Monchenkocyclops mehmetadami, Karaytuğ & Bozkurt & Sönmez, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5252/zoosystema2018v40a2 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:155D423A-9252-4B32-9471-B5CA7F36FED4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3811421 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/98007C64-35FB-47C8-8AD9-95387355ED28 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:98007C64-35FB-47C8-8AD9-95387355ED28 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Monchenkocyclops mehmetadami |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Monchenkocyclops mehmetadami n. sp.
( Figs 1-10 View FIG View FIG View FIG View FIG View FIG View FIG View FIG View FIG View FIG View FIG )
TYPE LOCALITY. — KIrksu Creek , Kozan, Adana, Turkey. Coordinates 37°32’08.46’’N, 35°53’41.54’’E GoogleMaps .
TYPE MATERIAL. — Holotype ♀ dissected on eight slides ( ZMADYU2015 /135) . Allotype ♂ also dissected on eight slides ( ZMADYU2015 /136). 1 paratype ♂ and 1 paratype ♀ are dissected on one slide each; 2 ♂ and 1 ♀ preserved in alcohol ( ZMADYU2015 /137); 1 ♂ and 1 ♀ on one SEM stub ( ZMADYU2015 /138). 2 ♂ and 2 ♀ preserved in alcohol ( MNHN). Date 13.VI.2015. Leg. Ahmet Bozkurt .
VARIABILITY. — Two ♀ and two ♂ had no seta on exp-1 of P1.
ETYMOLOGY. — The new species is named in honor of Prof. Dr Mehmet Adam (Başkent University, Turkey).
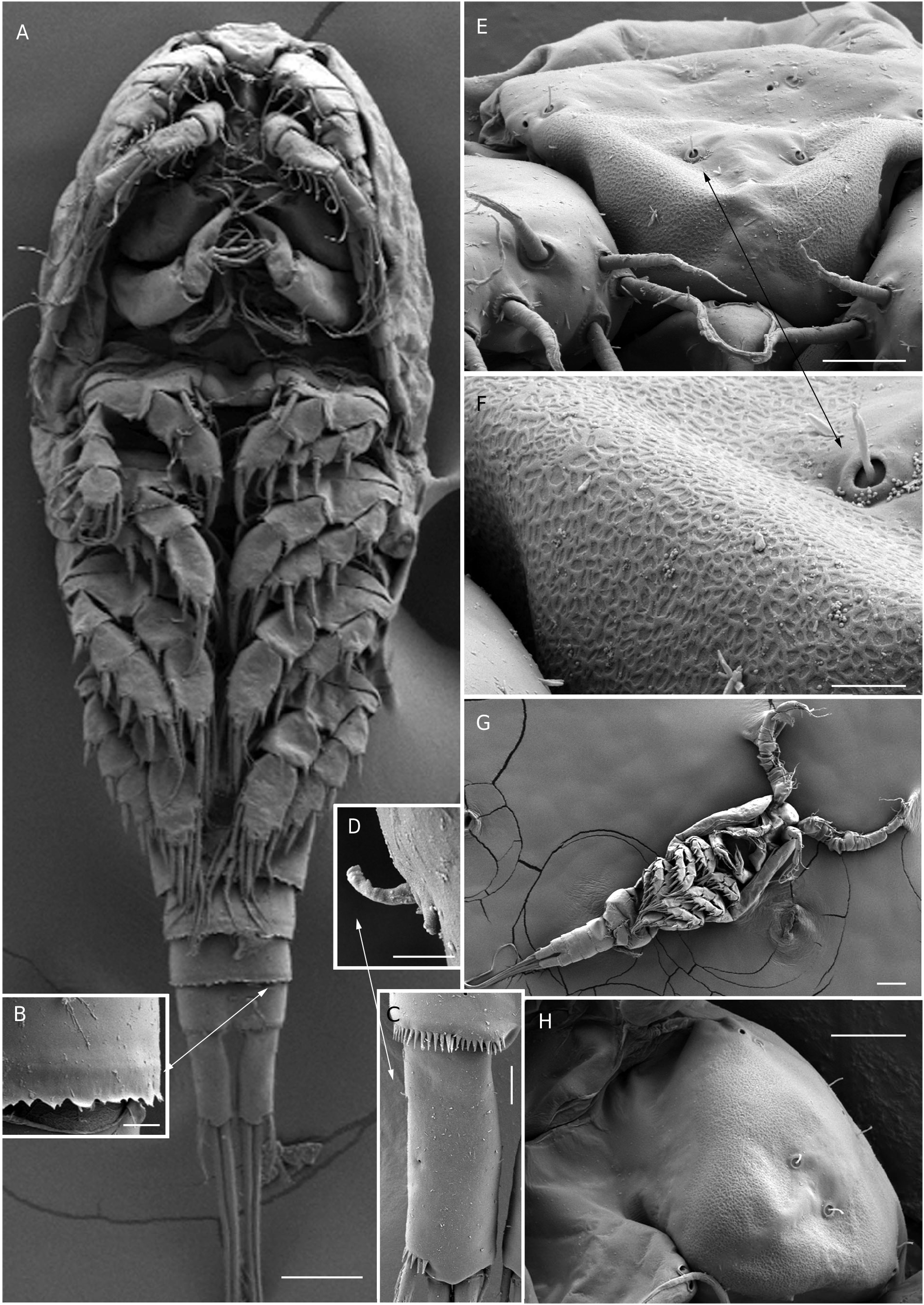
DESCRIPTION OF FEMALE (HOLOTYPE)
Total body length
Excluding caudal setae, 667 Μm (range: 618-779 Μm, mean = 668 Μm, n = 6); body width 242 Μm (range = 239-294 Μm, mean = 257 Μm, n = 6). Preserved specimens colorless; no live specimens observed. Pedigerous somite smooth along posterior margin ( Fig. 1A View FIG ). Urosomites ( Figs 2B View FIG ; 6A, B View FIG ) with fine hyaline frills along the posterior margin on ventral and dorsal surfaces. Integumental pore/sensilla pattern of the prosomites extremely difficult to observe/confirm, but in general similar to that of M. changi Karanovic, Yoo & Lee, 2012 ( Fig. 1A View FIG ). Seminal receptacle with relatively large anterior expansion and smaller posterior expansion as figured ( Fig. 6A View FIG )
Genital double-somite ( Fig. 6A, B View FIG ) large, with deep lateral recesses at level of sixth legs and swollen antero-ventrally, widest in anterior third and gradually tapering posteriorly, about 1.2 times as wide as long (dorsal view), hyaline fringe deeply and irregularly serrated. Copulatory pore very small, ovoid, situated ventrally at about midlength of double-somite ventrally; copulatory duct narrow, siphon-shaped, weakly sclerotized. Seminal receptacle ( Fig. 6A View FIG ) with relatively large anterior expansion and much smaller posterior expansion, extending over 49% of double-somite’s length; oviducts broad and weakly sclerotized. Ovipores situated dorsolaterally at 2/5 of double-somite length, covered by reduced sixth legs. Third and fourth urosomites similar in length and without ornamentation.
Anal somite ( Fig. 1C View FIG )
With short medial cleft, ornamented with one pair of dorsal sensilla, two pairs of small dorsal pores, with distal spinular row ventrally, extending dorsally to either side of anal operculum. Anal sinus wide with minute transverse spinules. Anal operculum slightly convex.
