Asphondylia zeyheriae Maia, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11606/1807-0205/2021.61.57 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C6D19E17-7204-47E9-A63C-15E98BEB306B |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C2878A-AE48-B468-FEB2-565FFD6E1A84 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Asphondylia zeyheriae Maia |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Asphondylia zeyheriae Maia View in CoL , sp. nov. ( Figs. 17-23 View Figure 17 View Figure 18 View Figure 19 View Figure 20 View Figure 21 View Figure 22 View Figure 23 )
Diagnosis: Male hypoproct rounded apically, deeply bilobed;ovipositor with needle part about 3.0-4.0X length 7 th sternite, pupa: antennal horn apical part 2.5 X length basal part, upper frontal horn simple, 0.4 X length antennal horn, lower facial horn tridentate,0.2X length antennal horn,face sclerotized between upper and lower facial horns, 8 th abdominal segment with 5 dorsal spines in the posterior row.
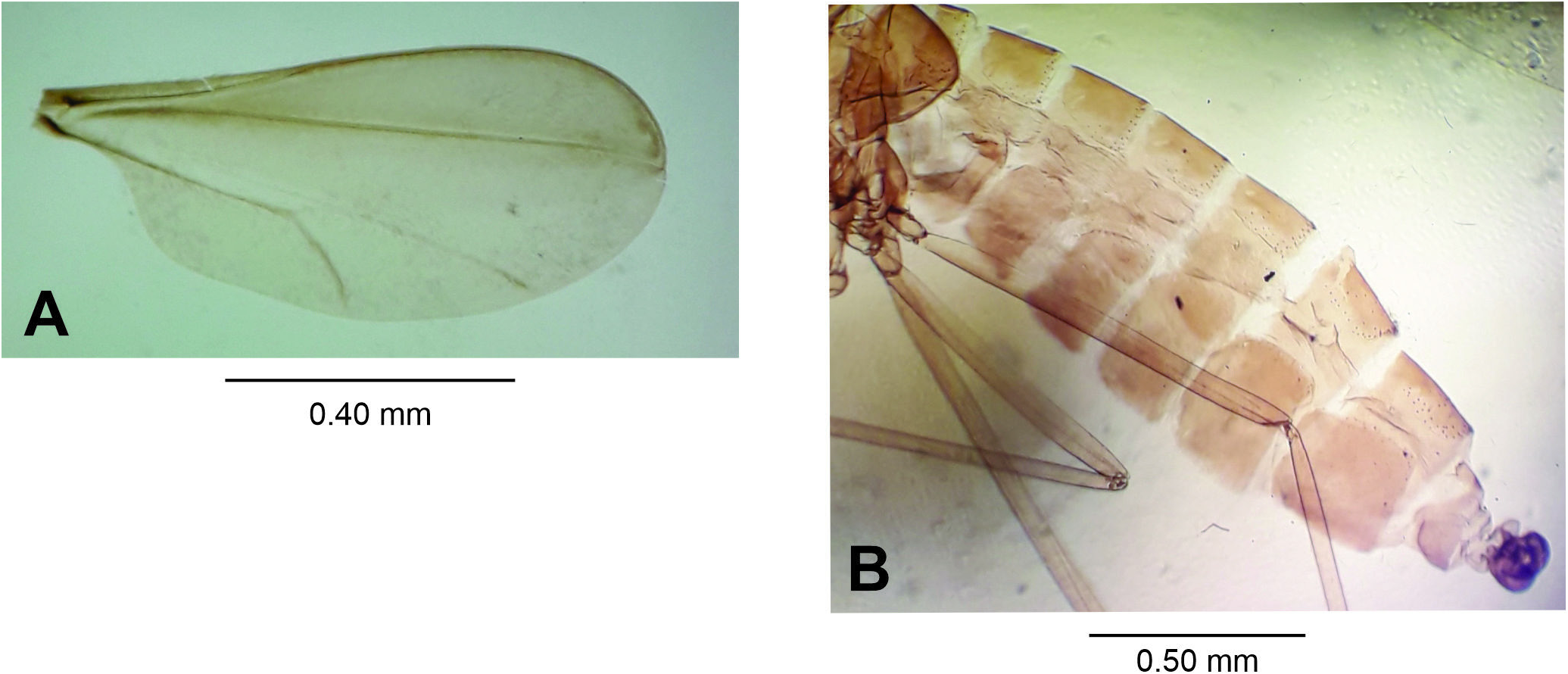
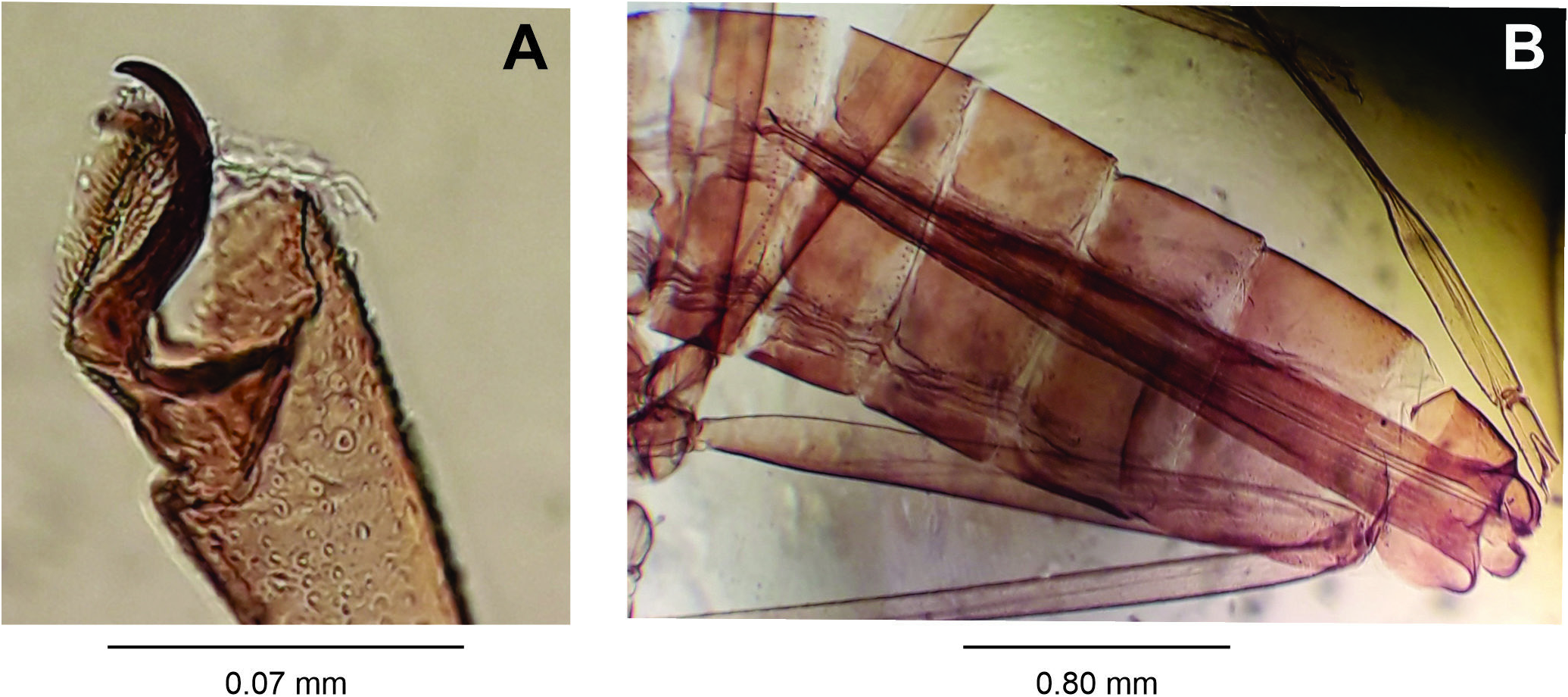
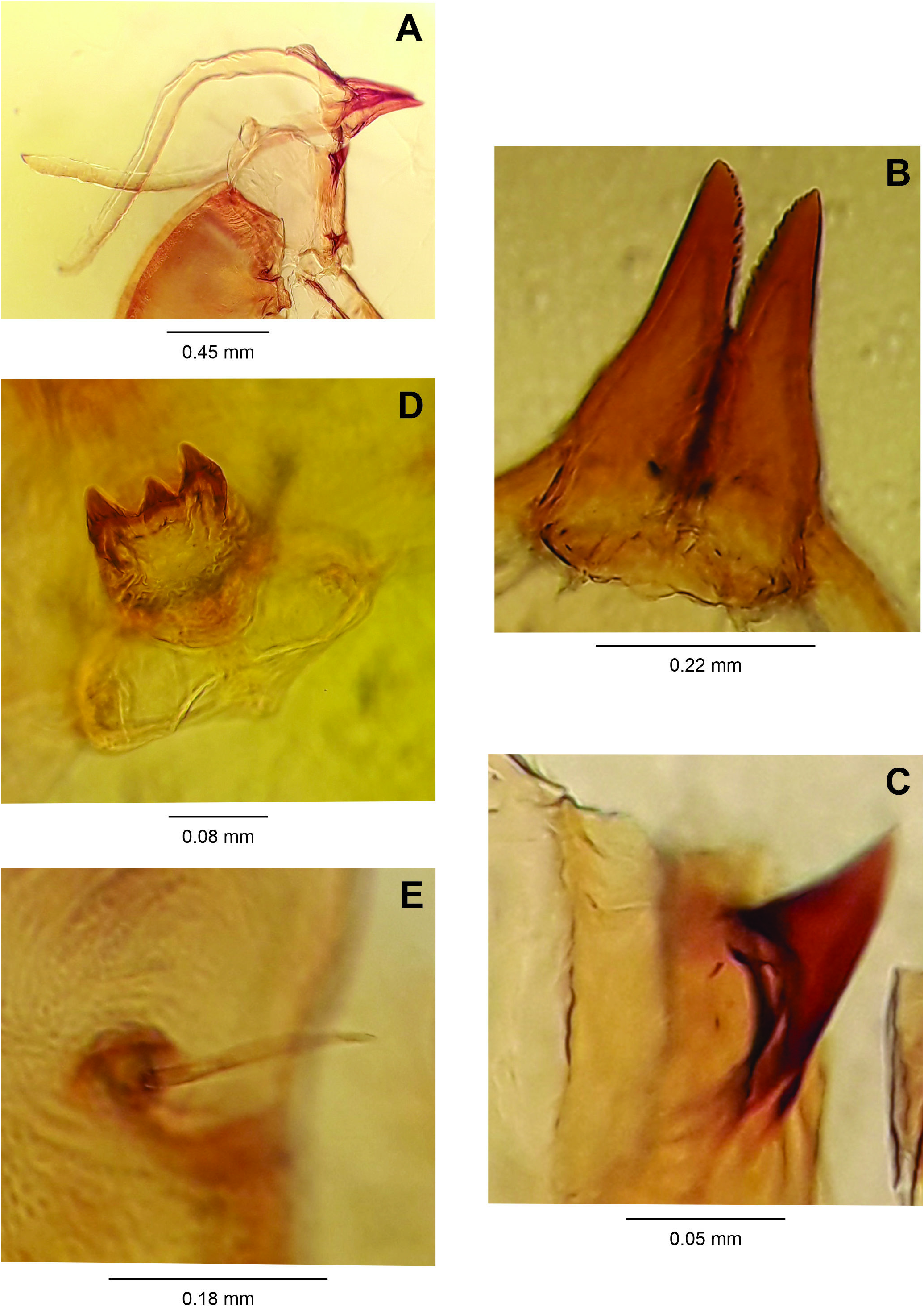
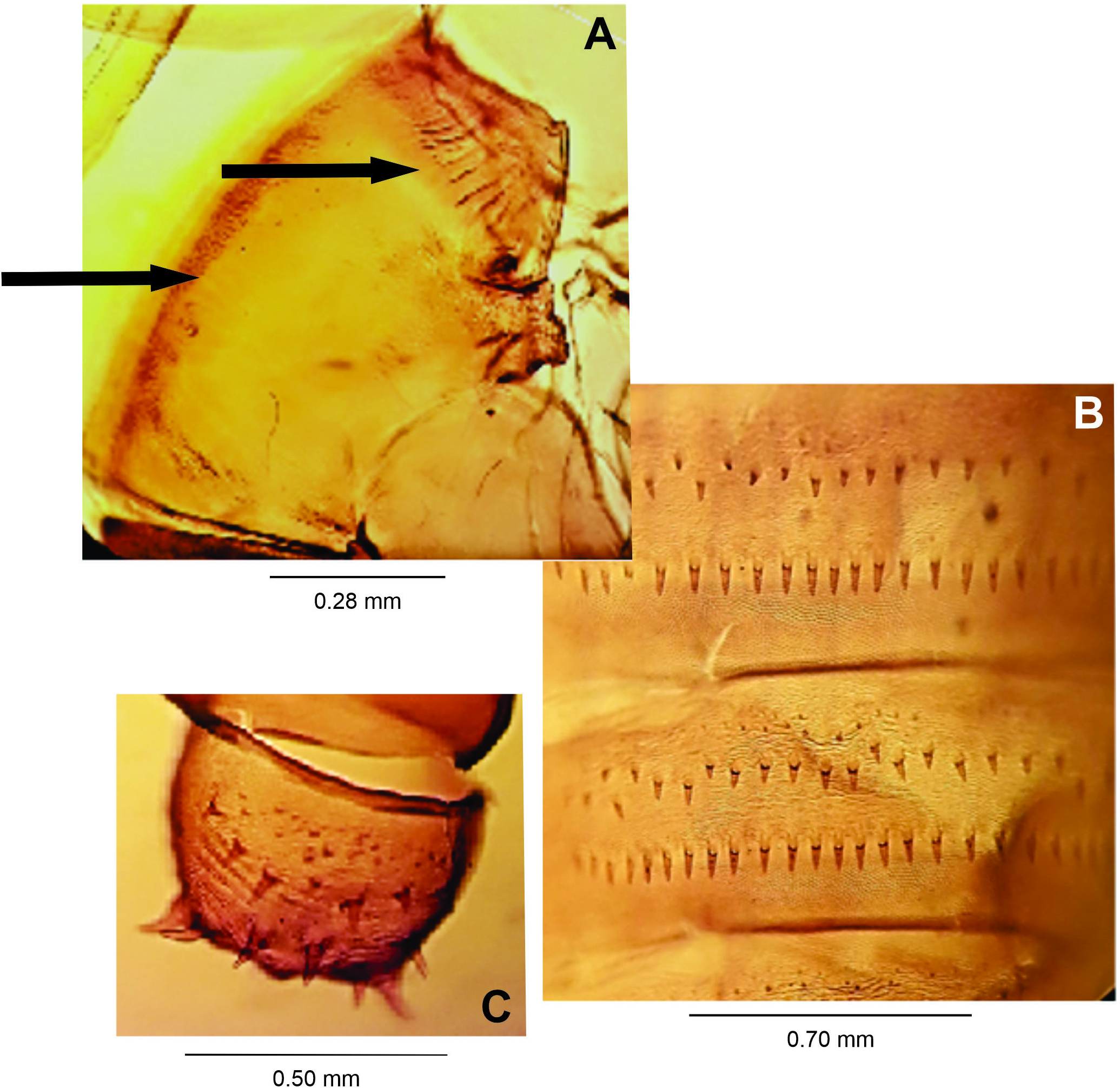
Male: Body length: 4.20 mm (N = 1). Head ( Fig. 17A View Figure 17 ): 0.55 mm long, 0.50 mm wide(N = 1), eye facets hexagonal, closely appressed; antennae: flagellomeres 1 and 2 not fused ( Fig. 17B View Figure 17 ), scape truncated conical, setose, 0.14 mm long, 0.05 mm wide (N = 1), pedicel globose, setose, 0.05 mm long, 0.05 mm wide (N = 1), 1 st- 10 th flagellomeres cylindrical (other flagellomeres missing), all 0.05 mm wide, circumfila longitudinally wavy, dense, anastomosing, equally spread along segments ( Fig. 17C View Figure 17 ), 1 st and 2 nd flagellomeres 0.22 mm long (N = 1), 3 rd- 6 th flagellomeres 0.20 mm long (N = 1), 7 th- 8 th flagellomeres 0.17 mm long (N = 1), proportion flagellomere neck-node: 1:11; frons with 18 setae (N = 1); mouth parts:labrum long-attenuate; hypopharynx of the same shape of labrum, with long lateral setulae anteriorly directed; labella elongate and convex, 0.05 mm long, 0.035 mm wide (N = 1), with lateral and mesal setae; palpus about 0.26 mm long (N = 1): 1 st segment globoid, 0.02 mm long, 0.02 mm wide, 2 nd segment 0.065 mm long, 0.025 mm wide, 3 rd segment 0.18 mm long, 0.15 mm wide (N = 1), all segments with setae. Thorax:scutum with two dorsocentral rows of setae,setae more abundant anteriorly and posteriorly, one lateral row of setae on each side of scutum, extending from base to distal margin, scales intermixed; scutellum with scattered setae; anepimeron setose, anepisternum setose; remaining pleural sclerites bare; legs: first tarsomere of each leg with an apical hook-like projection 0.04-0.05 mm long (N = 2) ( Fig. 17D View Figure 17 ), all legs broken; wing: length 2.80 mm (N = 1) ( Fig. 18A View Figure 18 ). Abdomen ( Fig. 18B View Figure 18 ): trichoid sensilla not visible; 1 st- 7 th tergites sclerotized, rectangular with a posterior row of setae, few lateral setae and mostly covered elsewhere with scales, 8 th tergite bare, narrow, mesally constricted; 2 nd- 8 th sternites more sclerotized than tergites; 2 nd- 6 th sternites rectangular with a posterior row of setae,several setae at midlength, few lateral setae,mostly covered elsewhere with scales; 6 th sternite with anterior and posterior margins slightly concave; 7 th sternite rectangular with a posterior row of setae, several mesal setae, few lateral setae, 8 th sternite rectangular, entirely covered with setae, more abundant posteriorly, and mostly covered elsewhere with scales. Terminalia ( Fig. 19A View Figure 19 ): gonocoxite short and stout, 0.16-0.18 mm long, 0.10 mm wide (N = 2), gonostylus spherical 0.05-0.06 mm long, 0.07 mm wide (N = 2), teeth 0.01 mm long, 0.025 mm wide (N = 2), hypoproct rounded apically, deeply bilobed.
