Megalepthyphantes gongshanensis, Irfan & Zhang & Peng, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/megataxa.8.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7535392 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AE87CE-BDF3-FF32-FF2E-3B7FFC50FA07 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Megalepthyphantes gongshanensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Megalepthyphantes gongshanensis sp. nov. (ṄƜDffl ƉƦ)
Figures 184–186 View FIGURE 184 View FIGURE 185 View FIGURE 186 , 189 View FIGURE 189
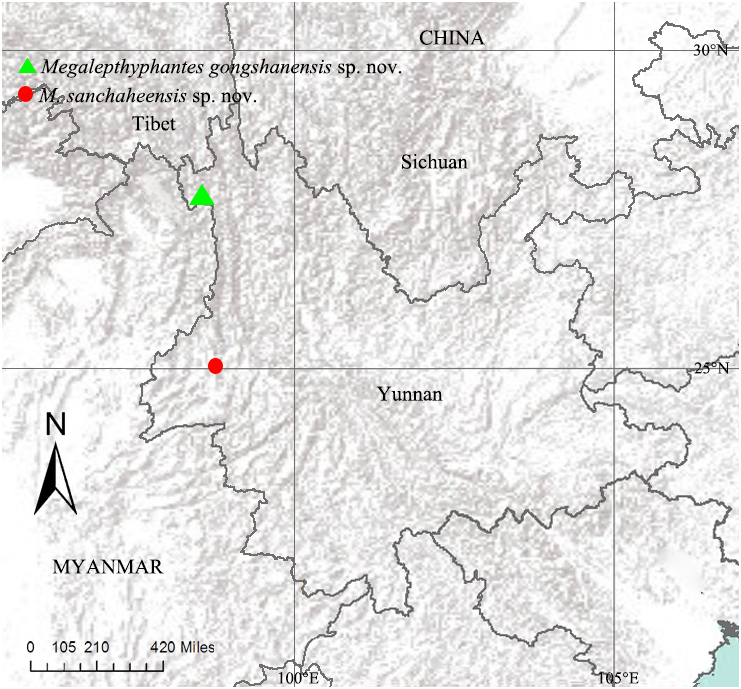
Types. Holotype ♂, CHINA, Yunnan, Gongshan County, Cikai Township, Gongshan , 27.74082°N, 98.66554°E, alt. 1505m, 21 September 2002, D. H. Kavanaugh leg. ( DHK –2002–023) GoogleMaps . Paratypes: 3♂ 3♀, same data as holotype male ( DHK –2002–023) GoogleMaps .
Etymology. This epithet derives from the type locality.
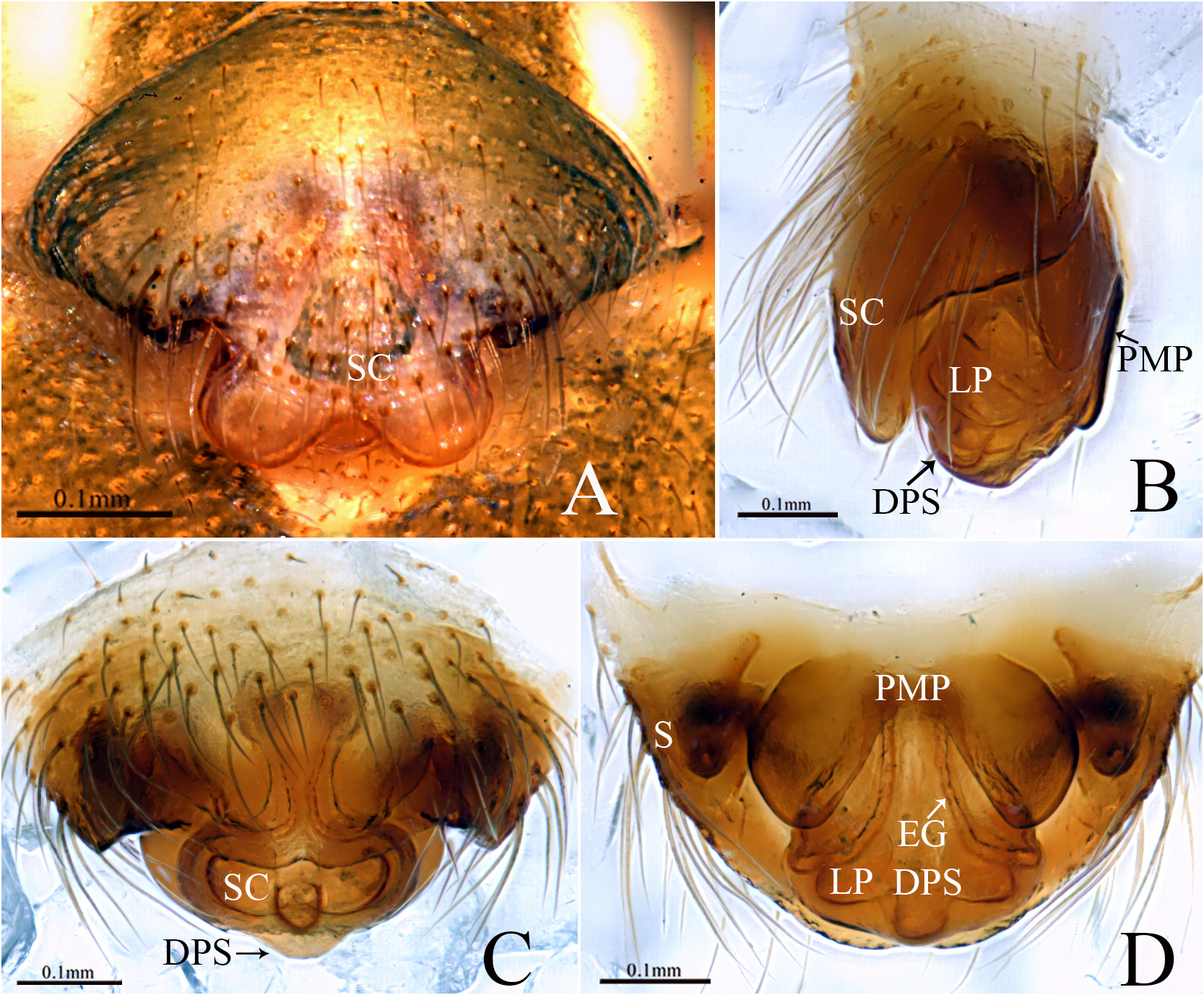
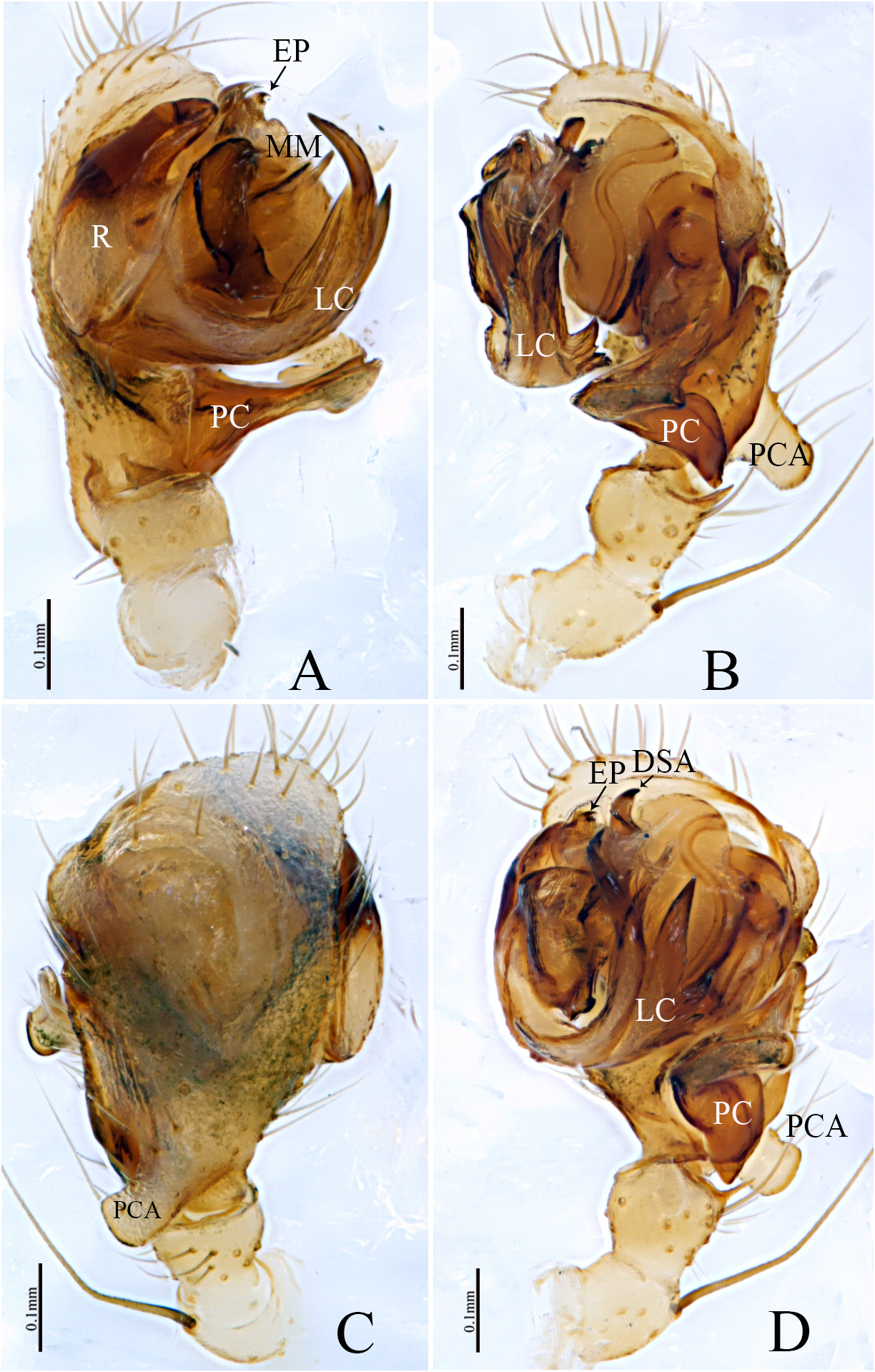
Diagnosis. The female of new species resembles that of Megalepthyphantes kronebergi ( Tanasevitch, 1989) and M. turkestanicus ( Tanasevitch, 1989) in having a similar scape and V-shaped posterior median plate ( Figs 184A–D View FIGURE 184 , 185A, C View FIGURE 185 ; Tanasevitch, 1989, figs 43, 45, 49, 51), but can be distinguished