Armascirus cerris, Kalúz, Stanislav, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.189555 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6223059 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B68B36-8D0A-8879-00F7-B639181CFD85 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Armascirus cerris |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Armascirus cerris , new species
Diagnostic features. This species can be destinguished from the other one in this paper by: the coxal I–IV setal formula 3-2-3-3 sts, the presence of dorsal hysterosomal median shield, the presence of spine- like seta on palpal genu, the long slender lateral hysterosomal platelets and by the distance between the bases of setae c1–c1 shorter than between f1–f1.
Description: Holotype, female, body length 930; width 340.
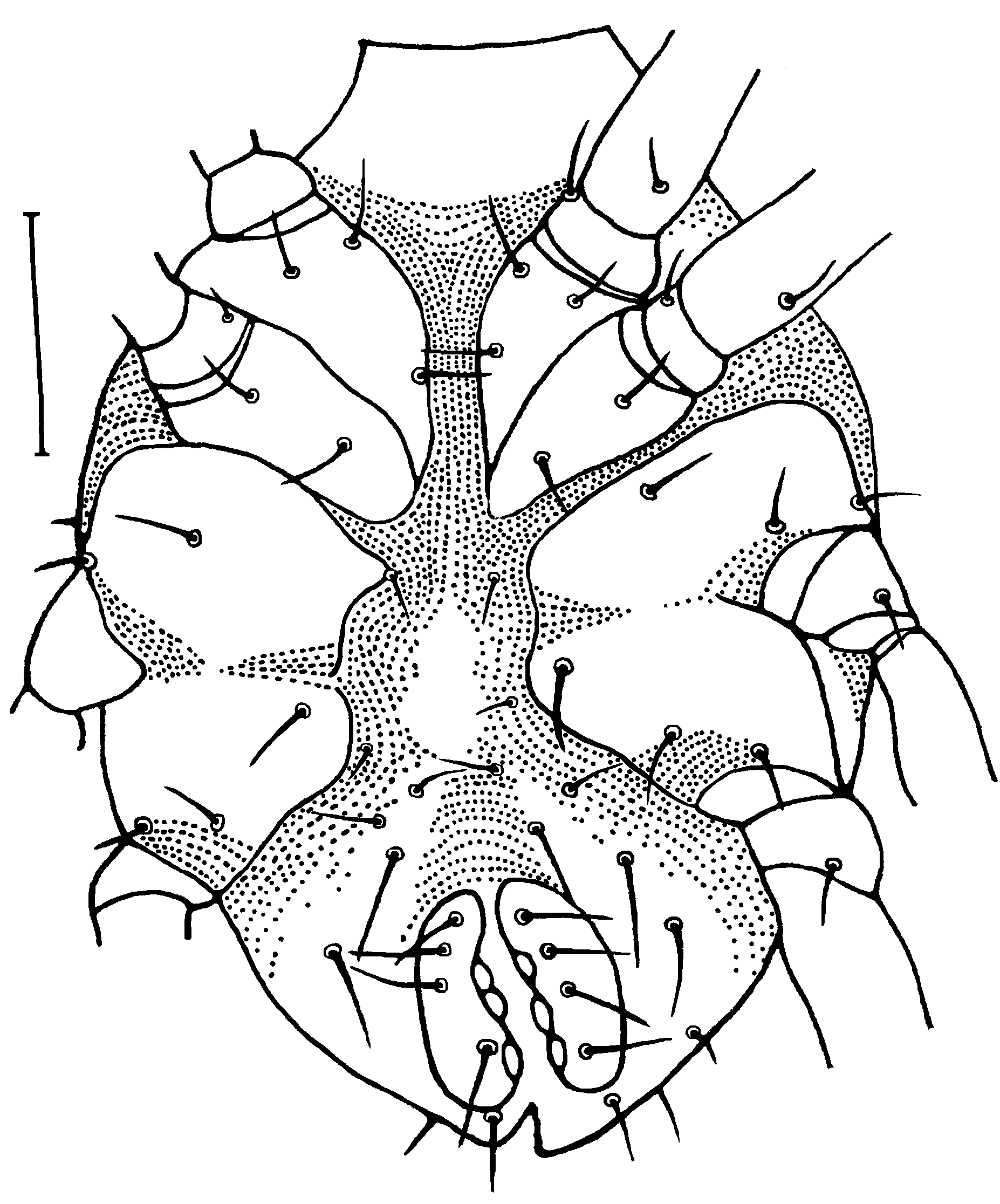
Dorsum ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ): Propodosoma with distally coneshaped reticulate shield bearing anterior ( vi) and posterior ( sce) sensillae and also propodosomal ve and sci setae. Propodosoma separated from hysterosoma by a fine striae with broken dashlike papillae. Fine striae anteriorly concave to transverse between the setae d1–d1. Hysterosoma with reticulate hysterosomal median shield and a pair of lateral reticulate plates. Six pairs of dorsal setae on hysterosoma; c1–h1, c2. Short setae c1, d1 and c2 equal in length (15), e1 longer (21), setae f1 (35) and h1 (41) two-three times the length of c1. The distance of bases c1–c1 (69) about 4-5 times the length of c1; d1–d1 (77) about five times the length of d1; e1–e1 (92) about six times the length of c1; f1–f1 (80) about 5 times the length of c1; e1–f1 (57) about 2,5 times the length of e1. The distance between the bases of f1–f1 1,6 longer than of h1–h1. The distance between the bases of setae h1–h1 equal the length of h1. The length:width ratio of the hysterosomal median shield is 1. The width of hysterosomal shield equal the distance between the bases of c1–c1 or d1–d1. A pair of long, slender and slightly medially concave lateral hysterosomal platelets closed to c2. The distance between the bases of setae c1–c1 equal d1–d1 and shorter than between f1–f1.
Ven t er ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ). Four coxal regions of two each (I–II and III–IV). Coxal plates weakly sclerotized, coxae I–II and III–IV contiguous and smooth. Coxae I–IV setal formula: 3-2-3-3. Venter of hysterosoma with a pair of simple setae on striated integument between coxae III and with 5-6 pairs of hysterosomal setae arranged anteriorly and laterally to the genital plates. Four pairs of simple setae on weakly sclerotized genital plates increase in length posteriorly. Ventral striations with small broken dashlike papillae. Venter of hysterosoma with 7 pairs of simple hysterogastral setae of unequal length, four of the shorter pairs situated between and behind the coxae III–IV and three pairs of the longer paragenital setae.
Gnathosoma ( Figs. 7 View FIGURE 7 , 8 View FIGURE 8 ). Palp ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 ). Five segmented palps 307 long, with gently punctate surface and a bare tibiotarsus. Palpal chaetotaxy as follows: trochanter - 0, basifemur - 1 dorsomedian simple seta; telofemur inner surface with 1 apical apophysis, dorso-apically with stout spine-like seta; genu with 1 stout spine-like seta ventrally, inner surface with 1 spine-like seta medially, apically with 1 elongate apophysis and with 1 dorsal spine-like seta, outer surface dorsally with 1 simple seta, palpgenual apophysis five times the length of adjacent spine-like seta; tibiotarsus inner surface proximally with 1 long simple seta and medially with 1 stout spine-like seta; outer surface with 1 ventro-lateral and 1 dorso-lateral simple seta; terminating with 1 solenidion (sensu Den Heyer 2006) and a small short claw. Palpal tibiotarsus nearly strait, apically slightly curved.
Chelicera ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Slender and 232 long, the surface with small randomly placed papillae and a pair of short cheliceral setae.
Hypognathum ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Subrectangular distally cone-shaped hypognathum (475 long) bears the two pairs of short adoral setae and the four pairs of hypognathal setae ( hg). The setae hg 3 are the longest and setae hg 4 the shortest. The coxal region of hypognathum with small randomly placed papillae.
Legs ( Figs. 8 View FIGURE 8 ). Coxae I–II and III–IV contiguous and smooth. Coxae I–IV setal formula: 3-2-3-3. Each leg with reliculate pattern on outer surface, inner surface without reticulation. Legs I–III shorter than leg IV. Chaetotaxy I–IV (excluding coxae) as follows: trochanters I–IV, 1-1-2-1 sts; basifemora I–IV, 5-5-4-2 sts; telofemora I–IV, 4-4-4-4 sts; genu I - 4 asl, 1 mst, 4 sts; genu II - 2 asl, 5 sts; genu III - 1 asl, 5 sts; genu IV - 2 asl, 5 sts; tibia I - 2 asl, 1 mst, 4 sts; tibia II – 1 asl, 5 sts; tibia III - 1 bsl, 5 sts; tibia IV - 1 T (smooth trichobothrium), 4 sts; tarsus I – 1 peo, 4 asl, 1 tsl, 16 sts; tarsus II - 1 bsl, 1 tsl, 16 sts; tarsus III – 1 tsl, 14 sts, tarsus IV – 15 sts.
Length of leg segments: Coxa, I (67), II (77), III (68), IV (95); Trochanter, I (23), II (23), III (54), IV (61); Basifemur, I (103), II (98), III (86), IV (126); Telofemur, I (53), II (59), III (43), IV (61); Genu, I (34), II (36), III (47), IV (53); Tibia, I (46), II (41), III (64), IV (80); Tarsus, I (247), II (175), III (189), IV (188).
Male and developmental stages: Unknown.
Material studied. Holotype ( Type serie No: SZ 6890): female on slide, South Slovakia, Cerová vrchovina Mts., Hostice village env. (N–48˚14΄46ʺ, E–20˚05΄52ʺ), 18. 6. 2007, Corneto-Crataegetum, collected from soil samples. Material collected by author. Type material is deposited in Slovak National Museum, Bratislava, Slovakia.
Etymology: The name of species ( cerris ) is derivated from the name of Cerová vrchovina Mts. with prevailing oak forests ( Quercus cerris ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Prostigmata |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |