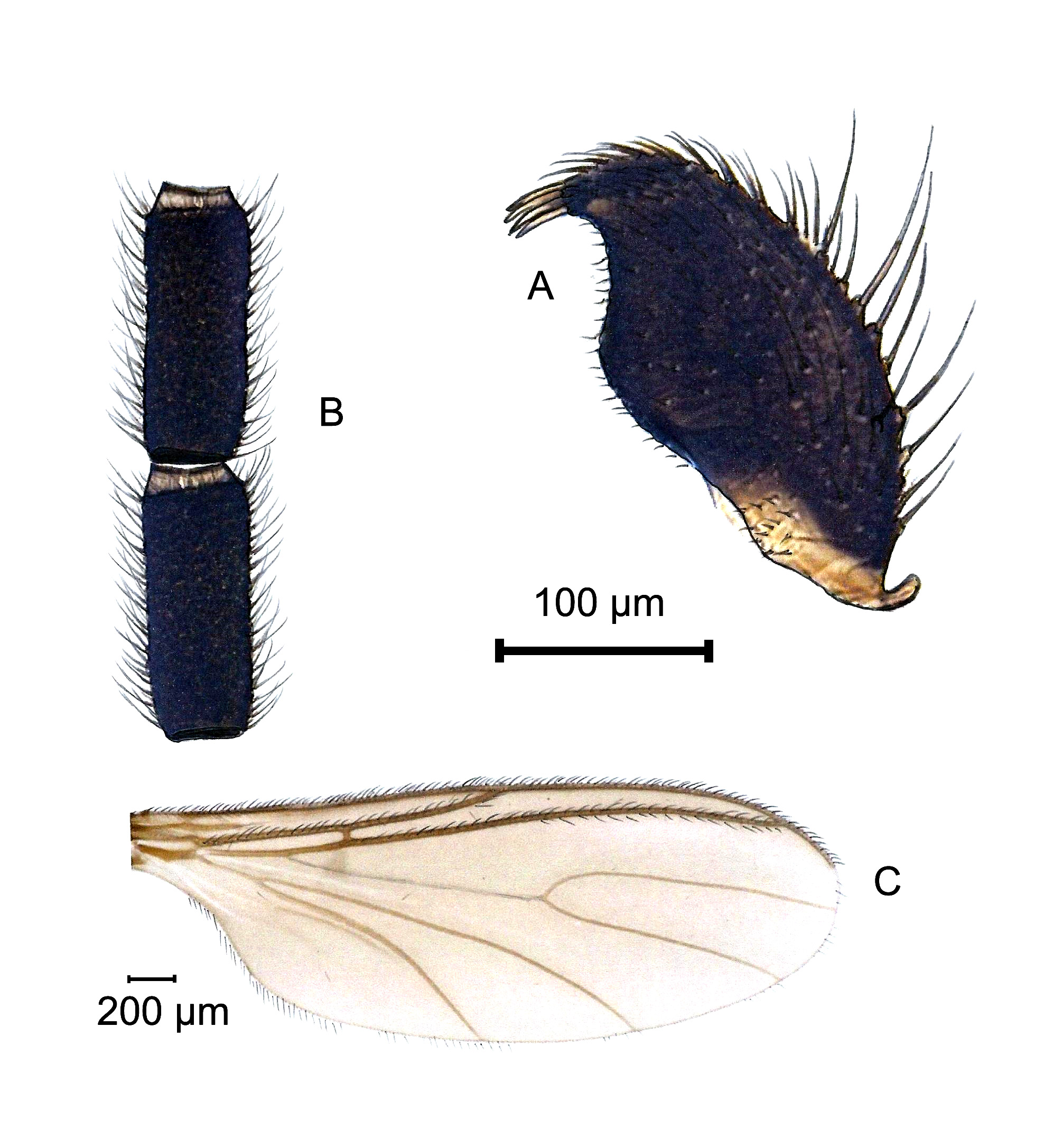
Bradysia loudoni View in CoL sp. n. *
( Fig. 11 A–C View FIGURE 11 )
Type locality: New South Wales, Mt. Kosciusko.
Holotype: Male, January 1978, in saw grass, leg. A. Stocker, ASCT 00053645 ( ASCU).
Paratypes: 2 males, same, locality, same data, ASCT 00053644 ( PWMP), ASCT 00053720 ( PABM). Description. Male. Head. Dark brown. Eye bridge 3–4 facets wide. Antenna long, dark brown, 4th flagellomere with l/w index of 3.0, hairs dense and shorter than the diameter of the basal node; neck very short, bicoloured. Palpus 3-segmented, brown, basal segment with 2 bristles and a deepened sensory area. Thorax. Dark brown. Scutum with rather long hairs, some lateral bristles longer; scutellum with 4 marginal bristles; postpronotum bare. Wing brownish; R1 long, = R; R5 with ventral macrotrichia in the distal third; C = 2/3 w; y somewhat shorter than x, without macrotrichia; M-fork long and narrow, posterior wing veins without macrotrichia. Haltere short, brown. Coxae and legs dark brown; apex of fore tibia with a comb of bristles; spurs of middle and hind tibiae equal in size, longer than the diameter of the apex; claws without teeth. Abdomen. Dark, with long and dense hairs. Hypopygium basally with short dense hairs, gonocoxites at the inner ventral margin with rather short sparse hairs; gonostylus short, the inner side bulbous, strongly pointed to the apex, without an apical tooth but with 4 apical spines. Tegmen wider than long, flatly rounded apically, with a large field of fine teeth. Aedeagus long. Body length: 4.8 mm.
* The species is named after Ben J. Loudon, a technical officer who worked at the Biological and Chemical Research Institute ( BCRI) of the New South Wales Department of Agriculture, Rydalmere , in the 1970s, where he and his colleagues established an extensive sciarid collection.
Comments. The species is characterized by the dark body colour, the large body size, the long flagellomeres and the bulbous gonostylus, strongly pointed to the apex, with 4 apical spines. It is similar to B. gibbosa Vilkamaa, Hippa & Mohrig in the shape of the gonostylus. It differs by the larger body size, the dark colour and the gonostylus with 4 apical spines.
Distribution. Australia: New South Wales.
| ASCU |
Agricultural Scientific Collections Unit |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.