Ceratomyxa ghannouchensis n. sp ., 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2019.1597202 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0DE35680-A3C9-45BA-B29B-0B7462CA7A43 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3680434 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C32F18-9627-FFD7-EB66-FE5BFCAD2760 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Ceratomyxa ghannouchensis n. sp . |
| status |
sp. nov. |
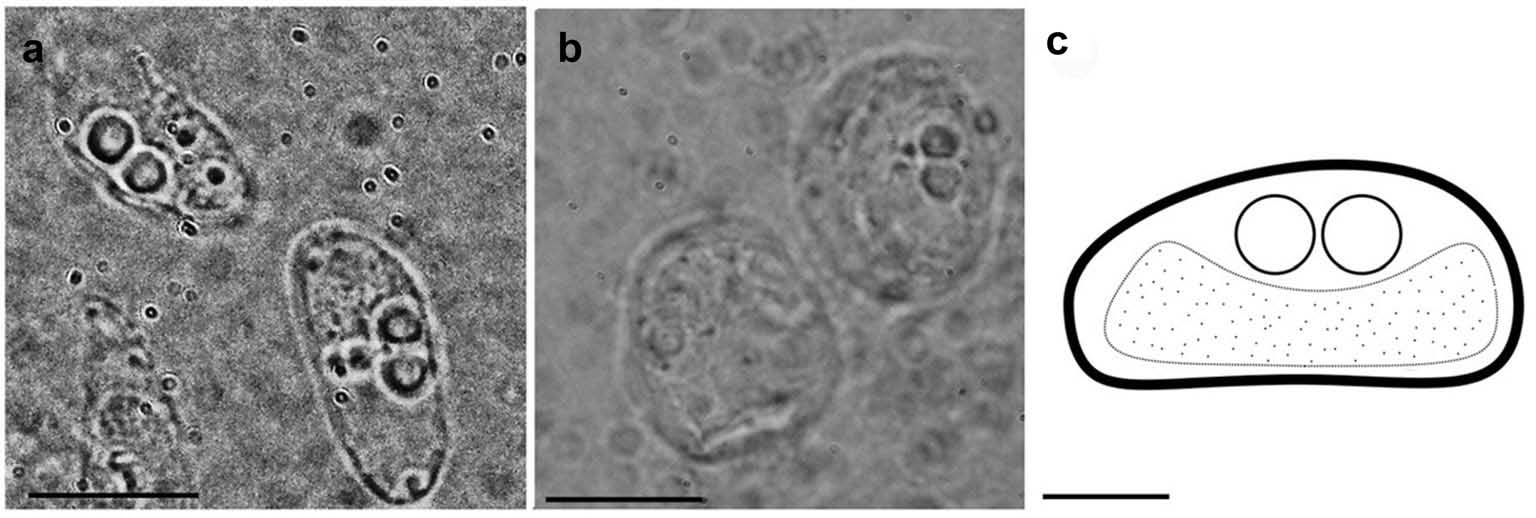
Ceratomyxa ghannouchensis n. sp. ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 )
Myxospores morphology
The myxospores were typical of the genus Ceratomyxa . Mature myxospores were stubby with convex anterior and almost straight to slightly concave posteriorı 5.8 ± 0.3 (5 – 7) µm in length and 11.7 ± 0.4 (11 – 13) µm in thickness. The valves were unequal in sizeı with one occasionally tapering to a greater degree than the other. The myxospores could be mixed with the plasmodia and myxospores of Ceratomyxa pallida . The sporoplasm almost filled the entire myxospores cavity. The polar capsules were equal in sizeı spherical in shape and measured 2 ± 0.2 (1.8 – 2.8) µm in diameter. A schematic drawing of the myxospore and plasmodiaı based on the LM observationsı is shown in Figure 1 View Figure 1 .
Vegetative stage
Monosporous plasmodia were rarely observed ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 ).
SSU rDNA sequence
A consensus sequence of 1425 bp of the SSU rDNA was generated from four sequenced cloned PCR products and was submitted to GenBank under accession number KT932821 View Materials . The sequence of C. ghannouchensis differs from all deposited sequences of Ceratomyxa in GenBank. The maximum of similarity was 94.8% observed with C. tunisiensis Thabetı Mansourı Al Omar and Tlig-Zouariı 2015 and 90.1% with C. leatherjacketi Fialaı Hlavničkováı Kodádkováı Freemanı Bartošová-Sojková and Atkinsonı 2015 ı reported from the marine fish unicorn leatherjacket Aluterus monoceros (L.) ( Tetraodontiformes : Monacanthidae ) on the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. For the remaining Ceratomyxid speciesı the nucleotide similarity was very low and varied between 85% with C. vermiformis and 67.7% with C. aegyptiaca .
Taxonomic summary Type host. Bogueı Boops boops (Linnaeus) ( Perciformes : Sparidae ). Location in the host. Coelozoicı in the bile. Prevalence. Twenty-one per cent (33 out of 157 examined specimens). Type location. Ghannouch in Gulf of Gabès. Type material. Syntype – air-dried slides stained with Giemsa no ZS145 were deposited in the parasitological collection of the Museum National d ’ Histoire Naturelleı Parisı collection. Molecular data. The small subunit ribosomal DNA sequence (1452) was deposited in GenBank under the accession number KT932821 View Materials . Etymology. The specific name refers to the locality: Ghannouch in the Gulf of Gabès.
Remarks
Compared to other Ceratomyxa speciesı some similarities were observed with Ceratomyxa arabica Al-Qahtaniı Mansourı Al-Quraishyı Abdel-Bakiı 2015 from Saudi Arabiaı Ceratomyxa buri Yokoyama and Fukudaı 2001 from Japanı Ceratomyxa castigastoides Meglitschı 1960 from New Zealandı Ceratomyxa obesa Jamesonı 1929 from Clinocottus analis from the USA and Ceratomyxa recta Meglitschı 1960 from Genypterus blacodes from New Zealand ( Table 1 View Table 1 ). The species found in this study can be distinguished from C. buri and C. castigastoides by its narrower myxospores. Additionallyı C. castigastoides and C. obesa have shorter myxospores and both C. buri and C. recta have larger polar capsules. The measurements of C. arabica (7.0 – 9.0 × 10.0 – 14.0) are in the same range for myxospores length and thickness of C. ghannouchensis n. sp. (5.0 – 10.0 × 8.0 – 16.0)ı and both measurements overlap. Howeverı C. arabica have unequal and subspherical polar capsules.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |