Amblyceps cerinum, Ng, Heok Hee & Wright, Jeremy J., 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.199168 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5625218 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03ACE724-C91E-FFEE-FF30-70F41BBD3E9F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Amblyceps cerinum |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Amblyceps cerinum View in CoL sp. nov.
( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 )
Amblyceps mangois View in CoL (in part)— Hora 1933: 617.
Amblyceps apangi View in CoL (non Nath & Dey)— Sullivan et al. 2008: 64; Ng & Wright 2009: 374.
Type material. Holotype: UMMZ 248850, 72.8 mm SL; India, West Bengal, Raidak I River at Shipra, just outside Buxa Tiger Reserve approx. 8 km toward Barobisha on Siliguri-Guwahati road, 26°31’12”N, 89°43’25”E; A. Rao, 30 January 2010.
Paratypes: BMNH 1932.4.22.2–5 (3), 28.1–30.8 mm SL; RMNH 16093 (2), 38.6–51.6 mm SL; India: West Bengal, Sevoke stream, Tista Valley; S. L. Hora, February 1931. CAS-SU 69784 (1), 42.8 mm SL; India: West Bengal, Kalimpong Duars and Siliguri Terai; S. L. Hora, November 1938. UMMZ 248834 (4), 59.0– 89.2 mm SL; collection data as for holotype. UMMZ 248835 (21), 61.4–97.3 mm SL; locality data as for holotype; A. Rao, 23 March 2010. UMMZ 244754 (7), 30.0–83.0 mm SL; locality data as for holotype; H. H. Ng et al., 13 April 2004.
Diagnosis. Amblyceps cerinum differs from all congeners except A. apangi , A. murraystuarti , and A. torrentis in having a truncate (vs. forked or strongly emarginate) caudal fin. It differs from A. apangi in having a longer adipose-fin base (32.4–38.3% SL vs. 24.3–32.0), a more slender caudal peduncle (9.2–11.2% SL vs. 11.3–15.4), a greater number of post-Weberian vertebrae (41–44 vs. 38) and in having the lateral line terminating just posterior to the vertical through the dorsal-fin insertion (vs. extending to the end of the caudal peduncle), from A. murraystuarti in having a more slender body (9.2–11.2% SL vs. 11.6–15.0), a longer caudal peduncle (21.9–24.5% SL vs. 19.6–22.6) and the posterior end of the adipose fin not broadly confluent with the dorsal procurrent caudal-fin rays and separated from them by a distinct notch (vs. adipose fin broadly confluent with dorsal procurrent caudal-fin rays and not separated by a distinct notch), and from A. torrentis in having a more slender body (9.2–11.9% SL vs. 15.3–17.3% SL) and caudal peduncle (9.2–11.2% SL vs. 13.8– 15.6), the upper jaw longer than the lower jaw (vs. jaws equal), and an incomplete lateral line terminating at the posterior base of the dorsal fin (vs. a complete lateral line terminating at the base of the caudal fin).
Description. Biometric data in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Body elongate, semi-cylindrical anterior to pelvic fins, compressed posterior to pelvic fins. Predorsal profile convex; gently sloping ventrally from dorsal-fin origin to tip of snout; contour smooth except for noticeable notch formed by origin of jaw adductor muscles on skull. Postdorsal profile relatively straight from dorsal-fin insertion to vertical through anal-fin origin, becoming gently convex posterior to vertical through anal-fin origin. Preanal profile convex from tip of snout to vertical through dorsal-fin origin, becoming convex from vertical through dorsal-fin origin to anal-fin origin. Postanal profile straight or slightly concave. Skin on flanks, head, and all fins covered with small, granular papillae, clearly visible under magnification. Lateral line incomplete, terminating at point slightly posterior to vertical through dorsal-fin insertion. No discernible difference in urogenital morphology between males and females.
Head depressed, broad, wedge-shaped in lateral profile. Snout long, acutely triangular when viewed laterally, broadly rounded when viewed dorsally. Anterior nostril located at base of nasal barbel, forming short, ovaline tube. Anterior margin of posterior nostril confluent with posterior base of nasal barbel; posterior margin surrounded by short flap of skin. Gill membranes narrowly joined at isthmus. Eye located dorsally, well posterior of nasal barbel, subcutaneous, ovoid, horizontal axis longest. Interorbital area markedly concave.
Mouth subterminal, upper jaw extending well beyond lower, lips thickened and papillate. Premaxillary teeth short, conical, posteriorly directed; arranged in semi-rectangular band with well developed posterior extensions. Mandibular teeth small, conical, arranged in narrow crescentic band. Maxillary barbel short, when adpressed reaching just beyond origin of pectoral fin. Nasal barbel short, when adpressed posteriorly, reaching far beyond posterior margin of eye. Lateral mandibular barbel reaching to posterior base of pectoral fin. Medial mandibular barbel short, less than ¼ length of head. All barbels lacking membrane.
Dorsal fin i,5 (4) or i,6 (21)*, origin at vertical through middle of pectoral fin; first element flexible, incompletely ossified. Pectoral fin i,7 (23)* or i,8 (2), first element flexible, incompletely ossified. Pelvic fin with i,5 (25) rays, located approximately at vertical through midpoint between dorsal-fin insertion and adipose-fin origin. Anal fin with iv,8 (3), iv,9 (4), v,8 (10)* or v,9 (6) elements, margin rounded, origin at point 1/3 distance between pelvic-fin origin and caudal-fin origin. Caudal fin with x,7,8,xii (1), xi,8,8,xi (2), xi,8,8,xii (4), xi,8,8,xiii (1), xii,8,7,xii (1), xii,8,8,xi (1), xii,8,8,xii (10)*, xii,8,8,xiii (1), xii,8,9,xiii (1) or xiii,8,8,xiii (1) rays; emarginate; upper lobe slightly longer than lower, terminating in short filament. Adipose fin long, low, upper margin convex; origin at vertical midway between adpressed tip of pelvic fin and anal-fin origin. Vertebral column with 41 (6), 42 (9)*, 43 (6) or 44 (3) post-Weberian vertebrae.
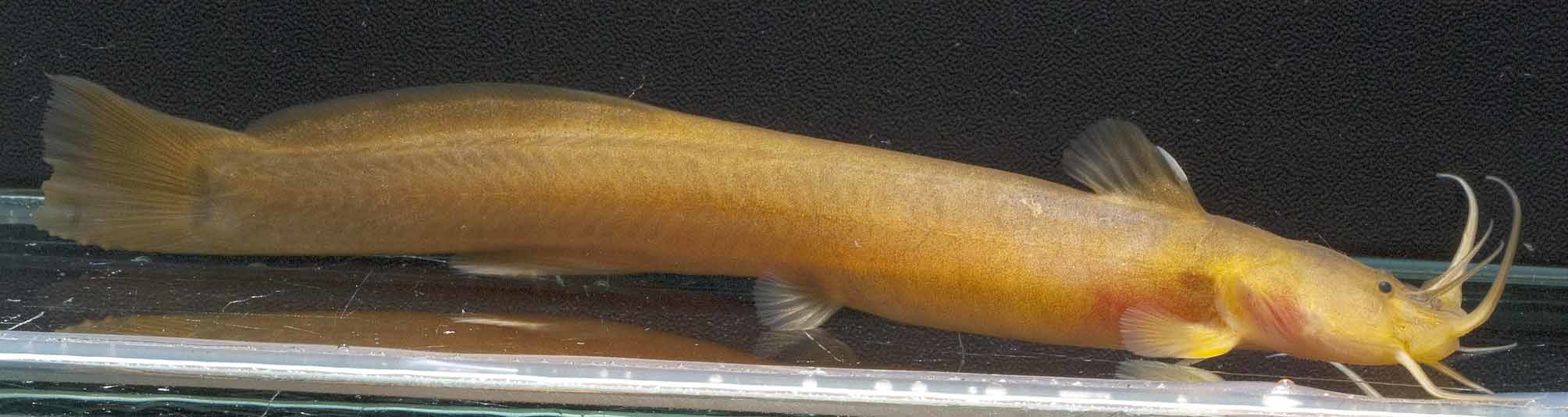
Coloration. In 70% ethanol: Dorsum and upper flanks reddish beige to light gray. Lower flanks beige, trending lighter toward cream-colored belly. Nasal and maxillary barbels with gray basally, becoming lighter distally. Mandibular barbels cream colored. Dorsum coloration extending onto base of dorsal and adipose fins; both fins with lighter outer margin, very thin on adipose fin. Pectoral, pelvic, and anal fins with very faint pigmented area at base, otherwise uniformly cream colored. Caudal fin uniformly dusky, upper rays slightly more so than lower. Live color similar, but with a strong brownish- or orange-yellow hue ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ).
Distribution and habitat. Amblyceps cerinum is known only from the Brahmaputra River drainage in northern West Bengal, India ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ). The type locality is a shallow, swift-flowing stream with a substrate of cobble and sand ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ). The fish were frequently found under cobble.
Etymology. The specific epithet derives from the Latin adjective cerinus, meaning wax-colored. This name is used in allusion to the yellowish coloration in life of this species.
TABLE 1. Biometric data for Amblyceps cerinum (n = 25).
| Holotype | Range | Mean±SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard length (mm) | 72.8 | 59.0–97.3 | |
| %SL | |||
| Predorsal length | 26.9 | 22.8–29.2 | 26.1±1.82 |
| Preanal length | 63.3 | 62.7–67.1 | 65.0±1.45 |
| Prepelvic length | 48.1 | 46.6–50.6 | 48.3±1.00 |
| Prepectoral length | 20.9 | 16.3–22.9 | 20.2±2.19 |
| Length of dorsal-fin base | 7.1 | 6.2–8.7 | 7.5±0.84 |
| Dorsal-spine length | 6.7 | 5.0–8.9 | 7.3±1.18 |
| Length of anal-fin base | 12.1 | 10.6–13.6 | 12.1±0.86 |
| Pelvic-fin length | 8.8 | 7.2–9.5 | 8.4±0.71 |
| Pectoral-fin length | 10.4 | 10.0–11.6 | 10.9±0.62 |
| Pectoral-spine length | 6.9 | 5.7–8.5 | 6.8±0.95 |
| Caudal-fin length | 14.7 | 14.0–18.0 | 16.2±1.30 |
| Length of adipose-fin base | 33.9 | 32.4–38.3 | 34.8±1.90 |
| Dorsal to adipose distance | 29.7 | 26.8–33.3 | 30.0±2.29 |
| Length of caudal peduncle | 23.8 | 21.9–24.5 | 23.4±0.99 |
| Depth of caudal peduncle | 9.8 | 9.2–11.2 | 9.9±0.59 |
| Body depth at anus | 11.7 | 9.2–11.9 | 10.4±0.95 |
| Head length | 23.8 | 19.8–24.3 | 22.6±1.64 |
| Head width | 13.0 | 12.4–16.4 | 14.3±1.29 |
| Head depth | 7.0 | 7.0–9.2 | 8.3±0.72 |
| %HL | |||
| Snout length | 34.7 | 33.1–43.1 | 37.7±3.22 |
| Interorbital distance | 20.2 | 20.2–26.7 | 23.3±2.17 |
| Eye diameter | 5.2 | 5.1–8.1 | 6.0±1.02 |
| Nasal barbel length | 33.5 | 31.5–48.3 | 38.9±5.41 |
| Maxillary barbel length | 78.6 | 78.6–110.1 | 88.5±10.35 |
| Inner mandibular barbel length | 35.3 | 30.8–51.7 | 40.5±6.19 |
| Outer mandibular barbel length | 64.2 | 49.4–79.4 | 79.4±67.4 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Amblyceps cerinum
| Ng, Heok Hee & Wright, Jeremy J. 2010 |
Amblyceps apangi
| Ng 2009: 374 |
| Sullivan 2008: 64 |
Amblyceps mangois
| Hora 1933: 617 |