Proxima DeLong & Freytag, 1975
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5091.4.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5B5E7026-B0D7-4BCC-BD17-4EB7045CF26F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5864214 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BF87F0-FFDB-FFCE-FF20-FC6FFA63F13F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Proxima DeLong & Freytag, 1975 |
| status |
|
Proxima DeLong & Freytag, 1975 View in CoL
( Figs 1–57 View FIGURES 1–12 View FIGURES 13–25 View FIGURES 26–32 View FIGURES 33–44 View FIGURES 45–51 View FIGURES 52–57 )
Proxima DeLong & Freytag, 1975: 111 View in CoL . Type-species: Proxima ocellata DeLong & Freytag, 1975: 111 View in CoL .
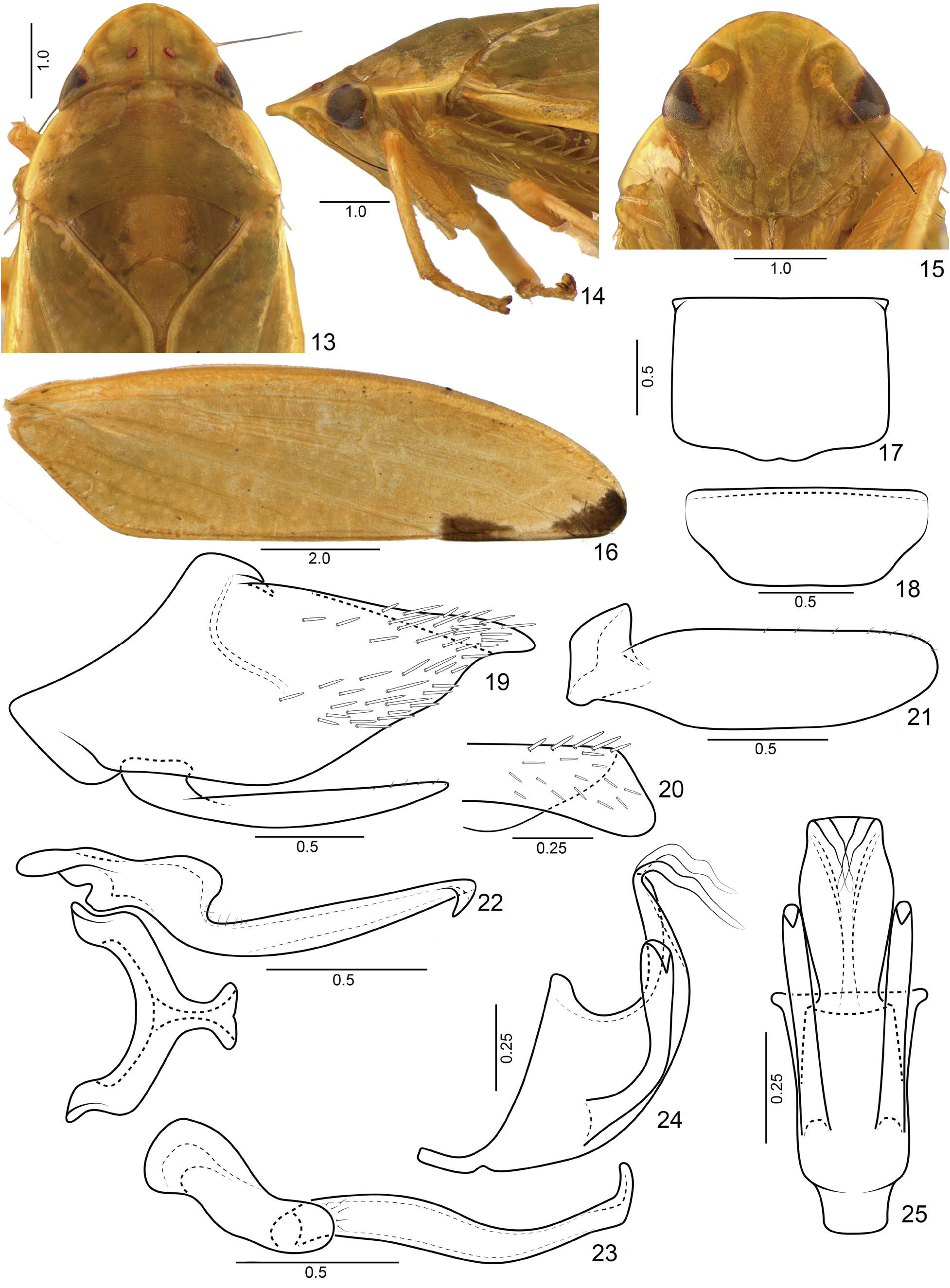
Diagnosis. Medium-sized leafhoppers ( Figs 52–57 View FIGURES 52–57 ), elongated, green in life, yellow when preserved. Crown ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–12 , 33 View FIGURES 33–44 ) distinctly narrower than pronotum; moderately produced anteriorly; surface with longitudinal striae between ocelli. Ocelli ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–12 , 33 View FIGURES 33–44 ) closest to midline and posterior margin. Transition crown-face ( Figs 14 View FIGURES 13–25 , 34 View FIGURES 33–44 ) distinct, thin, but not foliaceous; with up to four transverse carinae. Forewing ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 1–12 , 16 View FIGURES 13–25 ) semiopaque, often with extra-numerary veins; apex narrowed; appendix undeveloped. Male pygofer ( Figs 7 View FIGURES 1–12 , 19 View FIGURES 13–25 ) without processes. Connective ( Figs 9 View FIGURES 1–12 , 41 View FIGURES 33–44 ) Y-shaped. Aedeagus ( Figs 11 View FIGURES 1–12 , 24 View FIGURES 13–25 ) with pair of atrial processes; shaft with bifid apex. Female sternite VII ( Figs 26 View FIGURES 26–32 , 45 View FIGURES 45–51 ) with posterior margin emarginated medially. First and second valvulae of ovipositor ( Figs 28, 30 View FIGURES 26–32 , 47, 49 View FIGURES 45–51 ) with constant height throughout most of their length. First valvulae ( Figs 28 View FIGURES 26–32 , 47 View FIGURES 45–51 ) with long ventral interlocking device, reaching the apical fourth. Second valvulae ( Figs 30 View FIGURES 26–32 , 49 View FIGURES 45–51 ) dorsal margin with 3–4 prominent and well separated teeth.
Color. Green in life, yellow when preserved ( Figs 52–57 View FIGURES 52–57 ). Eyes and ocelli red.
External morphology. Head ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–12 , 13 View FIGURES 13–25 , 33 View FIGURES 33–44 ) distinctly narrower than pronotum, transocular width approximately three-fourths transhumeral width; moderately produced anteriorly, median length approximately three-fourths interocular width; anterior margin parabolic; crown surface slightly concave near ocelli, texture with longitudinal thin striae between ocelli and oblique striae between each ocellus and compound eye. Ocelli ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–12 , 13 View FIGURES 13–25 , 33 View FIGURES 33–44 ) closer to the midline than to compound eye, and closer to posterior margin in relation to anterior margin. Transition crown-face ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–12 , 14 View FIGURES 13–25 , 34 View FIGURES 33–44 ) distinct, thin, but not foliaceous; with up to four transverse carinae. Face ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ) slightly wider than high. Frons ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ), in lateral view, slightly tumid; in ventral view, height approximately twice the width; texture shagreen; surface slightly concave below anterior margin of the crown. Frontogenal suture ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ) distant from eye margin by slightly less than maximum width of clypeus and extending to anterior margin of crown. Antennal ledge ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ) carinate, oriented obliquely downward in relation to frons; not extending over frons. Epistomal suture ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ) indistinct. Maxillary plates ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ) not reaching clypeus apex. Gena ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ) with ventrolateral margin slightly excavated below eye. Clypeus ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1–12 , 15 View FIGURES 13–25 , 35 View FIGURES 33–44 ) approximately 1.3 times longer than wide; lateral margins slightly divergent apically; apical margin rectilinear or slightly excavated, in lateral view, almost flat. Pronotum ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–12 , 13 View FIGURES 13–25 , 33 View FIGURES 33–44 ), in dorsal view, with numerous transverse fine striae on disc and posterior third; lateral margins carinated, convergent anterad, longer than length of eye; in lateral view, ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 1–12 , 14 View FIGURES 13–25 , 34 View FIGURES 33–44 ), slightly declivous, continuous with head declivity. Mesonotum ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1–12 , 13 View FIGURES 13–25 , 33 View FIGURES 33–44 ) slightly wider than long, lateral angles with shagreen texture and other areas rugose; scutellum with thin transverse irregular striae, in lateral view, flat. Forewing ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 1–12 , 16 View FIGURES 13–25 , 36 View FIGURES 33–44 ) semiopaque, approximately 3.5 times longer than wide; venation slightly distinct, often with few extra-numerary veins on apical two-thirds or almost reticulated; apex narrowed; appendix narrow, poorly developed, extending to second apical cell. Profemur elongated, approximately four times longer than high; AD, AM, and PD rows reduced and poorly defined, with exception of apical setae AD 1, AM 1 and PD 1 respectively; AV row with 4−5 setae; PV row with 2−3 setae; IC row formed by slightly arched comb of fine setae, restricted to apical half. Protibia, in cross-section, approximately cylindrical; AD row composed only by undifferentiated setae; AV row with short setae, distal setae only as long as tibia diameter, thin at basal third and thick at apical two-thirds; PD row composed by 4−5 setae and undifferentiated intercalary setae; PV row composed by 6−8 setae and undifferentiated intercalary setae. Metafemur with setal formula 2:2:1 (rarely 2:2:1:1). Metatibia with AD, AV, and PD rows with 12−13, 16−20, and 24−27 macrosetae, respectively; AD row with 2− 3 intercalary setae between macrosetae; PV row with apical half composed of a longer and thicker setae, interspersed with 3−5 thinner and shorter setae, ending with 2−3 short and thin setae at apex. Metatarsomere I ventral surface with two rows of cucullate setae, inner row with 7−10 larger setae and outer row with 5−8 smaller setae; apex with 5−7 platellae; metatarsomere II apex with 3−4 platellae.
Male terminalia. Sternite VIII ( Figs 5 View FIGURES 1–12 , 17 View FIGURES 13–25 , 37 View FIGURES 33–44 ), in ventral view, wider than long; lateral margins parallel. Valve ( Figs 6 View FIGURES 1–12 , 18 View FIGURES 13–25 , 38 View FIGURES 33–44 ), in ventral view, wider than long; anterior margin with thickened integument. Pygofer ( Figs 7 View FIGURES 1–12 , 19 View FIGURES 13–25 , 39 View FIGURES 33–44 ) without processes; macrosetae present and scattered on apical half. Subgenital plate ( Figs 7 View FIGURES 1–12 , 19 View FIGURES 13–25 , 39 View FIGURES 33–44 ), in lateral view, not reaching pygofer apex; in ventral view (figs 8, 21, 40), longer than wide, outer margin with microsetae. Connective ( Figs 9 View FIGURES 1–12 , 22 View FIGURES 13–25 , 41 View FIGURES 33–44 ), in dorsal view, Y-shaped. Style ( Figs 10 View FIGURES 1–12 , 23 View FIGURES 13–25 , 42 View FIGURES 33–44 ), in dorsal view, with developed outer lobe; in lateral view ( Figs 10 View FIGURES 1–12 , 23 View FIGURES 13–25 , 42 View FIGURES 33–44 ), elongated; apex acute, basal portion with microsetae. Aedeagus ( Figs 11 View FIGURES 1–12 , 24 View FIGURES 13–25 , 43 View FIGURES 33–44 ) with pair of atrial processes; shaft with bifid apex, with or without processes.
Female terminalia. Sternite VII ( Figs 26 View FIGURES 26–32 , 45 View FIGURES 45–51 ), in ventral view, wider than long; posterior margin excavated medially. Internal sternite VIII membranous. First and second valvulae of ovipositor ( Figs 28, 30 View FIGURES 26–32 , 47, 49 View FIGURES 45–51 ), in lateral view, with constant height throughout most of their length and slightly curved dorsally. First valvula ( Figs 28, 29 View FIGURES 26–32 , 47, 48 View FIGURES 45–51 ) with dorsal sculptured area strigate and extending to ventral margin at apex. Second valvula ( Figs 31 View FIGURES 26–32 , 50 View FIGURES 45–51 ) with 3−4 prominent teeth on dorsal margin. Gonoplac ( Figs 32 View FIGURES 26–32 , 51 View FIGURES 45–51 ), in lateral view, with straight dorsoapical margin, short, approximately one-third of the length of gonoplac; ventral margin broad and slightly rounded, with few short setae; outer surface with many integumentary denticles; rounded apex.
Distribution. Brazil (Bahia, Espírito Santo, Maranhão, Minas Gerais, Paraná, Rio de Janeiro and Rio Grande do Sul states).
Taxonomic key to males of Proxima
1 Pygofer with apical portion curved dorsally ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1–12 ). Style with ventral margin conspicuously excavated medially ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 1–12 ). Aedeagus with atrial processes bifurcated and shaft with pair of preapical bifid processes ( Figs 11, 12 View FIGURES 1–12 )........................................................................................ P. ocellata DeLong & Freytag, 1975 View in CoL
- Pygofer with apex straight or folded inward ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 13–25 , 39 View FIGURES 33–44 ). Style with ventral margin not conspicuously excavated ( Figs 23 View FIGURES 13–25 , 42 View FIGURES 33–44 ). Aedeagus with atrial processes not bifurcated and shaft without processes ( Figs 24 View FIGURES 13–25 , 43 View FIGURES 33–44 ).............................. 2
2(1) Forewing with pair of dark maculae at apical third ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 13–25 ). Pygofer with apex folded inwardly ( Figs 19, 20 View FIGURES 13–25 ). Subgenital plate with inner margin not expanded ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 13–25 ). Style with blade slightly sinuous, slender along its entire length ( Fig. 23 View FIGURES 13–25 ). Aedeagus with atrial processes short, not reaching apex of shaft; shaft wide at the base and narrowing towards apex ( Figs 24, 25 View FIGURES 13–25 )............................................................................... Proxima nigromaculata View in CoL sp. nov.
- Forewing without distinct maculae ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 33–44 ). Pygofer with apex straight ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 33–44 ). Subgenital plate with inner margin strongly expanded ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 33–44 ). Style with blade approximately straight, expanded at base and narrowing towards apex ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 33–44 ). Aedeagus with atrial processes as long as shaft; shaft long and slender ( Figs 43, 44 View FIGURES 33–44 )....................... Proxima meloi View in CoL sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Tribe |
Gyponini |
Proxima DeLong & Freytag, 1975
| Laranjeira, Vanessa Cristina, Gonçalves, Clayton Corrêa, Domahovski, Alexandre Cruz & Takiya, Daniela Maeda 2022 |
Proxima
| DeLong, D. M. & Freytag, P. H. 1975: 111 |
| DeLong, D. M. & Freytag, P. H. 1975: 111 |