by the spermathecae bean-shaped in M. gongshanensis sp. nov. ( Fig. 184D View FIGURE 184 ). The male of the new species can be distinguished from all other congeners by the proximal end of paracymbium with a broad D-shaped projection pointing towards the retrolateral margin of the cymbium ( Fig. 185A View FIGURE 185 ). Proximal cymbial apophysis thumb-shaped with blunt end ( Fig. 185B–D View FIGURE 185 ). Lamella characteristca curved, with three long and one small branches, distal end serrated ( Fig. 185B, D View FIGURE 185 ).
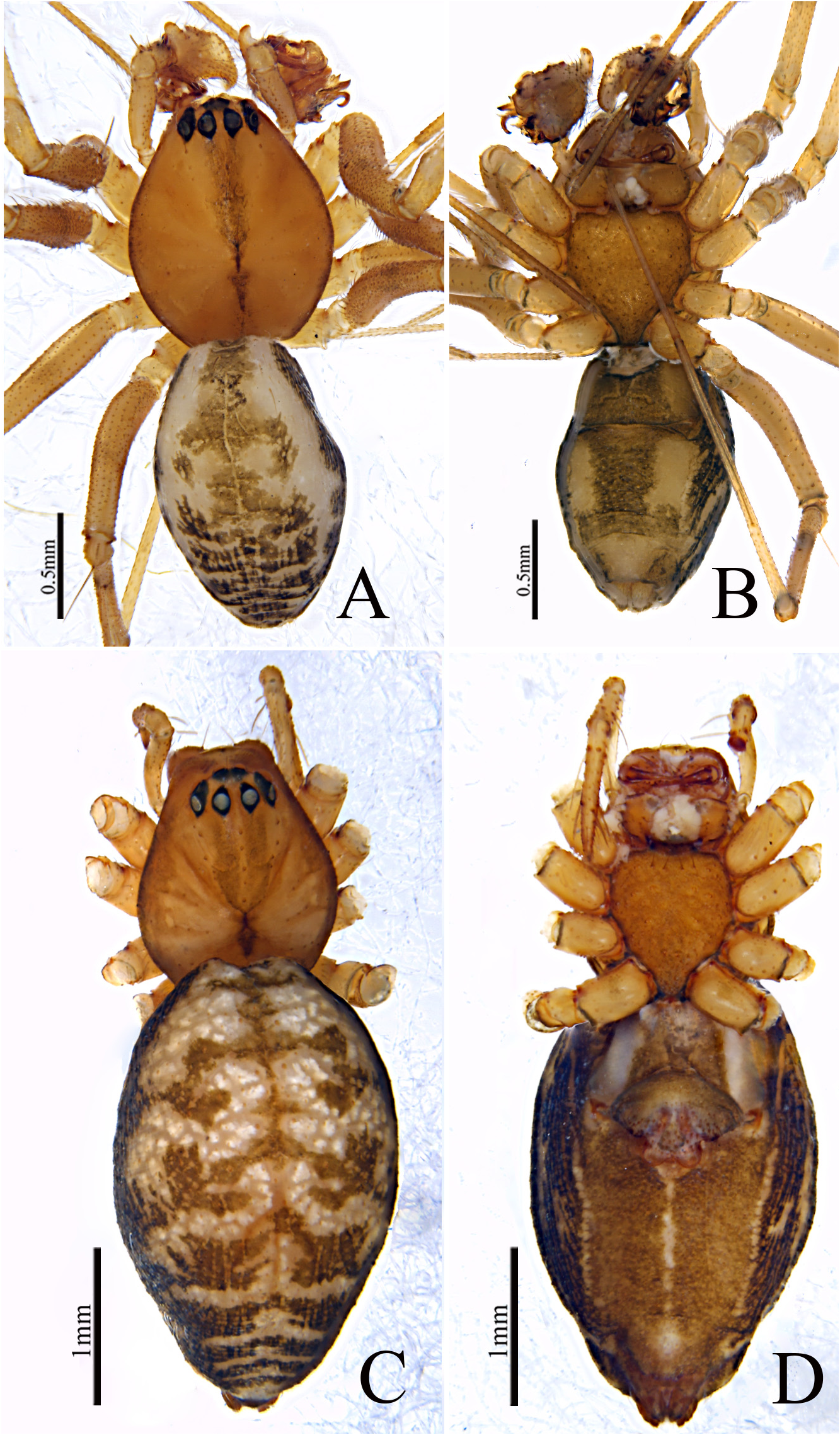
Description. Male ( holotype, Fig. 186A, B View FIGURE 186 ): Total length: 2.39. Carapace 0.98 long, 0.89 wide, brown, lateral margin dark brown; fovea, cervical and radial grooves distinct. Clypeus 0.18 high. Sternum longer than wide, brown,, sparsely covered with microsetae. Labium wider than long. Maxillae long, distal end broad with scopulae. Chelicerae with two promarginal and two retromarginal teeth. AER recurved, PER straight, slightly wider. Eye sizes and interdistances:AME 0.07, ALE 0.09, PME 0.08, PLE 0.08, AME–AME 0.03, PME–PME 0.06, AME– ALE, 0.05, PME–PLE 0.05, AME–PME 0.07, ALE–ALE 0.38, PLE–PLE 0.40, ALE–PLE contiguous. Length of legs: I 6.49 (1.69, 2.12, 1.62, 1.06), II 5.67 (1.54, 1.78, 1.44, 0.91), III 4.28 (1.27, 1.28, 1.07, 0.66), IV 5.6 (1.56, 1.71, 1.45, 0.88). Leg formula I-II-IV-III. Tm I 0.82 and Tm IV 0.53. Tibial spine formula: 2-2-2-2. Abdomen 1.41 long, 1.14 wide, oval, brown, dorsally with distinct black pattern; ventral side brown with a longitudinal light band at the center.
Palp ( Fig. 185A–D View FIGURE 185 ): Patella shorter than tibia with a long dorsal spine; tibia short, with a depression at the distal margin; two retrolateral and one dorsal trichobothria; proximal cymbial apophysis thumbshaped with blunt end. Paracymbium proximally wider than long, with a broad D-shaped ventral projection and fine spines, distal arm wider than long with blunt end. The ventral part of the distal suprategular apophysis small, covered by the tegulum with narrow hook-shaped dorsal tip. Radix longer than wide; Fickert’s gland situated embolus almost about half long of the radix. Lamella characteristca relatively sclerotized and curved, distal end leaf-shaped, three longer and one small shorter branches with serrated end.
Female (one of the paratypes, Fig. 186C, D View FIGURE 186 ): Total length: 4.50. Carapace 1.61 long, 1.27 wide, brown, lateral margin dark brown; fovea, cervical and radial grooves distinct. Clypeus 0.42 high. Sternum longer than wide, brown,, sparsely covered with microsetae. Labium wider than long. Maxillae long, distal end broad with scopulae. Chelicerae with three promarginal and three retromarginal teeth. AER recurved, PER straight, slightly wider. Eye sizes and interdistances:AME 0.11, ALE 0.13, PME 0.11, PLE 0.12, AME–AME 0.04, PME–PME 0.09, AME–ALE, 0.10, PME–PLE 0.07, AME–PME 0.11, ALE–ALE 0.53, PLE–PLE 0.57, ALE–PLE contiguous. Length of legs: I 11.85 (3.21, 3.77, 3.01, 1.86), II 10.51 (2.97, 3.25, 2.65, 1.64), III 7.56 (2.26, 2.23, 1.94, 1.13), IV 10.26 (2.79, 3.05, 3.89, 1.53). Leg formula I-II-IV-III. Tm I 1.41 and Tm IV 1.18. Tibial spine formula: 2-2-2- 2. Abdomen 2.89 long, 1.84 wide, oval, brown, dorsally with distinct black pattern; ventral side brown with a longitudinal light band at the center.
Epigyne ( Fig. 184A–D View FIGURE 184 ): Protruding; scape broad, wider than long, with a deep notch posteriorly in ventral view; distal part of scape with relatively small stretcher; entrance groove inside lateral pockets; lateral pockets ear lobe shaped extending laterally; posterior median plate broad, V-shaped with round lateral end on each side; spermathecae bean-shaped, curved, situated dorsolaterally.
Distribution. Known only from the type locality ( Fig. 189 View FIGURE 189 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |