Gomphonema linearoides Levkov, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.30.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4924779 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AC87D2-B842-FFD6-00FD-FE4D22A8D969 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Gomphonema linearoides Levkov |
| status |
sp. nov. |
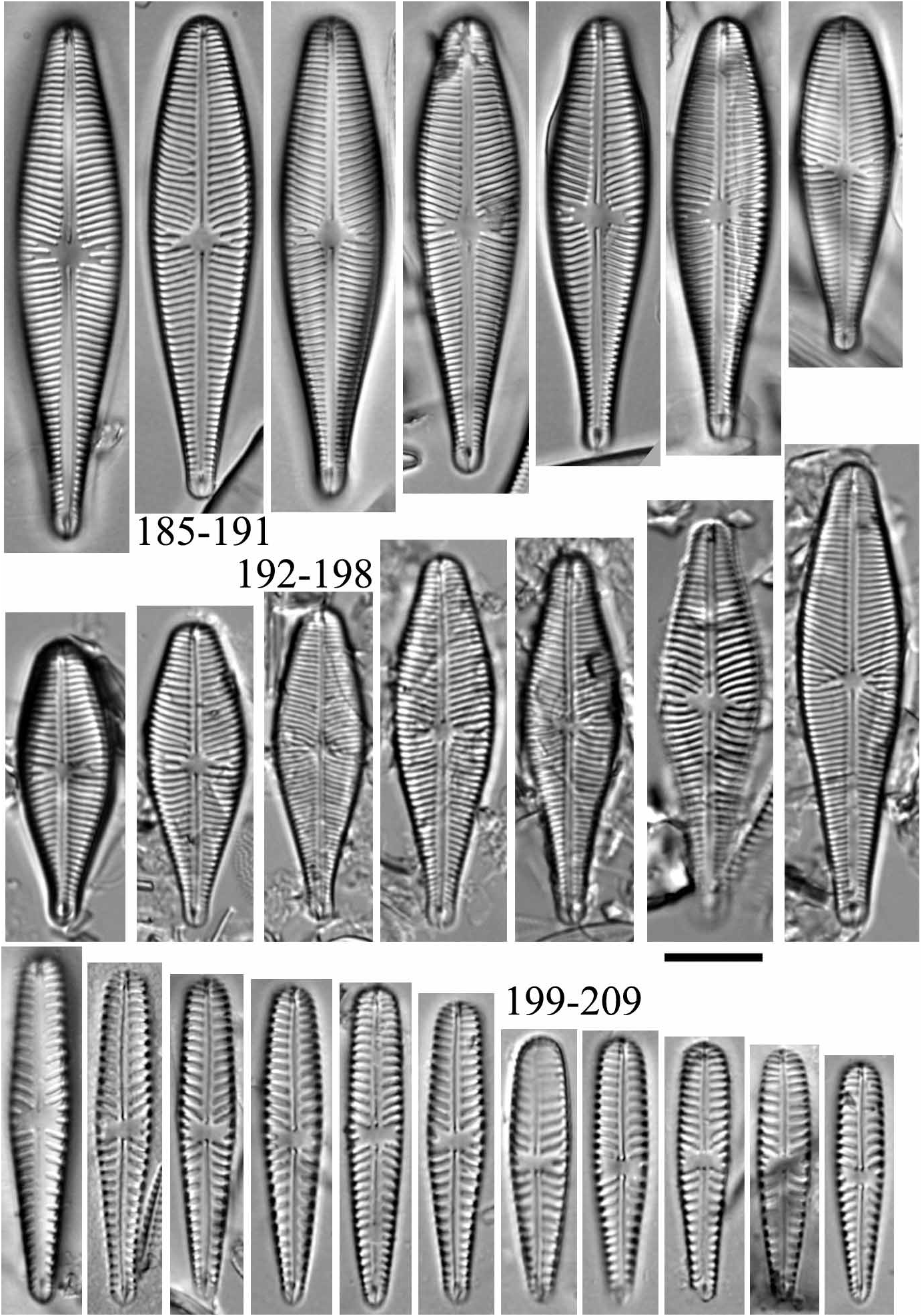
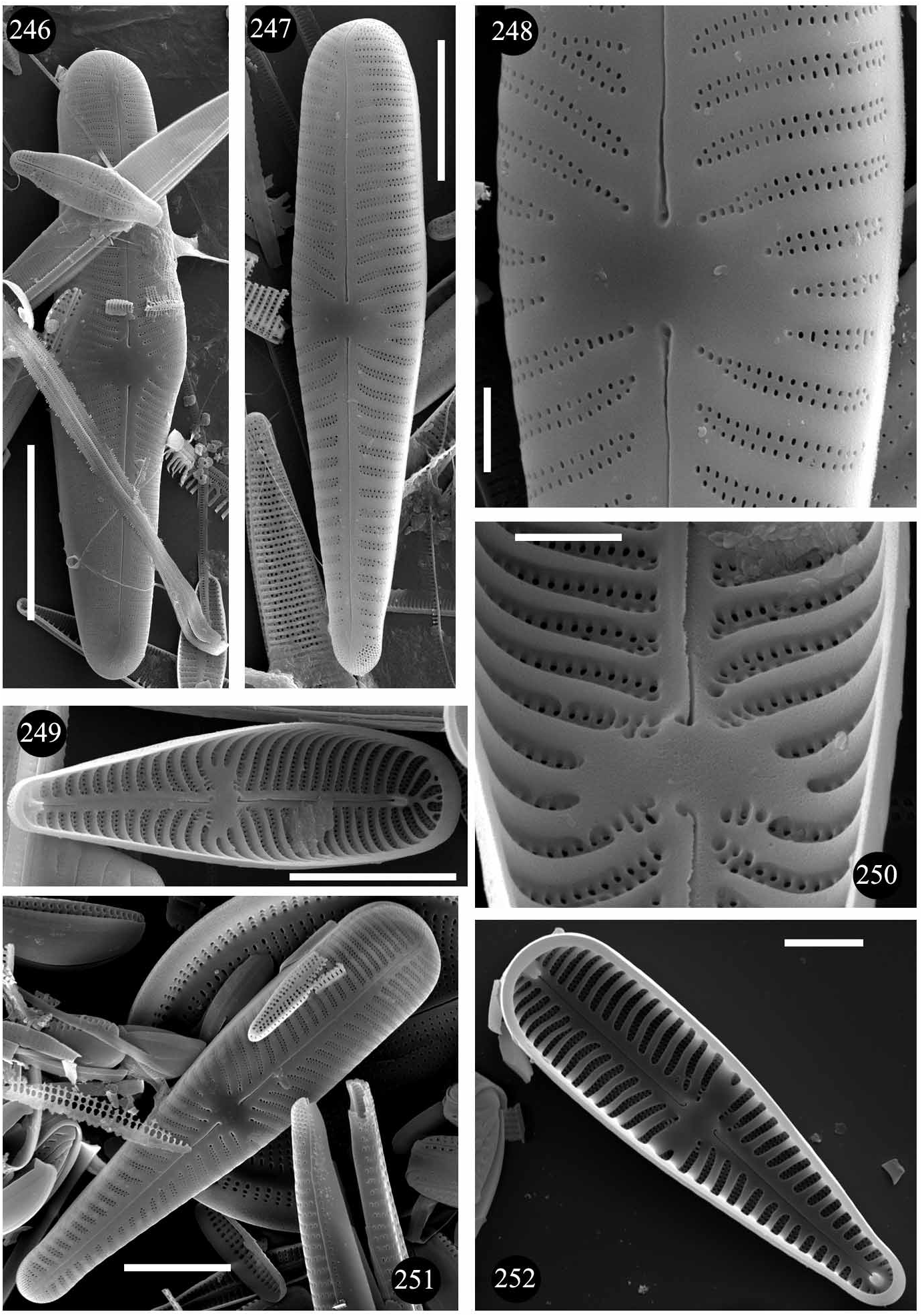
Gomphonema linearoides Levkov , sp. nov. ( Figs 199–209 View FIGURES 185–209 , 246–250 View FIGURES 246–252 )
Valvae distinctius lineari-clavatae verticibus distincte obtusius rotundatis quam basipoli. Longitudo valvae 24–35 µm, latitudo valvae 5.1–6.5 µm. Raphe filiformis poris centralibus distinctis. Area axialis angusta linearis, area centralis lata , rectangularis. Stigma solitaria abest. Striae transapicales valde radiate in media parte, leviter radiate vel parallelae sub apices, 7–11 in 10 µm.
Type:— MACEDONIA. Lake Ohrid, St. Naum springs, above ground springs, macrophytes, collection date : 25 April 2003 (accession No. MKNDC 000632 View Materials ). Slide BM 101479 ( holotype). Slide MKNDC 000632 View Materials (isotype).
Valves distinctly club-shaped, narrowly linear, head poles more obtusely rounded than foot poles. Valve length 24–35 µm, valve width 5.1–6.5 µm. Raphe filiform with distinct central pores. Axial area narrow, linear. Central area broad panduriform. Striae strongly radiate in valve middle, becoming slightly radiate to parallel near apices, 7–10 in 11 µm (LM).
Raphe on post-initial cells not passing to valve mantle ( Fig. 246 View FIGURES 246–252 ). Distal raphe endings at head pole are modified. Interstriae of vegetative cells broader than striae ( Figs 248, 249 View FIGURES 246–252 ). Striae biseriate, composed of two rows of alternating, round areolae ( Figs 247, 248 View FIGURES 246–252 ). Internally, proximal raphe endings unilaterally hooked ( Figs 249, 250 View FIGURES 246–252 ) ( SEM).
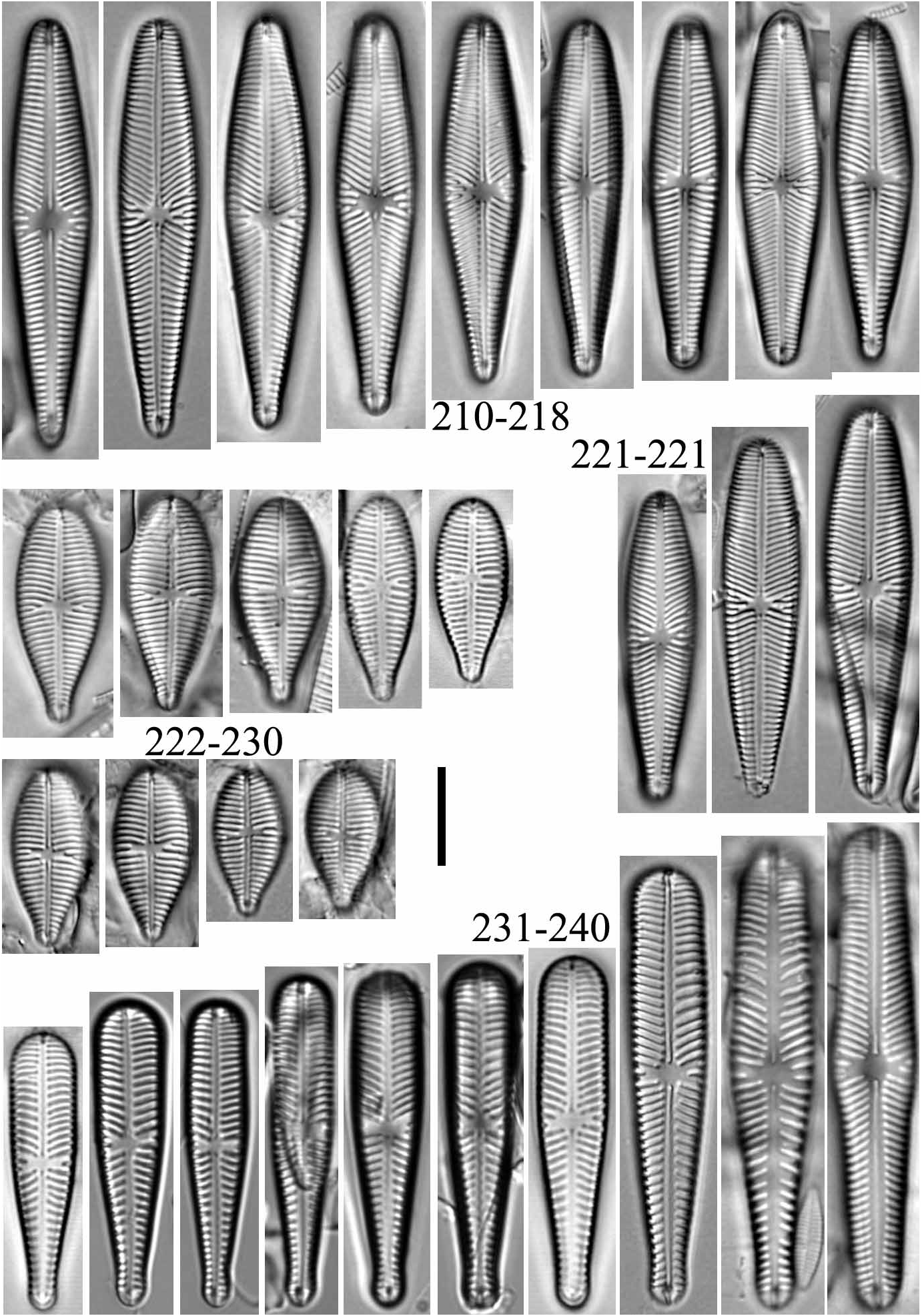
Observations:—Two main characters are important for the differentiation of G. linearoides from other members of the G.olivaceum complex: its linear valves and low striae density. It can be distinguished from G. fonticolum ( Figs 231–240 View FIGURES 210–240 , 251, 252 View FIGURES 246–252 ) by the shape of the head pole (truncate in G. fonticolum ), shape of the base pole (subcapitate in G. fonticolum ) and striae density ( 9–14 in 10 µm in G. fonticolum ). Gomphonema olivaceum var. staurophora Pantocsek (1889: 56 , fig. 12: 206) has a low striae density (11.0– 12.5 in 10 µm) and similar valve outline but significantly differs with respect to the shape of the central area extending to the valve margins. Gomphonema olivaceum var. minutulum Mayer (1919: 207 , fig. 9: 26) has smaller, clavate valves (L= 15–20 µm) which makes differentiating the pair simple.
| BM |
Bristol Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |