Hoya rotundiflora Rodda & Simonsson, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.27.1.4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4923660 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AB3F04-8A10-FF82-FF03-CD5BFE0E92AE |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Hoya rotundiflora Rodda & Simonsson |
| status |
sp. nov. |
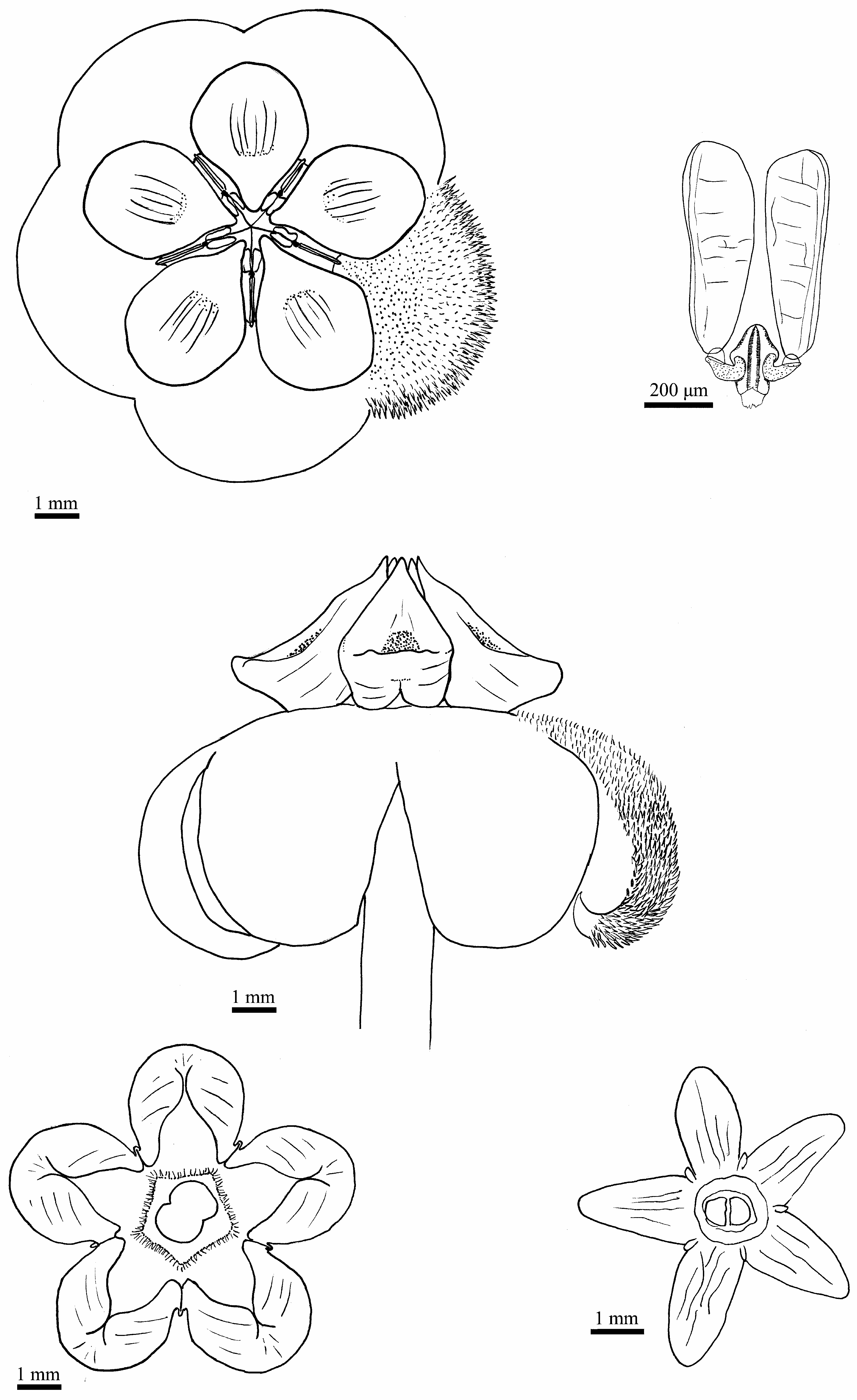
Hoya rotundiflora Rodda & Simonsson View in CoL , sp. nov. ( Figs. 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
Habitum ad Hoyam lyi et Hoyam thomsonii accedit sed corolla revoluta, corona lobis erectiores et folia margine revolutis recedit.
Type:— Ex hort. Sweden, Stockholm, 1 September 2009, Torill Nyhuus 2009.1 (holotype K) .
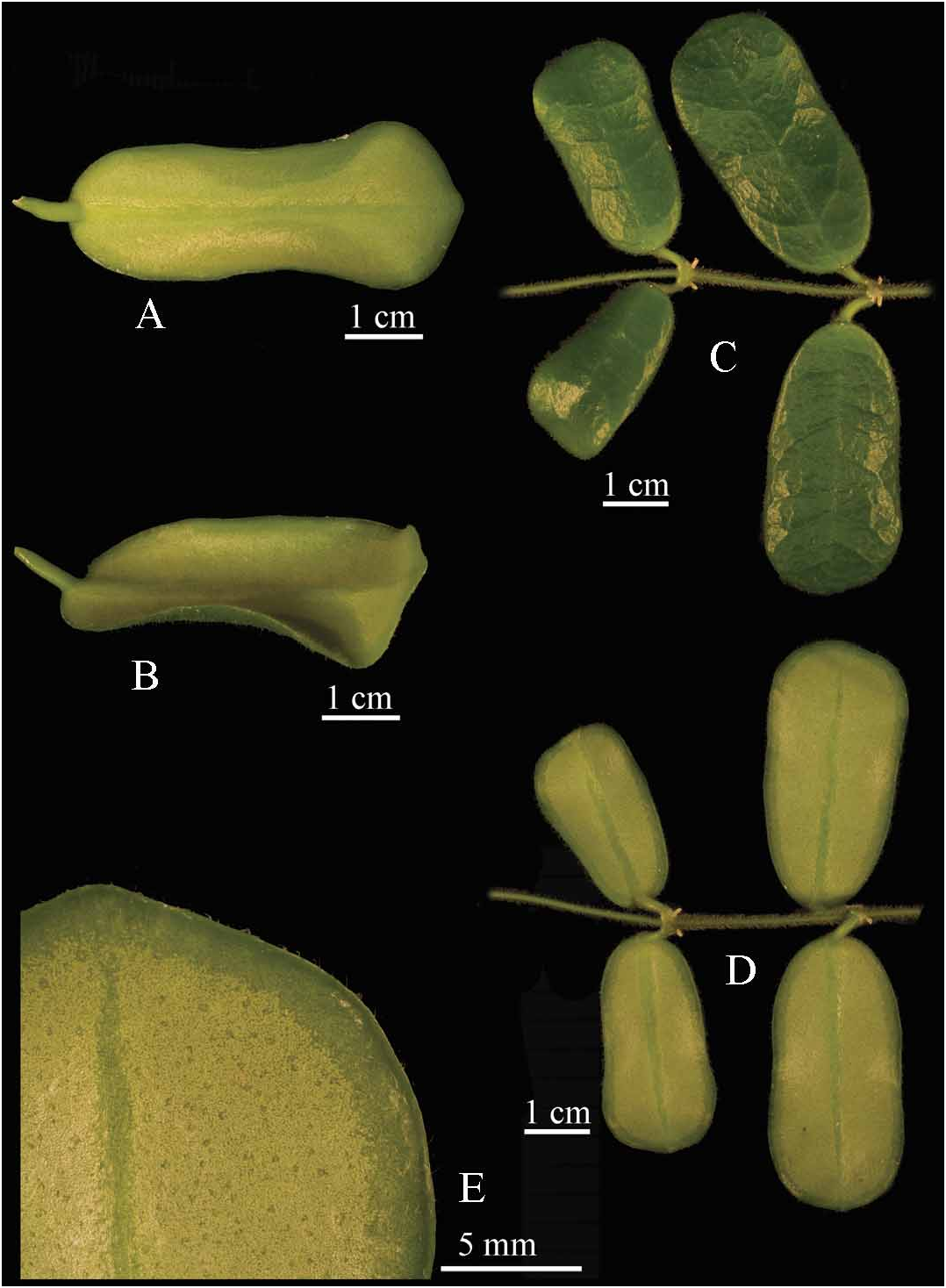
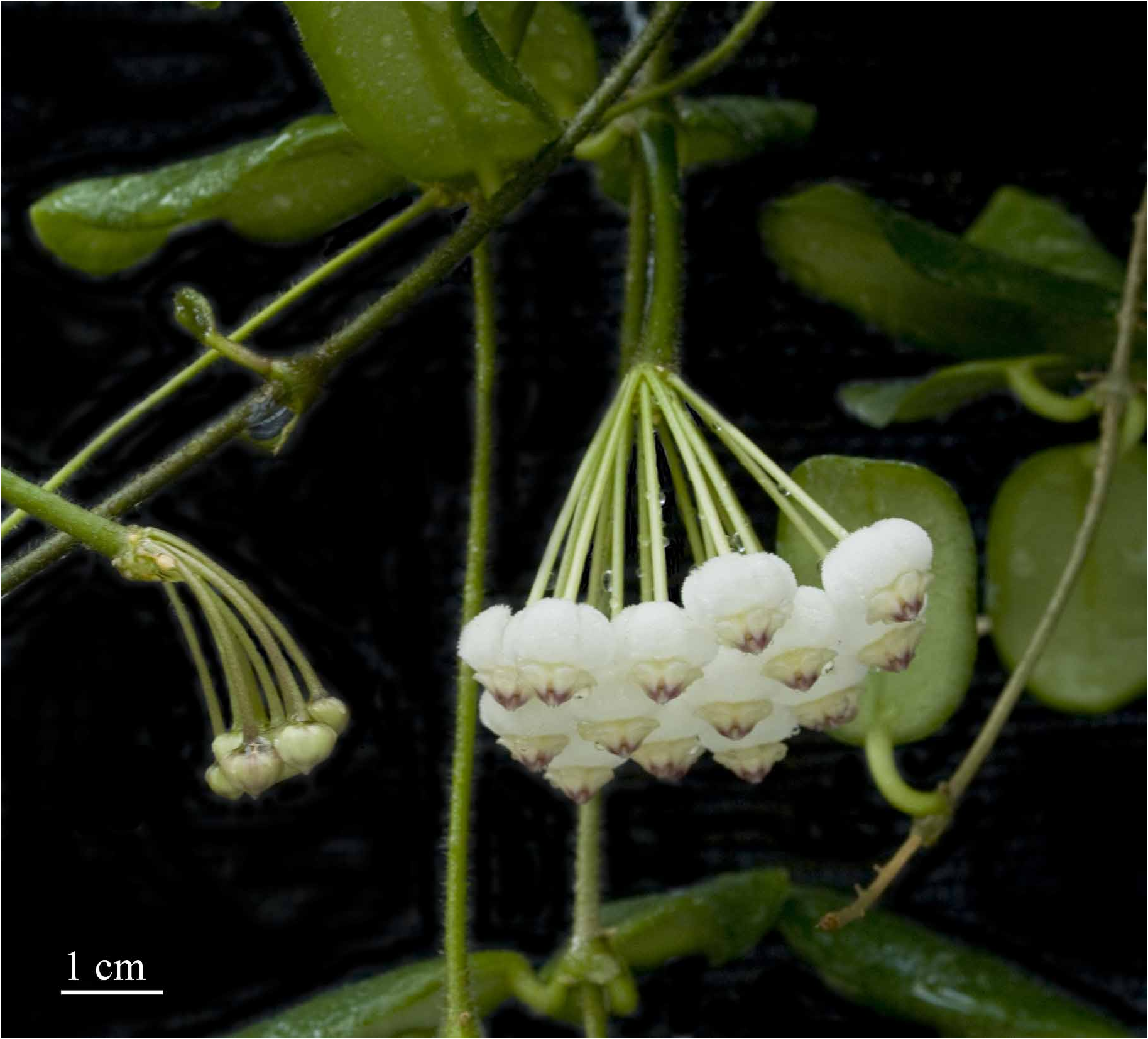
Pendulous to weakly climbing vine with white latex in all parts. Stems pendulous to weakly twining, cylindrical, ca. 3 mm in diameter, pilose; older stems lignified, glabrous; internodes 2–10 cm long with inactive adventitious roots 1–2 mm long located 0–2 mm below each petiole. Leaves ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ) opposite, petiolate; petiole 3–10 × 1–2 mm, pilose; lamina oblong-pandurate, 3–5 × 1.5–2.5 cm, widest point 1/8–1/5 length from the apex, fleshy coriaceous, adaxial surface dark green, abaxial surface light green with a distinctive darker margin 2–3 mm wide around the edge ( Fig. 2e View FIGURE 2 ), abaxial surface glabrous, adaxial surface hirsute, apex round, base round or obtuse, margin slightly revolute on the lateral sides and apex only, ciliate; midrib clearly visible on both abaxial and adaxial surface, secondary veins 4 to 6 each side, less conspicuous, branching from the midrib at a wide acute or an almost right angle. Inflorescences ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ) one per node, interpetiolar, positively geotropic, umbelliform, convex, with up to 20 flowers, persistent; peduncle 5–35(–70) × 1.5–3.0 mm, pilose, pedicels filiform, 17–20 × 1.0– 1.5 mm, glabrous. Flower buds globular, white. Flowers weakly sweetly scented (lasting about one week in cultivation), from the base of the corolla lobes to the inner apex of the corona 7–10 mm long, corolla 9–12 mm in diam. Sepals ( Fig. 1d View FIGURE 1 ) ovate, ca. 2.5 × 1.0 mm, apex round, alternating with single glands, glabrous, a few long hairs at the junction between the sepals and the pedicel. Corolla revolute, white; lobes lanceolate, 9–11 mm long, acute at apex; free portion of lobes 7–8 × 4.5–5.5 mm, distance between each sinus 3.5–4.0 mm, abaxially glabrous, hirsute adaxially, hairs up to 0.3 mm long, lobe apex (ca. 1 mm long) glabrous, margins ciliate. Corona staminal ( Fig. 1a,b,c View FIGURE 1 ) fleshy, dull white to light yellow, laterally spreading, ca. 3 mm high, 6.5–7.5 mm in diameter; corona lobes held at 30–40 degrees to the filament tube, outer process rounded to obtuse, flattened, only partially folded beneath ( Fig. 1c View FIGURE 1 ), inner process acute, held at about the same height as the anther appendages. Distance between center and outer corona process 3.3–3.6 mm; distance from center to corona sinus 1.5–1.8 mm; beneath corona, distance between filament tube and anther skirt (beneath guide rail) 0.6–0.8 mm. Pollinaria erect, ca. 830 × 430 µm; pollinia elongated, compressed, 660 × 220 µm, with a lateral pellucid margin; retinaculum 260 × 160 µm; translator 70–100 µm long. Ovary lanceolate, about 1.7 mm long, light green. Fruits and seeds not seen. All measurements from fresh type material.
Phenology: — Hoya rotundiflora is commonly seen flowering in cultivation during the summer months, which is consistent with the flowering periods of plants from a monsoonal area such as south Myanmar. A similar flowering season has been observed for Hoya pandurata Tsiang (1939: 125) and H. chinghungensis (Tsiang & P.T.Li) Gilbert et al. (1995: 9) both originating from this geographical area (personal observations).
Habitat and distribution: —Little is known about the original habitat of this species. It has been observed to be difficult to grow and flower in constantly warm areas such as Bangkok ( S. Somadee, personal communication) and therefore it is likely to inhabit higher elevated areas where winter temperatures are lower and where there is a greater disparity between day and night temperatures.
The type plant can be traced back to a market in Sangklaburi in Kanchanaburi province, Thailand, where it was first found in 2005. The plant was collected near the border in neighboring Myanmar but the exact locality has been kept secret by the seller .
IUCN Red List category: —Population size and distribution range of Hoya rotundiflora cannot be estimated, as it is so far known from only a single collection. Due to the high horticultural interest in Hoya it is surprising that no further collections belonging to this taxon have been made since its first introduction into cultivation in 2007. This may suggest that the species may have a very restricted distribution range and small population size containing a limited number of mature individuals or its habitat may be inaccessible, for example being on steep karst formations. Further, Hoya populations are often under pressure because of frequent collection to supply the horticultural trade and therefore H. rotundiflora is hereby suggested as vulnerable according to IUCN Red List criteria ( IUCN 2001).
Additional specimen examined: — Ex Hort., 15 June 2010, Rodda Hort 2010/1 ( L, SING, TO) .
| K |
Royal Botanic Gardens |
| A |
Harvard University - Arnold Arboretum |
| S |
Department of Botany, Swedish Museum of Natural History |
| L |
Nationaal Herbarium Nederland, Leiden University branch |
| SING |
Singapore Botanic Gardens |
| TO |
University of Turin |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Asclepiadoideae |
|
Genus |