Hipposideros papua, Thomas & Doria, 1886
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3739808 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3810871 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BD87A2-C668-A21A-FF48-F5F3F8EB514E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hipposideros papua |
| status |
|
84. View Plate 19: Hipposideridae
Biak Leaf-nosed Bat
Hipposideros papua View in CoL
French: Phyllorhine papoue / German: Biak-Rundblattnase / Spanish: Hiposidérido de Biak
Other common names: Biak Roundleaf Bat, Geelvink Bay Leaf-nosed Bat
Taxonomy. PhyUorhina papua Thomas & Doria, 1886 View in CoL ,
“Rorido nell’ Isola di Misori [= Biak Island], Baja del Geelvink [= Cenderawasih Bay], nella N. Guinea [= Papua Province, Indonesia].”
Hipposideros papua was formerly included in the bicolor species group, but its position in the phylogeny is unclear and its taxonomy requires further study. Monotypic.
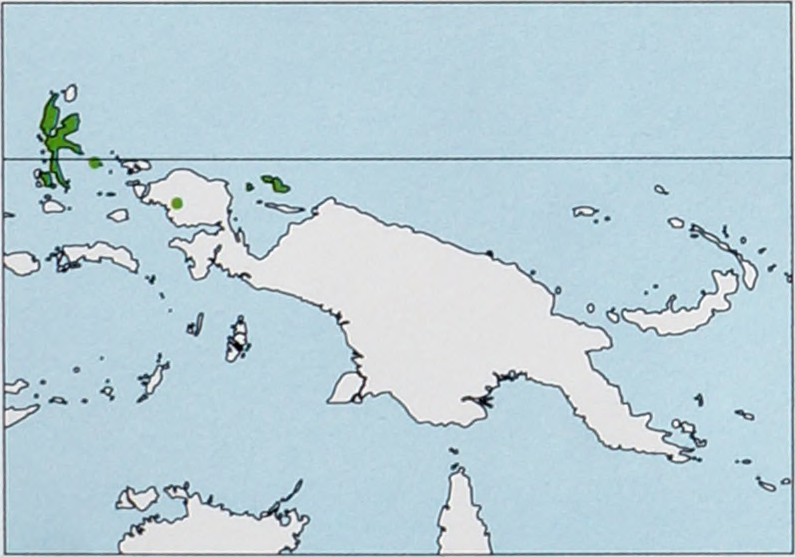
Distribution. Moluccas (Halmahera and Bacan), West Papuan Is (Gebe), Schouten Is (Numfor, Supiori, and Biak), and W New Guinea (Bird’s Head Peninsula). View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 48-9—58-9 mm, tail 22-34-8 mm, ear 13-3—17-8 mm, hindfoot 6-5—7-7 mm, forearm 49-5—52-7 mm; weight 9-3—10-1 g. The Biak Leaf-nosed Bat has large triangular ears that are slighdy concave below tip. Anterior noseleaf is large, with three supplementary lateral leaflets (the third one very small or absent in some cases). Upper margin of posterior noseleaf is semicircular and has three vertical septa, which separate four cells on frontal surface. A frontal sac is present in males and absent in females. Pelage is dark brown on dorsum and paler on ventral part.
Habitat. The Biak Leaf-nosed Bat has been reported in primary tropical moist woodland habitats at elevations of 100-300 m.
Food and Feeding. The Biak Leaf-nosed Bat probably forages in primary forests. Its diet is based on insects.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. The Biak Leaf-nosed Bat roosts in caves. Call frequency of the F segment is c.123 kHz.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. The Biak Leaf-nosed Bat is gregarious and has been observed in caves roosting in small groups.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCNRed List. Although it occurs in a relatively small range, the Biak Leaf-nosed Bat is a relatively common species within this, and its population is thought to be stable. The main potential threats to this species might be roost disturbance and habitat degradation.
Bibliography. Bates, Rossiter eta/. (2007), Bonaccorso (1998), Helgen (2008b),Tate (1941a), Wiantoro (2011).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hipposideros papua
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
PhyUorhina papua
| Thomas & Doria 1886 |