Biskratrombium persicum Majidi, Hajiqanbar and Saboori, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.47121/acarolstud.1209774 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0192D41B-837D-434D-B1F6-AE55C6B29A39 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8156031 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AA879D-627C-FF90-FFC3-FD48FA0BFEC9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Biskratrombium persicum Majidi, Hajiqanbar and Saboori, 2020 |
| status |
|
Biskratrombium persicum Majidi, Hajiqanbar and Saboori, 2020
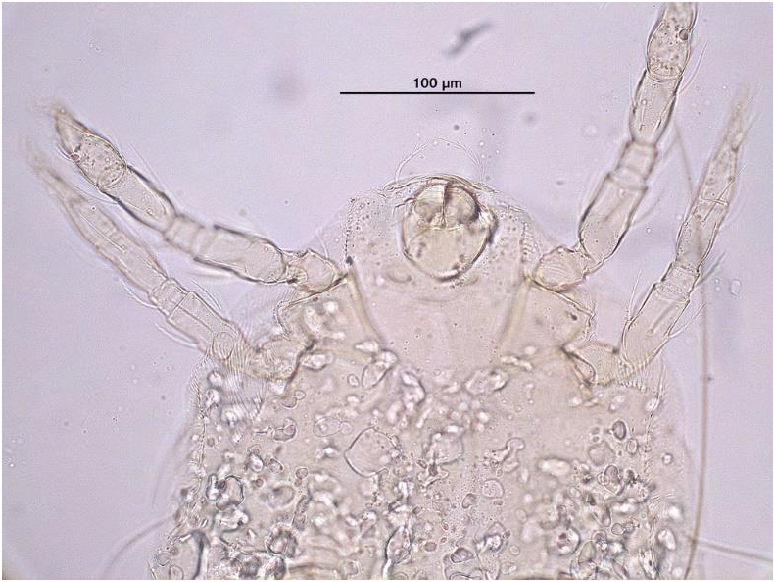
In the study conducted i n Muğl a, the presence of a larva of Biskratrombium persicum ( Fig. 2 View Figure 2 ) was determined as ectoparasitic on adult female Phlebotomus alexandri . The specimen form Türkiye is identified as Biskratrombium persicum by the presence of eupathidia on palpal tarsus; the longest seta on palpal tarsus is not a solenidion; scutum, scutellum and platelets smooth; setae on scutellum placed in the middle. Scutum’s lateral borders slightly concave.
Short description
Cheliceral blade curved and simple. Palpf emur and palpgenu without seta. Ey es absent. Scutum trapez oidal in shape; lateral borders slightly concave, posterio r border convex, slightly concave at anterior border. Scutum with three pai rs of non-s ensillary ( AM, AL and PL) and one pair of sensillary setae ( S). The width of scutellum less than the scutum, bearing one pair of barbed setae c 1. Legs segmentation formula: 6–6–6. Tarsi I and II eac h bearing o nly two trifurcate claws, while tarsus III with two trifurcate claws and a claw-like empodium.
Host information
Phlebotomus papatasi View in CoL View at ENA , P. alexandri and Sergentomyia mervynae ( Majidi et al., 2020) .
Distribution
Iran ( Majidi et al., 2020) and Türkiye (present study).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Prostigmata |
|
SuperFamily |
Trombidioidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |