Neacomys dubosti (Voss, Lunde & Simmons, 2001)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4876.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:190EC586-E14B-4AEF-A5EF-3DA401656159 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4566497 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A587ED-3222-FFC8-83E9-FA282F9FF852 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Neacomys dubosti |
| status |
|
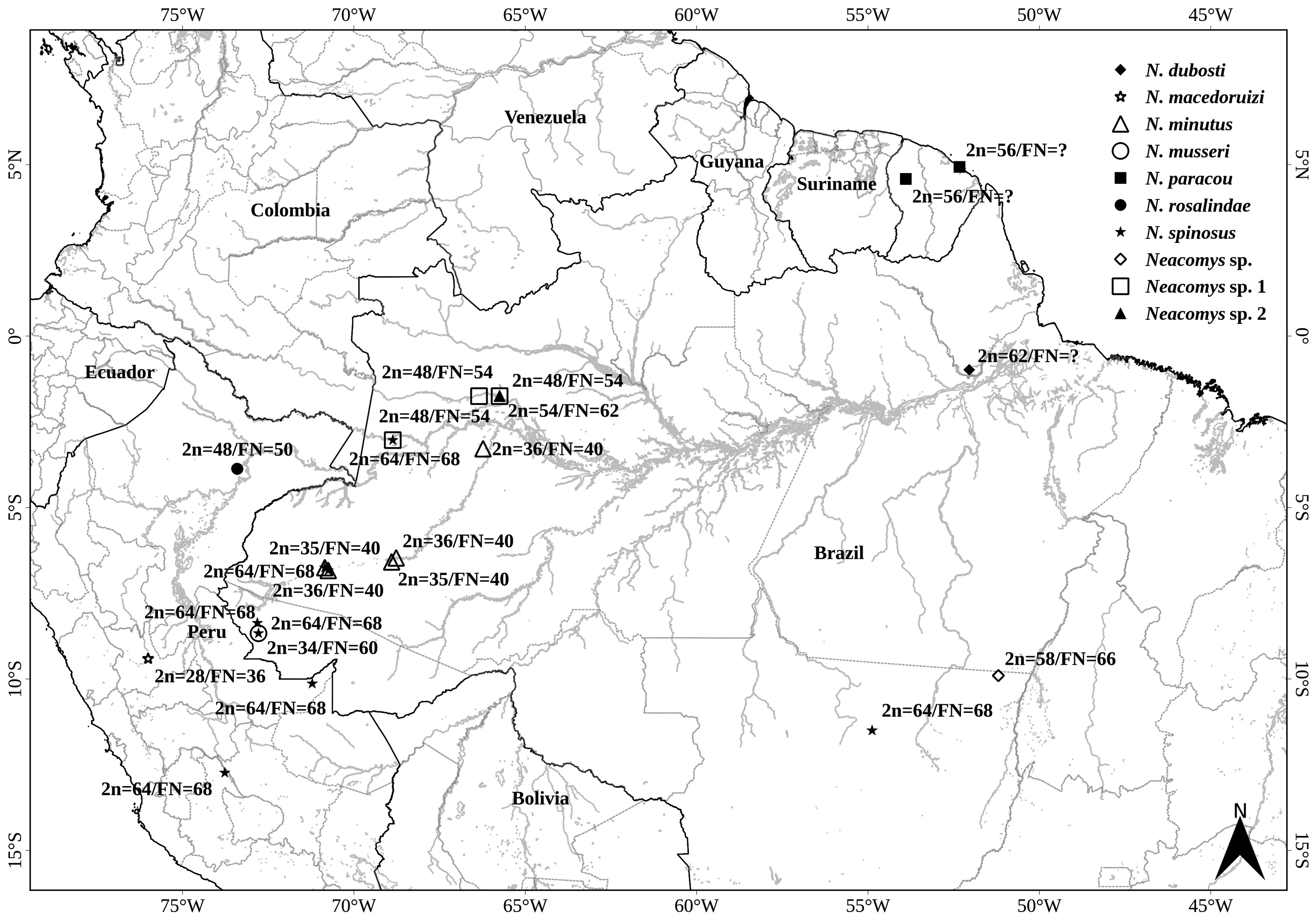
Karyotype: 2n = 64 and FN = 68. Autosomal complement: three small metacentric pairs, and 28 acrocentric pairs. Sex chromosomes: X, a medium submetacentric; Y, a small acrocentric. C-banding metaphases exhibited blocks of constitutive heterochromatin on the pericentromeric region of all autosomes. The X chromosome presented the short arm entirely heterochromatic. The Y chromosome presented the long arm entirely heterochromatic. G-banding was also performed. FISH with 18s rDNA sequences revealed signals of NOR on the short arm of six acrocentric pairs, and one of these chromosomes also had a NOR on the distal region of the long arm. FISH with telomeric sequences revealed signals exclusively at the ends of all chromosome arms and no interstitial signals were observed ( Silva et al. 2015, pp. 4, Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ). According to Silva et al. (2015) this karyotype was similar to N. spinosus reported by Patton et al. (2000) (2n = 64 and FN = 68), except for the morphology of the X chromosome, which was subtelocentric in N. spinosus and submetacentric in N. dubosti . Another diploid number of 62 was reported by Voss et al. (2001) for a sample from Amapá, state of Brazil ( Table 6, Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.