Pseudoceros stellans, Dixit & Bayyana & Manjebrayakath & Saravanane & Sudhakar, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4657.2.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3708F04B-C342-464B-882E-583C4101C977 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3800371 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E661D723-D688-46F7-A548-933D79C9625E |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:E661D723-D688-46F7-A548-933D79C9625E |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Pseudoceros stellans |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pseudoceros stellans sp. nov. Dixit
( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 , 7 View FIGURE 7 & 8 View FIGURE 8 )
Material examined: Holotype: One specimen (13 × 9 mm) as serial sections (16 Slides), remainder of animal in 70% ethanol. Collected on 21.5.2018, 15 m depth, Agatti Island (10°52′28′′N 72°11′11′′E), Lakshadweep, India (Regn. no. IO /IT/POY/00006) GoogleMaps
Type locality: Agatti Island , Lakshadweep, India .
Etymology: From the Latin stellans (adjective) — starry or star studded; for stars like appearance on dorsum
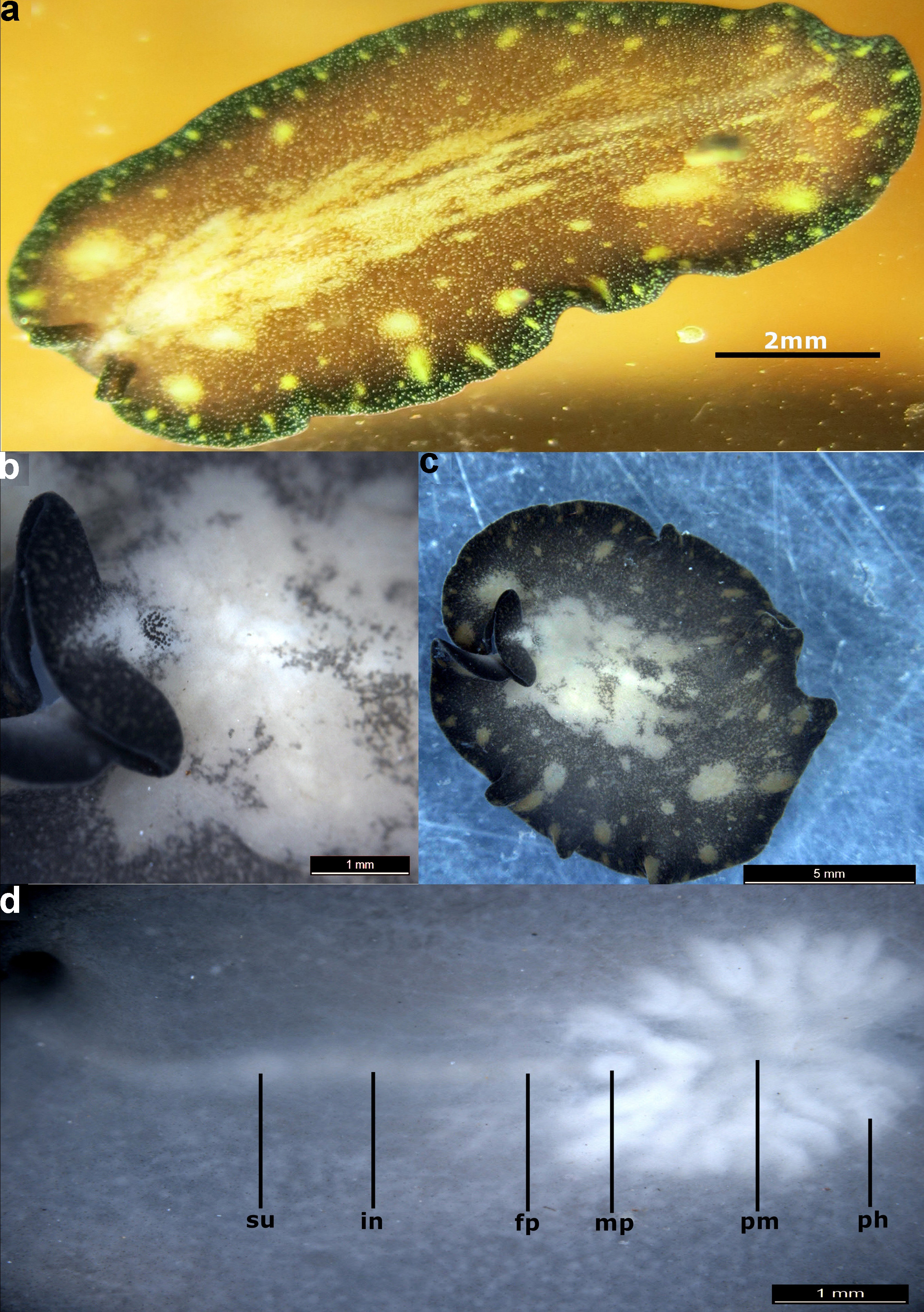
Diagnosis: Background body colour brown with numerous small white to yellow microdots on dorsum. Different sized yellow blotches present on dorsum but most of the small white blotches are present on marginal area. Half of the median area is marbled with irregular white shading, thus appearing as depigmented area. A thick black marginal band run around whole body including pseudotentacles. This marginal band is studded with microdots and small yellow blotches. Pseudotentacles are simple folding of the anterior margin, black and spotted with white dots on dorsal side. Cerebral eye cluster horseshoe shaped.
Description: Live. Body small, oval and margin without ruffles. Background body colour brown ( Fig. 6a View FIGURE 6 ). Numerous small white to yellow microdots present all over dorsum. White dots are numerous near median area and gradually turns yellow towards margins. Many yellow blotches of different sizes on dorsum near margins ( Fig. 6a View FIGURE 6 ). Anterior half of median area is marbled with irregular white shading. Marginal band thick and black with minute yellow microdots and small yellow blotches. Pseudotentacles are simple foldings of the anterior margin, black and spotted with white dots on dorsal side. Cerebral eye cluster horseshoe shaped ( Fig. 6b View FIGURE 6 ), tentacular eyes hard to recognize due to black colour of pseudotentacles. Ventral surface light brownish in colour.
Preserved. Specimen brown in colour after fixation ( Fig. 6c View FIGURE 6 ). Ventrally dull whitish in colour. Male and female pore are 0.6 mm apart, while female pore and sucker are 2 mm apart ( Fig. 6d View FIGURE 6 ). Mouth and male pore are 1.2 mm apart while mouth and sucker are 3.9 mm apart. Pharynx ruffled with eight to nine folds and male pore is situated between last pair of pharyngeal folds. Cerebral eye cluster with about 60 - 65 eyes.
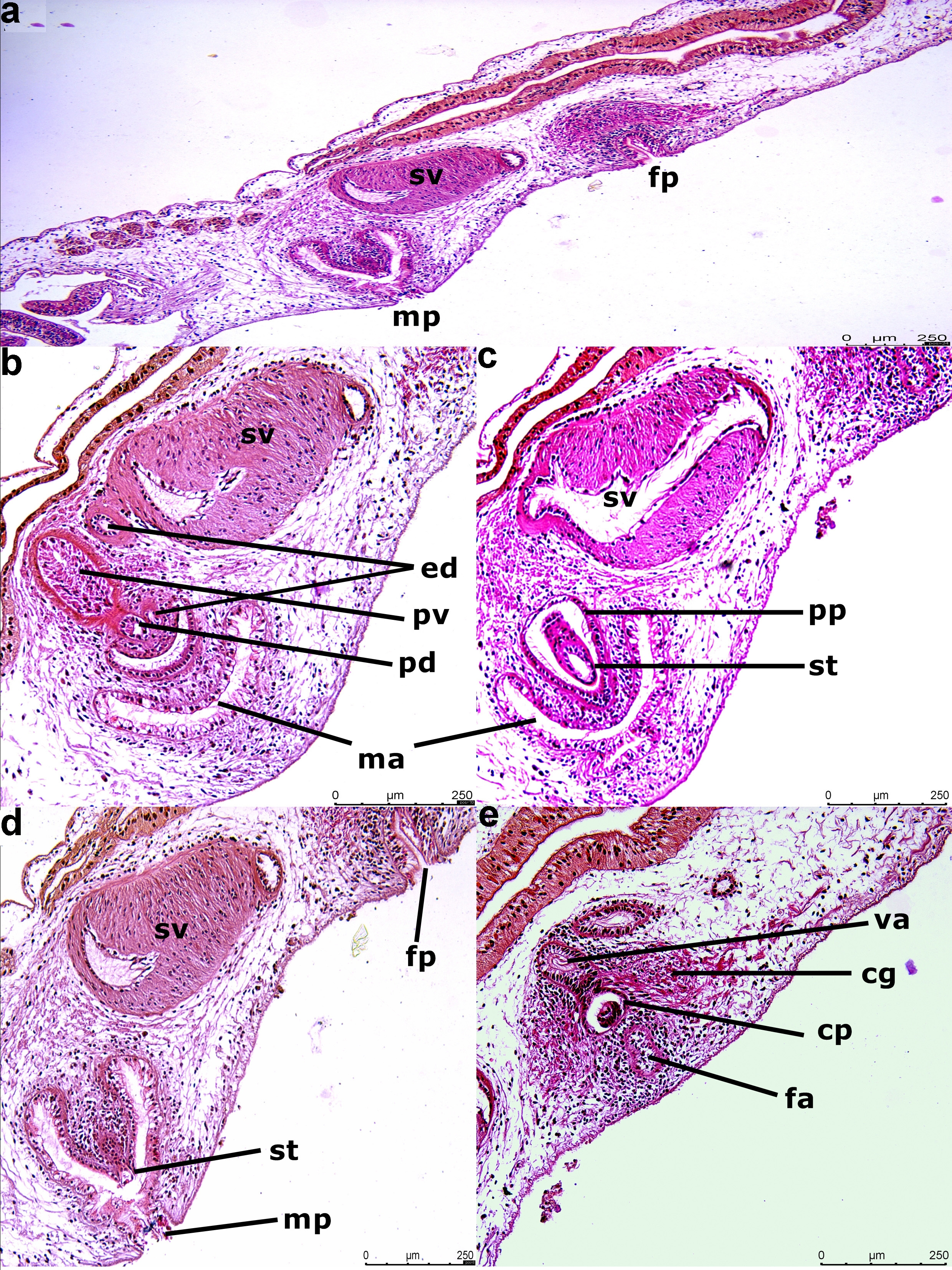
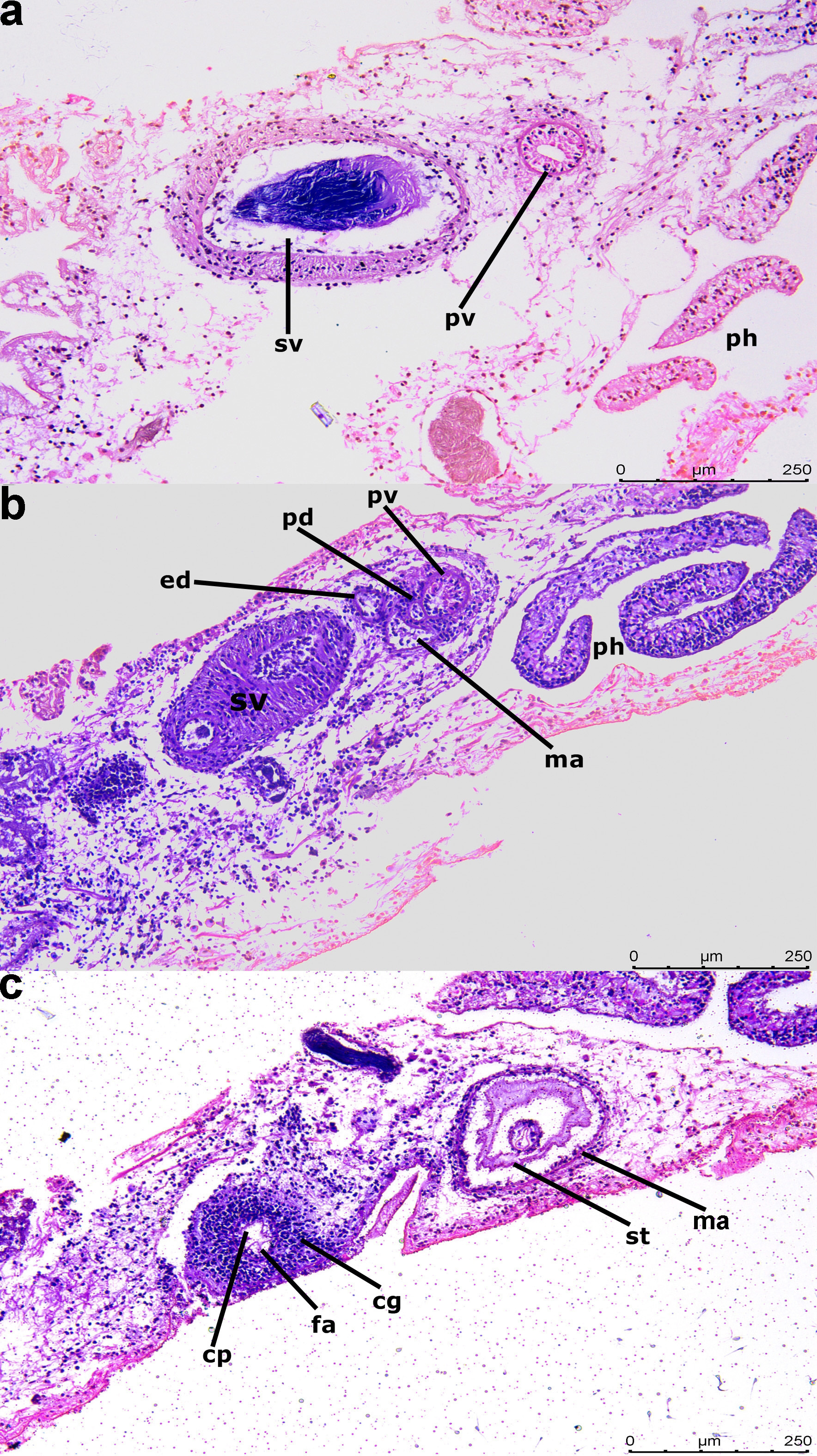
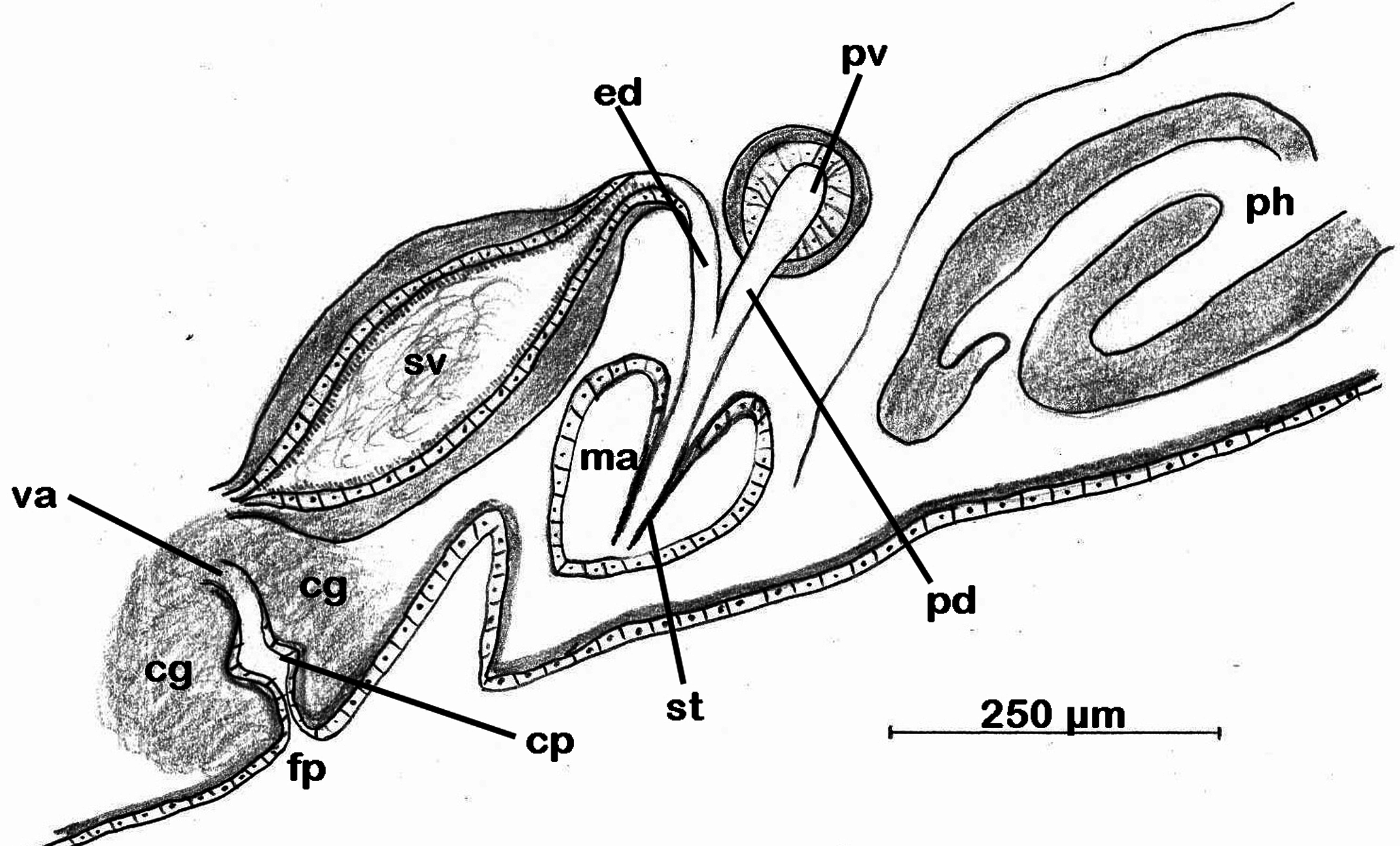
Reproductive system: Male copulatory apparatus consists of seminal vesicle, free prostatic vesicle ( Fig. 7a View FIGURE 7 ), penis papilla, penis stylet housed in male atrium which open outside via male pore. An oval seminal vesicle (317 x 157 µm) is present ( Fig. 7b View FIGURE 7 ). Its rounded part oriented towards prostatic vesicle while tapered part is oriented towards cement glands. A free, small, circular and thick walled prostatic vesicle (80 x 58 µm) is present anterior to seminal vesicle ( Fig. 7 a, b View FIGURE 7 ). Thickness of prostatic vesicle’s wall varies from 15 to 20 µm. Male atrium conical (283 µm x 187 µm) housing conical penis papilla (170 µm) with a stylet ( Fig. 7c View FIGURE 7 ). Female copulatory apparatus consists of vagina, cement pouch surrounded by dense cement glands and female atrium. The vagina opens to a short female atrium via cement pouch which receives secretion from cement glands ( Fig. 7c View FIGURE 7 ).
Taxonomic remarks: Presence of ruffled pharynx, male copulatory apparatus just behind pharyngeal cavity, free prostatic vesicle, marginal tentacles formed by upfolding of anterior margin, centrally located sucker behind female pore ( Faubel 1984) places Pseudoceros stellans sp. nov. in the family Pseudocerotidae while presence of characters such as smooth dorsal surface, single male copulatory apparatus with seminal vesicle ( Fig. 4a View FIGURE 4 ) and armed penis papilla, pseudotentacles as simple folds of anterior margin, female pore equidistant from male pore and sucker ( Faubel 1984; Newman and Cannon 1998) place this newly described species in the genus Pseudoceros . All of the above mentioned characters can be recognised in the present species from Agatti Island. The newly described species differs from all other congeners on the basis of dorsal colour and spots. Although there are some species under the genus Pseudoceros with spots ( Pseudoceros astrorum Bulnes and Torres, 2014 Pseudoceros heroensis Newman and Cannon, 1994 ; P. josei Newman and Cannon, 1998 ; P. kylie Newman and Cannon, 1998 ; P. laingensis Newman and Cannon, 1998 ; P. leptostictus Bock, 1913 , P. lindae Newman and Cannon, 1994 ; P. nigropunctatus Dixit, Raghunathan and Chandra, 2017 and P. vishnui Dixit, Raghunathan and Chandra, 2017 ) but the colour, size, arrangement, density and distribution of spots varies from species to species and is used for species identification. Pseudoceros josei , in terms of background colour and spots size and arrangement shows some affinity with the presently described species but it doesn’t have black marginal band. The spots turn white towards the margin ( Newman and Cannon, 2005) which is opposite in case of P. stellans sp. nov. where spots turns yellow towards margin. Pseudoceros astrorum is also characterised by dark brown background with spots but it has a white marginal rim which is not present in P. stellans sp. nov. Pseudoceros kylie also possess dark brown background with cream microdots but has bright orange broken band just before the rim while the marginal band is black and continuous in P. stellans sp. nov. Other species such as P. laingensis (purple spots), P. leptostictus (small black and orange spots), P. lindae (golden yellow spots), P nigropunctatus (black spots with cream halo) and P. vishnui (purple to violet spots) possess spots with different types of colours, distribution and different type of marginal bands. Thus, in the light of above mentioned characters and comparisons, P. stellans sp. nov. is reported as a new species to science.
| IO |
Instituto de Oceanografia da Universidade de Lisboa |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |