Bradysia gibbosa Vilkamaa, Hippa & Mohrig, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4450.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:624934AE-AEF3-4366-81B2-0997054B3DBD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5989670 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A487A5-FFF3-FF91-FF74-FA2CFCFEF85D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bradysia gibbosa Vilkamaa, Hippa & Mohrig, 2012 |
| status |
|
Bradysia gibbosa Vilkamaa, Hippa & Mohrig, 2012 View in CoL
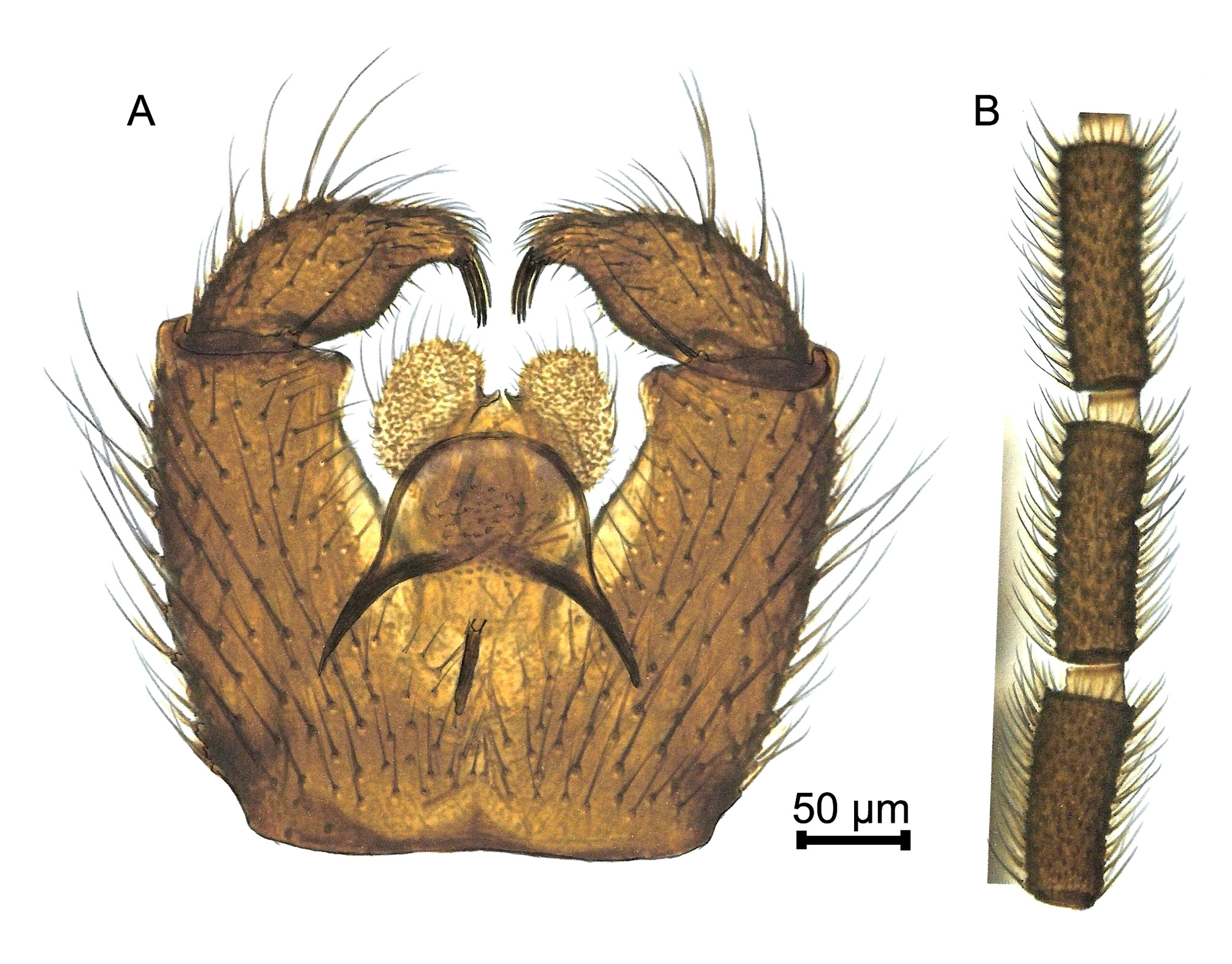
( Fig. 10 A–B View FIGURE 10 )
Bradysia gibbosa Vilkamaa, Hippa & Mohrig, 2012 View in CoL [ Vilkamaa et al. (2012b): 33 –34, fig. 6 A–D].
Material: 1 male, 22.iv.1978, New South Wales, Royal National Park, leg. B.J. Loudon, ASCT 00053698 ( PWMP); 1 male, 19.ii.1978, Dharug Nat. Park, leg. B.J. Loudon & A.J. Stocker, ASCT 00053419 ( PWMP); 2 males, 7. iv.1979, New South Wales, Barrington Tops Nat. Park, light trap, leg. G.R. Brown, ASCT 00053632 ( PABM) /53633 ( ASCU).
Comments. The species is characterized by flagellomeres having weakly bicoloured necks, whitish halteres and a strongly bulbous gonostylus with 3 spines at the apex. It is similar to B. loudoni sp. n. It differs by being smaller in body size, having shorter flagellomeres and only three spines at the apex of the gonostylus. It belongs to the B. hilaris group.
Distribution. Australia: New South Wales; New Caledonia.
| ASCU |
Agricultural Scientific Collections Unit |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.