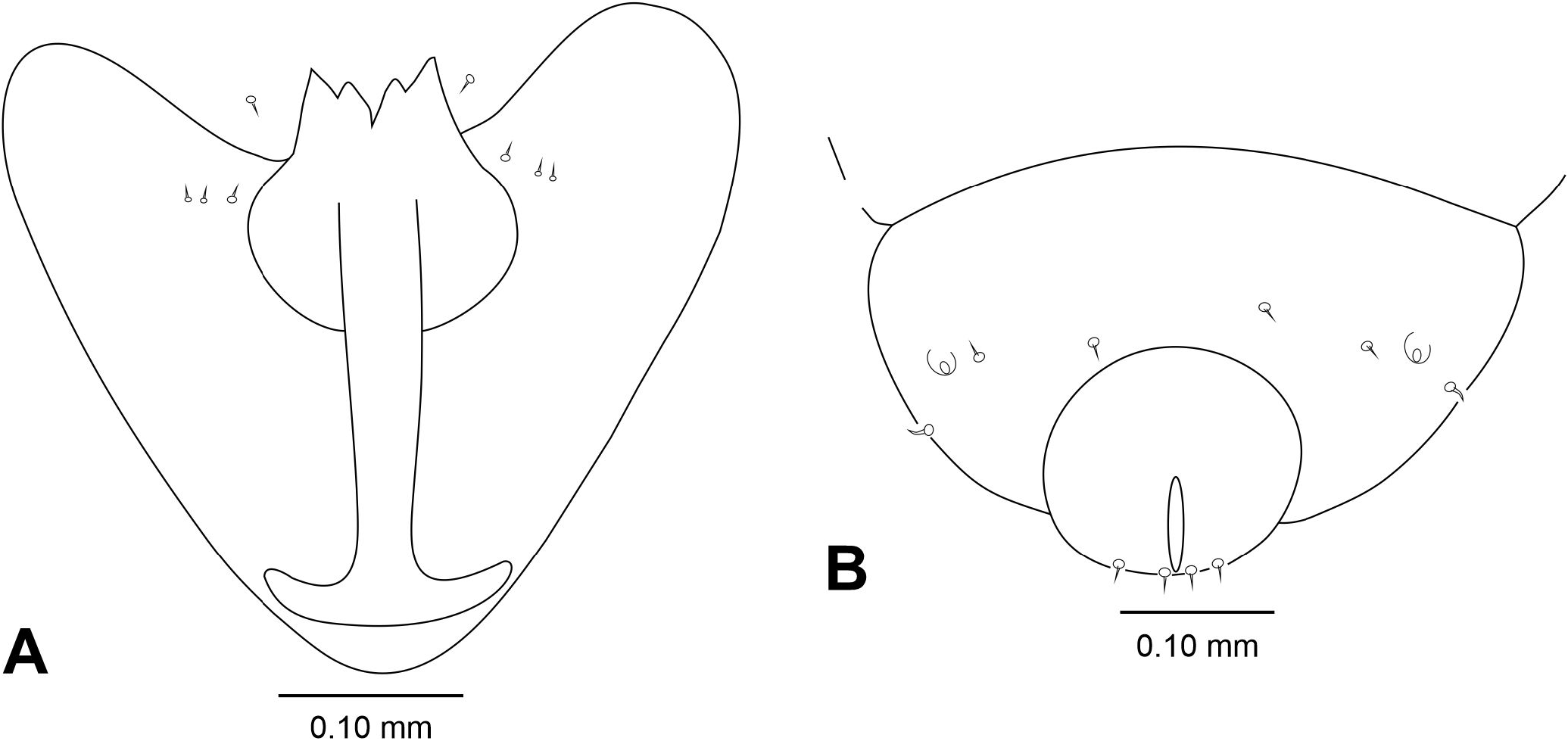
Female: Body length: 4.40-6.50 mm (N = 3). Head: 0.65-0.70 mm long, 0.56-0.65 mm wide (N = 2), antennae: scape 0.16 mm long (N = 1), pedicel 0.06 mm long (N = 1), 1 st- 11 th flagellomeres cylindrical, all 0.05 mm wide, circumfila comprising two longitudinal bands connected sub basally and apically by two transverse bands ( Fig. 19B View Figure 19 ), 1 st flagellomere 0.30 mm long (N = 1), 2 nd and 3 rd flagellomeres 0.25 mm long (N = 1), 4 th and 5 th flagellomeres 0.22 mm long (N = 1), 6 th and 7 th flagellomere 0.20 mm (N = 1), 8 th flagellomeres 0.18 mm long (N = 1); 9 th flagellomere 0.15 mm long (N = 1), 10 th flagellomere 0.10 mm long (N = 1), 11 th flagellomere 0.07 mm long (N = 1), 12 th flagellomere 0.05 mm long (N = 1) ( Fig. 19C View Figure 19 ); mouthparts: palpus 0.24 mm long (N =2): 1 st segment globose 0.02-0.03 mm long, 0.02 mm wide (N = 2), 2 nd segment cylindrical 0.08 mm long, 0.03 mm wide at midlength (N = 3), 3 rd segment cylindrical 0.13 mm long and 0.02-0.03 mm wide at midlength (N = 3). Thorax: anepimeron setose; legs: tarsal claws curved beyond midlength, anisomorphic, less robust on foreleg than on mid and hindlegs,empodium as long as claws( Fig.20A View Figure 20 );apical hook-like projection of first tarsomere with 0.04-0.05 mm long (N = 3); wing:length 3.30-4.10 mm (N = 4). Abdomen ( Fig. 20B View Figure 20 ): trichoid sensillae not visible, 1 st- 7 th tergites as in male, 8 th tergite with posterior margin with lobes 0.20 mm long (N = 2), 2 nd- 6 th sternites as in male, 7 th sternite with anterior and posterior margins more sclerotized mesally, 0.65 mm long, 2.41 X length sternite 6 (N = 1), setose (except basally), and mostly covered elsewhere with scales; sternite 8 not sclerotized; ovipositor: needle part 2.10-2.62 mm long (N = 4), 3.23-4.00 X length sternite 7 (n = 4). Other characters as in male.
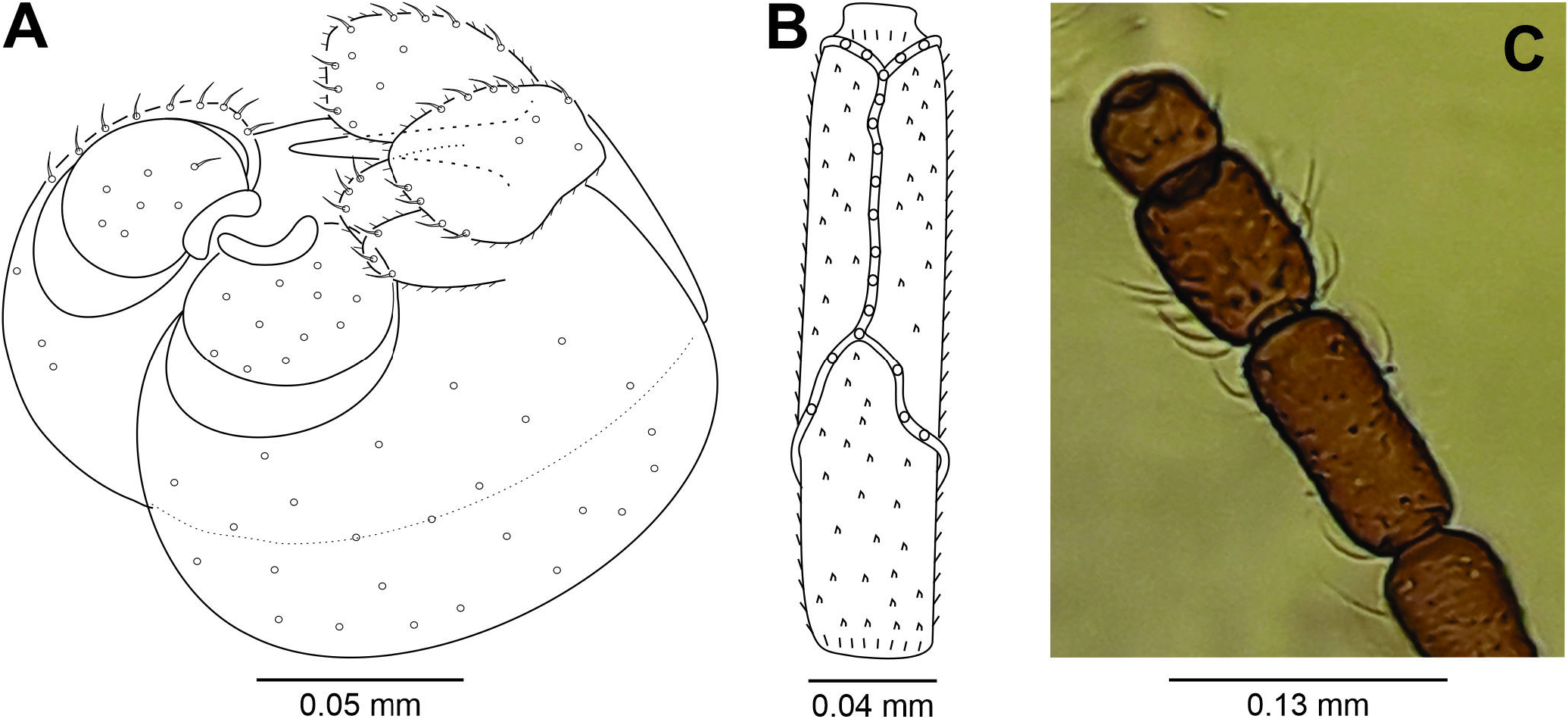
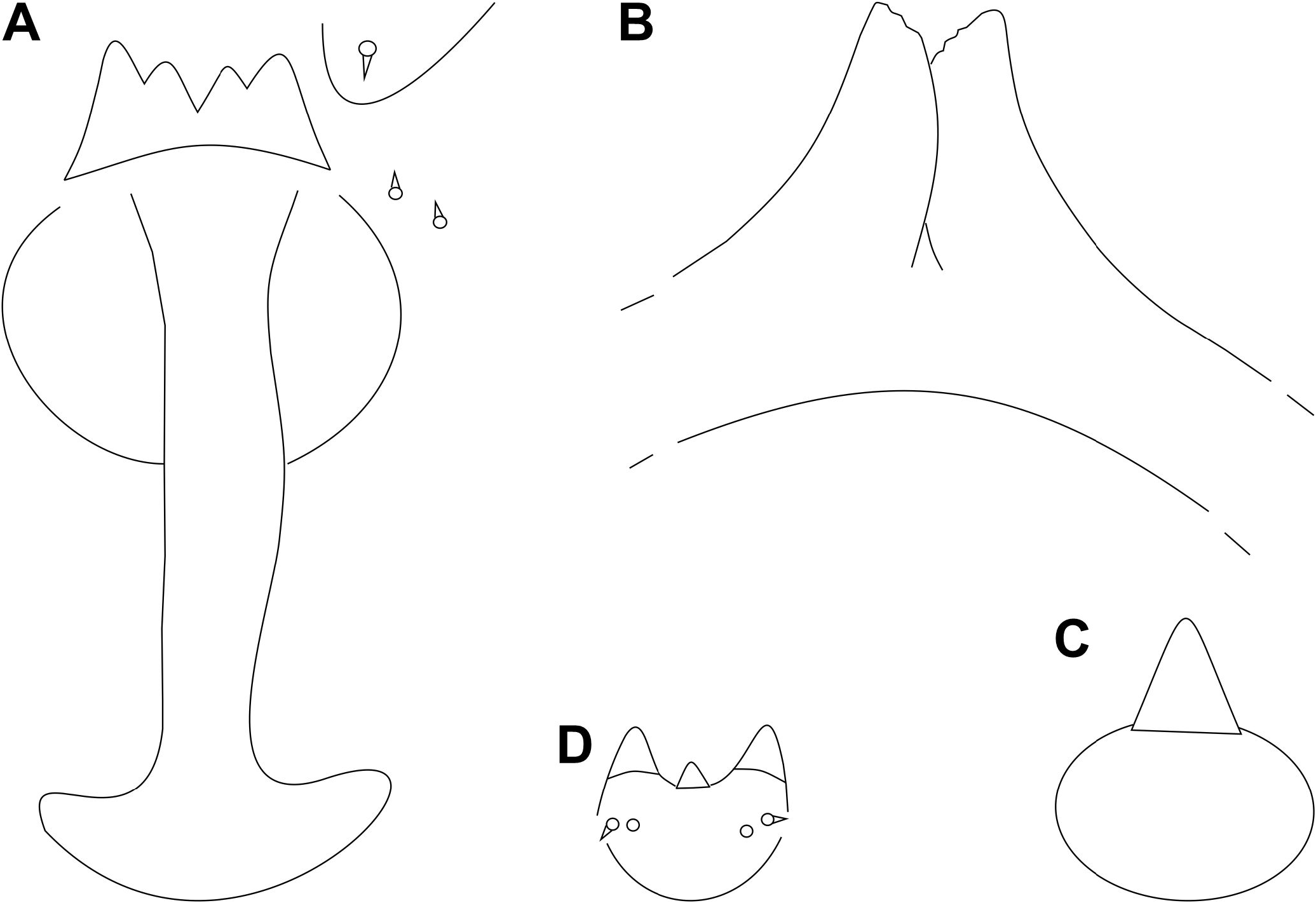
Pupa: Color: brownish. Body length: 5.00- 6.40 mm (N = 2). Head ( Fig. 21A View Figure 21 ): antennal horn 0.48 mm long (N = 1), triangular, with inner margin serrated ( Fig. 21B View Figure 21 ); apical seta 0.06 mm long (N = 1); upper facial horn simple, 0.17-0.20 mm long (N = 2), triangular ( Fig. 21C View Figure 21 ); lower facial horn tridentate, 0.10 mm long (N = 2), triangular ( Fig. 21D View Figure 21 ); face sclerotized between upper and lower facial horns ( Fig. 21A View Figure 21 ); two pairs of lower facial papillae: one pair setose, the other bare; three pairs of lateral facial papillae: one pair setose, two bare; upper cephalic margin thickened laterally. Thorax: prothoracic spiracle 0.11-0.13 mm long, setiform, slightly curved (N = 3) ( Fig. 21E View Figure 21 ), integument wrinkly ( Fig. 22A View Figure 22 ). Abdomen: segments 2-8 with transverse rows of crescent dorsal spines ( Fig.22B View Figure 22 );posterior row with 23 spines in the 2 nd segment, 21-24 in the 3 rd, 22-25 in the 4 th, 21-24 in the 5 th, 19-20 in the 6 th, 10-14 in the 7 th and 5 in the 8 th (N = 2) ( Fig. 22C View Figure 22 ).
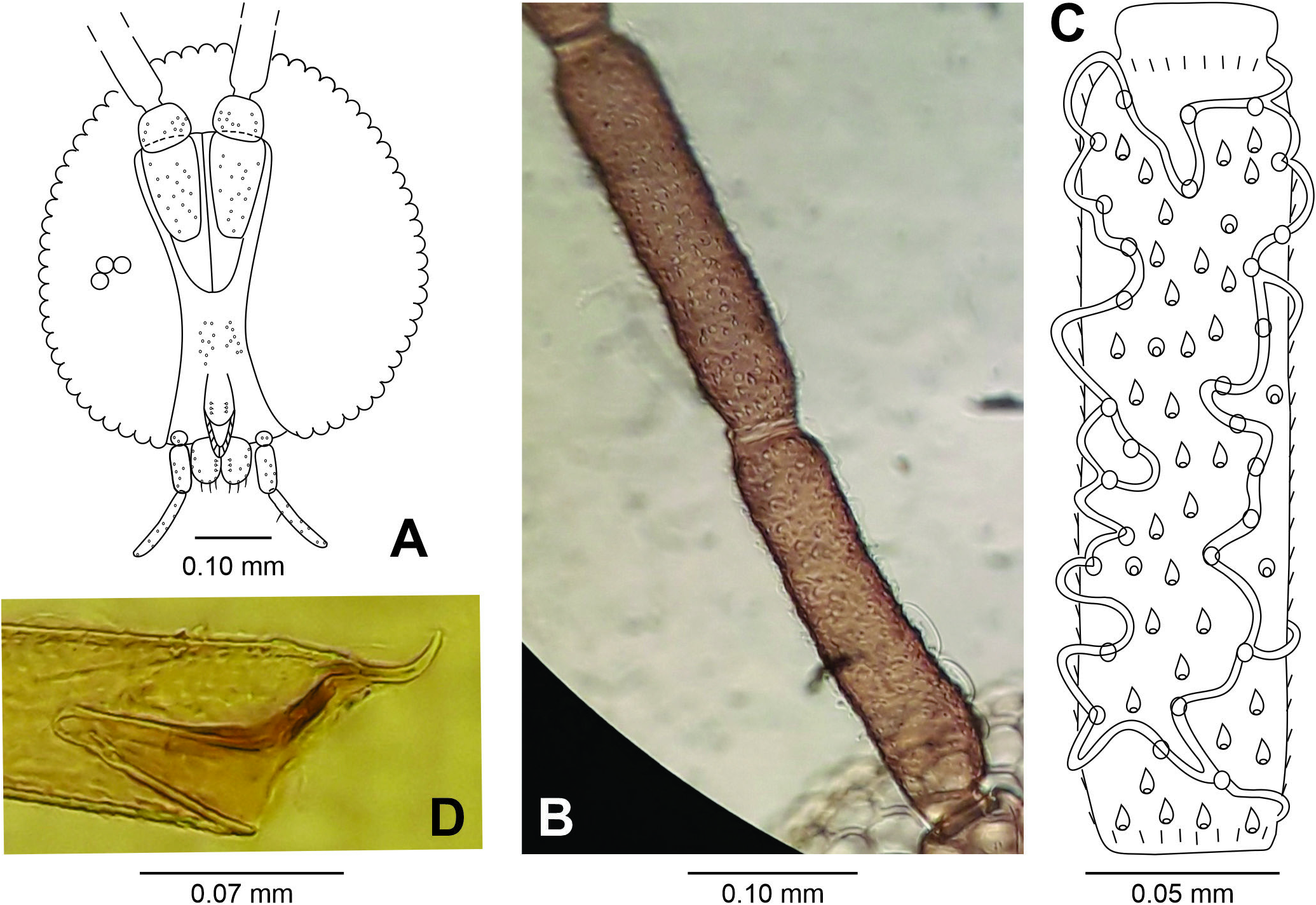
Larva: Body length: 3.70-3.90 mm (N = 1); cephalic head 0.30mm long, 0.54mm wide.Prothoracic spatula( Fig.23A View Figure 23 ) 0.38-0.40 mm long (N = 2), four-toothed,inner teeth short- er than outer, three setose lateral papillae on each side. Terminal segment with four setose papillae ( Fig. 23B View Figure 23 ).
Gall: On flower bud. No other morphological features are available in the labels of the specimens.
Material examined: Holotype male, BRAZIL, Minas Gerais, Uberlândia,E.E. do Panga , III.2005, J.F.Andrade col.( MNRJ).
Paratypes: Same data as holotype, 1male, 3 females,and 5 pupal exuviae ; Minas Gerais, Serra do Cipó , 25.VI.2002, N. Bittencourt col., 2 larvae ; VII.2002, same collector, 1 female and 2 pupal exuviae ( MNRJ) .
Etymology: The name “ zeyheriae ” is the genitive of the host plant genus.
Remarks: Asphondylia zeyheriae induces galls on Zeyheria montana Mart. (Bignoniaceae) , a plant endemic to Brazil with records in the Amazon Forest, Atlantic Forest, Caatinga, and Cerrado ( Lohmann, 2020). This is the first gall midge species reported on this plant.
Only one other congeneric species, Asphondylia godmaniae Möhn, 1959 , from El Salvador, induces galls on Bignoniaceae .It is known only from larva and pupa ( Möhn, 1959).The described stages of Asphondylia godmaniae and A. zeyheriae are morphologically very similar, but their larvae differ mainly in the body length ( 1.9 mm in the former and 3.7-3.9 mm in the latter),and shape and relative length of the spatula teeth (compare Fig. 23A View Figure 23 with Fig. 24A View Figure 24 ). Pupae of both species differ in body length ( 2.3-2.4 mm in A. godmaniae and 5.0- 6.4 mm in A. zeyheriae ) and face integument (sclerotized area between upper and lower facial horns present only in the new species).In both species, the distal part of the antennal horn is longer than the basal part, but in the new species this difference is more accentuated;the upper facial horn is longer and more pointed in A.zeyheriae than in A.godmaniae , and the lower facial horn has the lateral teeth slightly longer than the middle tooth in the new species, while in A. godmaniae this difference is greater (compare Figs.21 View Figure 21 B-D with Figs. 24 View Figure 24 B-D).
| MNRJ |
Museu Nacional/Universidade Federal de Rio de Janeiro |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.