Caudal rami ( Figs 1C View FIG ; 2C View FIG )
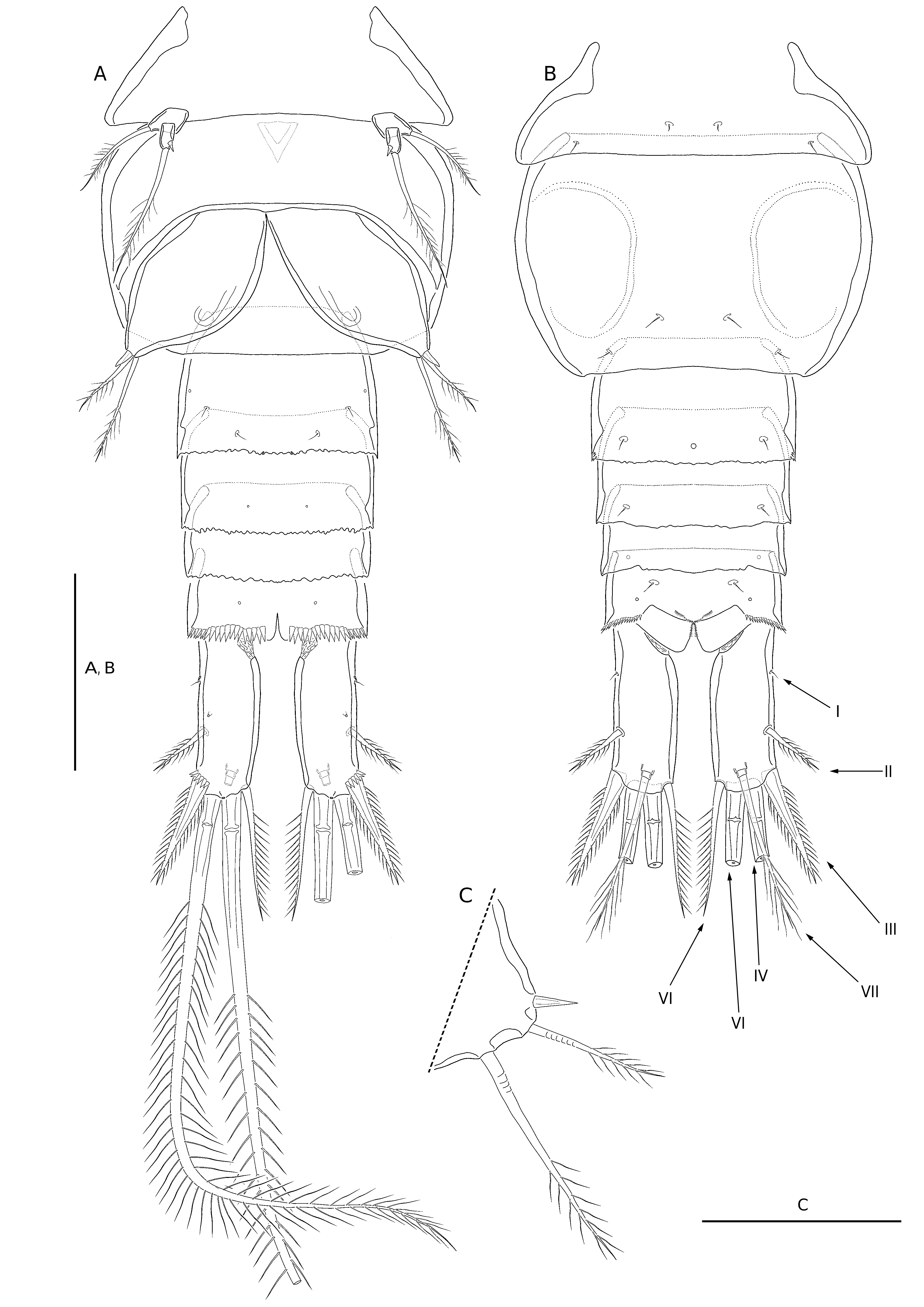
Cylindrical, parallel, inserted close to each other, about 3.8 times longer than broad (measured in dorsal view); armed with seven setae, armature consisting of seven setae: seta I with minute spinule ( Figs 1C View FIG ; 6A, B, D View FIG ); setae II and III plumose; seta IV and V plumose with fracture plane, seta V longest; seta VI located at inner distal corner semispinulose, about as long as seta III; seta VII plumose and triarticulate at base.
Rostrum ( Fig. 2A, E, H View FIG ) not demarcated at base, ornamented with integumental pits ( Fig. 2F View FIG ) broadly rounded and furnished with single central sensilla frontally (arrowed in Fig. 2E, F View FIG ). The difference observed between female and male rostrum ( Fig. 2E, H View FIG ) is due to wrinkling during the critical point drying procedure.
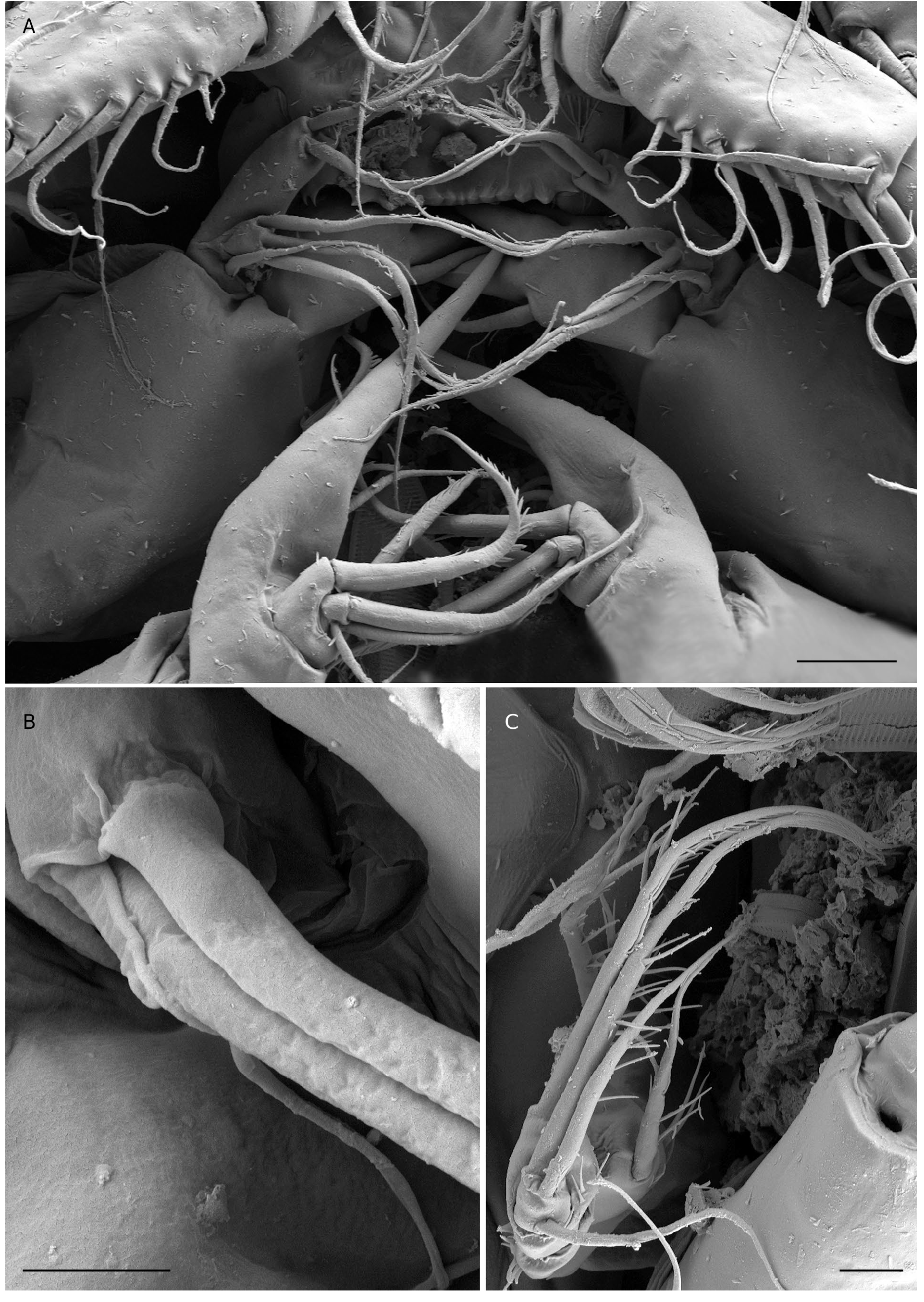
Antennule eleven-segmented ( Fig. 3A View FIG )
With spinular row on the first segment proximoventrally. Segment 5 with spiniform seta (arrowed in Fig. 3A View FIG ). Segment 8 with characteristic aesthetasc (arrowed in Fig. 3A View FIG ). Setal formula 8, 4, 8, 4, 2, 2, 3, 2 + aesthetasc, 2, 2 + aesthetasc, 7 + aesthetasc. Most setae sparsely pinnate or plumose as figured. One apical seta on eleventh segment fused basally to an aesthetasc.
Antenna ( Fig. 3B View FIG )
Five-segmented, strongly curved along caudal margin, comprising very short coxa, much longer basis and threesegmented endopod. Coxa small and without armature or ornamentation. Basis cylindrical with spinular rows on caudal and frontal surfaces as figured, and armed with two inner pinnate setae (exopodal seta absent). First endopodal segment with inner distal naked seta and spinules along outer margin. Second endopodal segment with nine setae, one of which at inner distal corner more robust; ornamented with spinules along outer margin. Third endopodal segment armed with seven setae around apex; outer margin ornamented with spinules.
Labrum ( Fig. 3C View FIG )
Ornamented with paired groups of long spinules on anterior surface. Free posterior margin almost straight, with sharp teeth in midsection between produced and sharply and inwardly pointed lateral corners.
Mandible ( Fig. 3D, E View FIG )
Composed of coxa and small palp. Cutting edge of gnathobase with several apical teeth, and dorsalmost unipinnate seta. Palp represented by three naked setae, two of which long and one short ( Fig. 4B View FIG ).
Maxillule ( Fig. 3F View FIG )
Composed of praecoxa and two-segmented palp. Praecoxal arthrite armed with four setae articulating at base (proximalmost one more robust, longest and plumose) and five spines (three of which fused to segment). Proximal segment of the palp ( Fig. 3I View FIG ) representing fused coxa and basis, bearing one strong spinulose seta and two pinnate setae apically, plus outer pinnate seta representing exopod. Distal segment of palp, representing endopod, armed with three unipinnate setae ( Fig. 3I View FIG ).
Maxilla ( Fig. 3G View FIG )
Five-segmented comprising praecoxa, coxa, basis and two- segmented endopod. Praecoxa partly fused to coxa on anterior surface and arthrodial membrane indicating segmental boundary; praecoxal endite with two spinulose setae. Coxa with proximal endite represented by single plumose seta; distal endite cylindrical, with strong spinulose spine and plumose seta apically. Basis drawn out into powerful curved claw ( Fig. 4A View FIG ) bearing coarse spinules along middle part of inner margin; accessory armature consisting of strong spinulose curved spine and naked seta. First endopodal segment with one unipinnate and one naked seta, second segment with two naked and one unipinnate setae ( Fig. 4A View FIG ).
Maxilliped ( Figs 3H View FIG ; 4C View FIG )
Much smaller than maxilla and four-segmented comprising syncoxa, basis, and two-segmented endopod. Syncoxa armed with two spinulose setae representing endites. Basis armed with two long spinulose setae; ornamented with two transverse rows of spinules near outer margin posteriorly and patch of spinules anteriorly near inner margin. First endopodal segment with long spinulose seta. Second endopodal segment with three setae, two of which naked; other pinnate.
Legs 1-4
With three-segmented exopod and two-segmented endopod ( Fig. 5 View FIG A-E).
Praecoxa
Represented by triangular sclerite at outer proximal angle; each with row of spinules on outer corner of margin. Coxa with spinular row near the proximal outer corner posteriorly. All setae on endopods and exopods slender and plumose, except apical seta on exopod of first leg, which pinnate along outer margin and plumose along inner ( Fig. 5A View FIG ); no modified setae observed. All spines strong and bipinnate. Segments of both rami with spinules near the bases of all spines. Intercoxal sclerite without any surface ornamentation, except on posterior surface of fourth leg. Exp-1 with posterior spinular row near distal margin.
Leg 1 ( Fig. 5A View FIG )
Coxa ornamented with distal row of minute spinules on anterior surface, armed with long and plumose seta on inner-distal corner; basis armed with outer plumose seta and spinulose spine on inner margin near base of endopod (arrowed and indicated by a star in Fig. 5A View FIG ), with two posterior rows of shorter and stronger spinules on anterior surface (one at base of inner seta, other at base of endopod), and one cuticular pore on anterior surface close to outer margin; exopod with row of slender inner spinules on first and second segment, inner seta of exp-2 better developed than other exopodal setae; endopod armed with one inner seta on first segment, second segment with three inner setae, one apical spine, and one outer seta, ornamented with slender spinules along outer margins of both segments, single terminal pore on anterior surface of second segment; second endopodal segment with small outer notch in outer margin showing ancestral segmentation.
Legs 2-4 ( Fig. 5 View FIG B-D)
Coxa armed with plumose inner seta, and bearing distal row of spinules and small pore on anterior surface (with complex spinular rows in leg 4 as figured in Figure 5E View FIG ); basis with naked outer seta (plumose in leg 3), with very small spiniform outgrowth at outer distal corner in leg 3, with few setules along inner margin; inner margin of all exopod segments, outer margin of all endopodal segments and outer margin of exp-2 with few setules (except leg 4), with three outer spines on exp-3; second endopodal segment with outer notch showing ancestral segmentation, and longer than first segment. Enp-1 of leg 2 and leg 4 with posterior spinular row located terminally ( Table 1 View TABLE ).
Leg 5 ( Fig. 3J View FIG )
Inserted laterally, relatively small, two-segmented. Proximal segment short, almost rhomboidal in shape, armed with single slender plumose outer basal seta. Exopod small and cylindrical, armed with apical long plumose seta and subapical small inner spine; Leg 6 ( Fig. 6B, C View FIG ) represented by one plumose seta and two short spines dorsolaterally, inner spine fused to plate, outer articulated basally.
DESCRIPTION OF MALE (ALLOTYPE)
Smaller than female ( Figs 1B View FIG ; 2G View FIG )
Body length excluding caudal setae, 470 Μm (range = 464- 588 Μm, mean = 505 Μm, n = 5); body width, 167 Μm (range = 167-173, mean = 170 Μm, n = 5). Urosomites without any surface ornamentation ( Fig. 7A, B View FIG ). Genital somite 1.6 times as wide as long in dorsal view. Abdominal somites with finely serrated hyaline fringe dorsally, less serrated ventrally ( Figs 7A, B View FIG ; 8B View FIG ). Caudal seta I extremely small as in female, and originating below a small spinule ( Fig. 8A View FIG ). Fifth leg similar to that of female but smaller ( Fig. 8E View FIG ). Sixth leg ( Fig. 8C, D View FIG ) armed with one inner and two outer plumose setae.
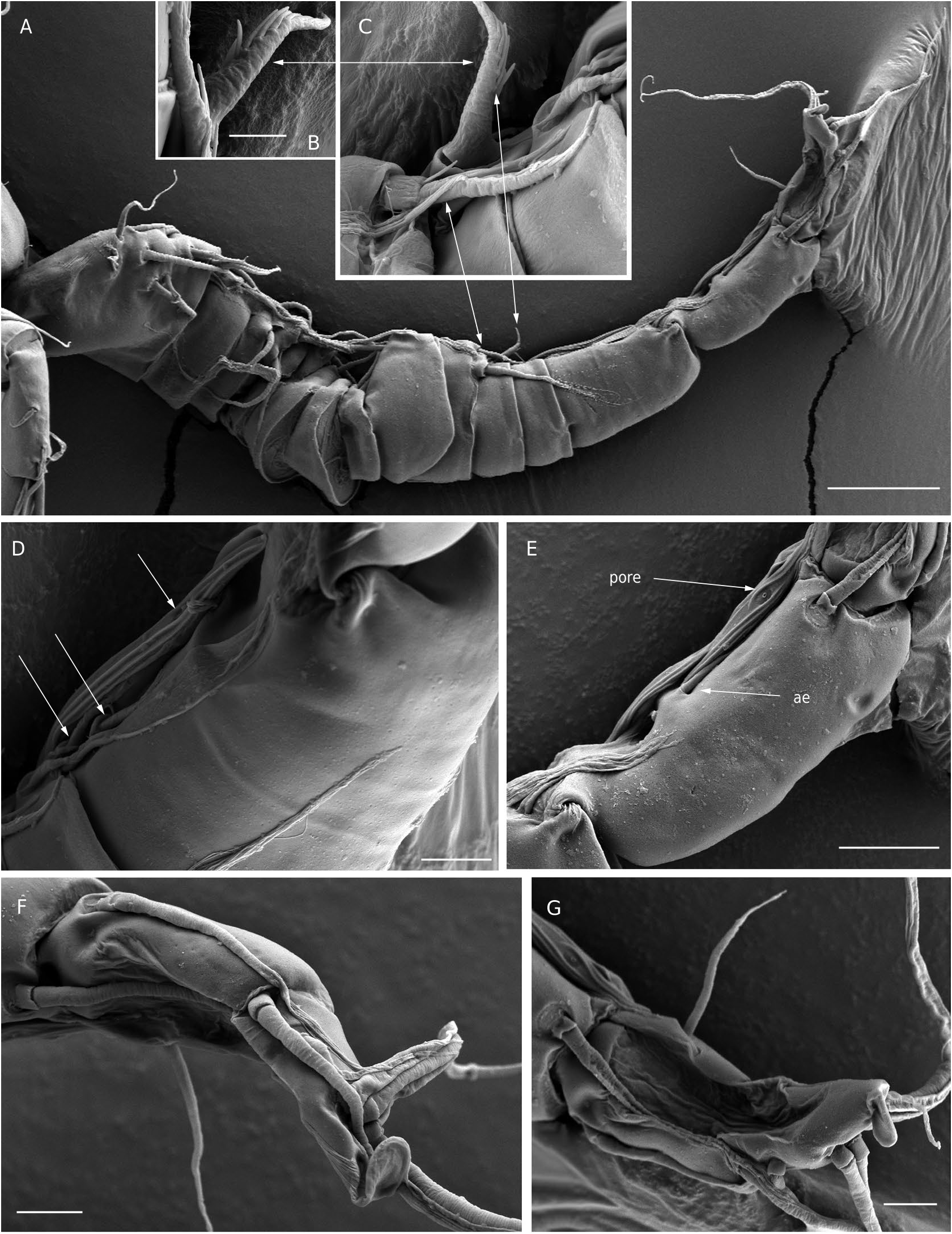
Antennule ( Figs 9 View FIG A-C; 10A-G)
