Astymachus Howard, 1898
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2020.1747654 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:324E4AF7-3032-4573-98AC-CABAE316F33E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4330528 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C387B2-FFCD-FFDC-FDDC-FE8CFB5F4714 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Astymachus Howard |
| status |
|
Astymachus Howard View in CoL View at ENA
Type species Astymachus japonicus Howard View in CoL , by monotypy.
Astymachus Howard, 1898: 238 View in CoL .
Diagnosis. Body, including head, strongly dorso-ventrally flattened and non-metallic; head opisthognathous, acutely triangular to very flat in profile with occipital margin curved backwards behind each eye to meet foramen medially which is virtually touching mandibles; eyes small, shorter than distance between them; face with an indistinct, shallow, longitudinal median groove; antennal torulus high on face, connected to mouth margin by a groove and separated from it by about 3 – 4× its own length, most often generally pale yellow but occasionally brown; wings hyaline, usually with infuscate areas, discal setae short and sparse. Female: funicle 6-segmented, proximal segments transverse, F1 sometimes quadrate, 1 – 2 distal segments conspicuously larger and subquadrate, clava entire or appearing 2-segmented with a faint or incomplete suture; mandible with 3 teeth; notaular lines absent; gaster elongate, clearly longer than head and thorax combined; ovipositor clearly exserted and about 2× as long as mid tibia or gonostylus, exserted part at least about half as long as mid tibia and with sheaths dark brown, broadened and flattened from side to side. Male: funicle 6-segmented, segments subequal in size, subquadrate becoming slightly larger distally, setae slightly shorter than diameter of segments; clava entire; genitalia with digiti long and slender, about 10× as long as broad; aedeagus slender, about 12 – 20× as long as broad, as long as mid tibia or slightly longer, apex strongly pointed.
Biology. Parasitoids of aclerdids ( Hemiptera : Aclerdidae ) feeding on grasses ( Poaceae ), other recorded hosts are probably incorrect.
Distribution. Southern USA (probably introduced), South Africa, Pakistan to China, Korea and Japan.
Comments. All known species of Astymachus are strongly dorsoventrally flattened. This allows them to gain access to their aclerdid hosts in extremely tight spaces between the stem and leaf bases of certain grasses such as bamboo, reeds or sugarcane.
Key to species of Astymachus (females)
1 Wings shortened, fore wing reaching less than halfway along gaster, well short of cercal plates; TI – TV of gaster each with a narrow, pale brown cross band; maxillary palp 3-segmented ............................................... ............................................... 1. eximius Hayat
- Wings not shortened, fore wing reaching at least two-thirds along gaster, well past cercal plates; gaster completely yellow or if with some brownish suffusions these not forming crossbands; maxillary palp 4-segmented ................................................................ 2
2(1) Thorax and abdomen brown, the pro- and mesonotum with a broad, pale, longitudinal median band .......................................... .......................................... 2. exilis Prinsloo View in CoL
- Thorax and abdomen entirely yellow ................................................................................... 3
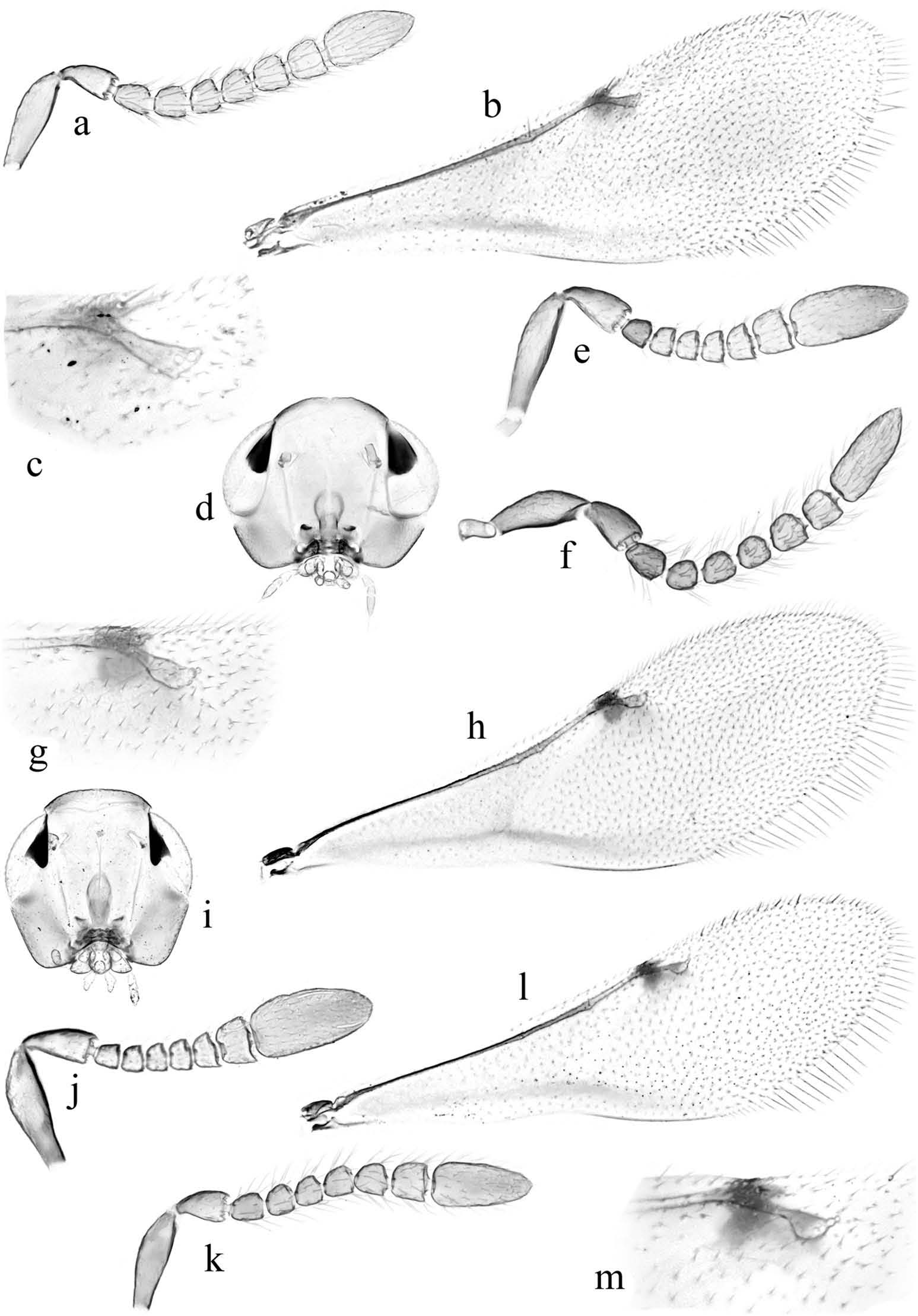
3(2) Funicle with linear sensilla on F5 and F6 ( Figure 2 View Figures 2 (b)) ........ 3. saccharum sp. nov.
- Funicle with linear sensilla on F6 only ( Figures 2 View Figures 2 (h), (n), 3(e), (j)) .............................. 4
4(3) Discal setae below apex of venation about as long as distance between sockets ( Figure 2e View Figures 2 ) ............................................. ............................................. 4. felix Singh and Hayat View in CoL
- Discal setae below apex of venation at most about one-half as long as distance between sockets ( Figures 2 View Figures 2 (g), (k); 3(g), 3(m)) .............................................................. 6
5(4) Fore wing ( Figure 2 View Figures 2 (e)) generally conspicuously infuscate with marginal vein more strongly infuscate, almost black, area below marginal vein also conspicuously darker than remainder of wing and extending at least level with apex of stigmal vein; marginal vein at least about as long as stigmal vein....... ............................................................................................................... 5. phainae Sugonjaev View in CoL
- Fore wing generally hyaline ( Figures 2 View Figures 2 (i); 3(b), h, l) or extremely weakly infuscate with only a small, weakly infuscate area on marginal vein that below this does not reach level with apex of stigmal vein, or hardly so; marginal vein not appearing to reach anterior wing margin (except perhaps in japonicus View in CoL ) and conspicuously shorter than stigmal vein ................................................................................................................................. 6
6(4) Ovipositor less than 2× as long as mid tibia.................. .................. 6. lasallei sp. nov.
- Ovipositor more than 2× as long as mid tibia ......................................................................... 7
7(6) Scutellum, excluding axillae, with at least 25 setae ............ 7. phragmitis Trjapitzin View in CoL
- Scutellum, excluding axillae, with fewer than 15 setae ................................................. 8
8(7) Head in facial view not more than 1.7× as long as eye ( Figure 3d View Figures 3 ); fore wing at least about 3.8× as long as mid tibia.......................................................... 8. japonicus Howard View in CoL
- Head in facial view at least 1.9× as long as eye ( Figure 3i View Figures 3 ); fore wing about 3.5 – 3.7× as long as mid tibia........................................................................................ 9. srilankae sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Astymachus Howard
| Noyes, John S. & Higashiura, Yoshimitsu 2020 |
Astymachus
| Howard LO 1898: 238 |