Indistinctly 17-segmented. Segments 8-10 partially fused anteroventrally. Sixteenth and seventeenth (apical) segments partly fused on ventral side. Geniculation located between segments 14 and 15. Armature formula as follows: 8+ 3ae; 4; 2; 2+ae; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2+1ae; 2; 2; 2; 2+1ae; 2 +1 modified plate-like element +1 cone-like element +1 ae; 1+2 modified plate-like elements+1 ae+ 1 cone like element; 4+1 ae; 8+1 ae. Segmental fusion pattern as follows I-V, VI-VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII, XIII, XIV, XV, XVI, XVII, XVIII, XIX-XX, XXI- XXIII, XXIV-XXV, XXVI-XXVIII. Segment 1 with the slender seta A (arrowed in Fig. 9B View FIG ); seta G present; aesthetascs linguiform; the seta G present (arrowed in Fig. 9B View FIG ). Segment 10 (= ancestral segment XV) produced on one side into sheath enclosing segment 11 ventrally; armed with two setae. Segment 12 armed with short naked seta, plus short, strong (but not highly modified) chitinized spine (arrowed in Figs 9B View FIG ; 10 View FIG A-C). Segment 14 (= ancestral segments XIX-XX) armed with a minute proximal seta and one distal seta, plus one modified plate-like modified element attached to segment, and one aesthetasc embedded between the segment and the modified element (arrowed in Fig. 10D View FIG ); main part of modified element lying along surface of segment and ornamented with longitudinal ridges and small central pore (arrowed in Fig. 10D View FIG ). Segment 15 armed with one normal seta, two plate-like modified elements (as proximal element on segment 14) each ornamented with longitudinal ridges and a central pore (arrowed in Fig. 10E View FIG ) and one aesthetasc (arrowed in Fig. 10E View FIG ). Segmental boundary between 16 and 17 (apical segment) unclear and especially difficult to determine ventrally. Apical segment tapering distally; armed with 8 setae (one seta located near the terminal margin of segment 16) and one setiform aesthetasc fused basally to one seta, mostly originating on outer (posterior) surface, six setae biarticulate proximally ( Figs 9C View FIG ; 10F, G View FIG ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |