Marmosops ( Sciophanes ) woodalli ( Pine, 1981 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4890.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:54F20D85-7110-465D-914C-26FA34847A02 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4328170 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C3945D-FFD8-FFCF-FF04-8BD8FD4BFD07 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Marmosops ( Sciophanes ) woodalli ( Pine, 1981 ) |
| status |
|
Marmosops ( Sciophanes) woodalli ( Pine, 1981)
Marmosa parvidens woodalli Pine, 1981: 62 .
Marmosops pinheiroi: Voss et al. 2001: 49 View in CoL (part); name combination.
Holotype. USNM 393532 About USNM consists of skin and skull of an adult female collected on 14 June 1968, Ronald H. Pine field no. 5054.
Type locality. Nova Área Experimental, Utinga ( 1º27’S, 48º29W; the wooded area surrounding the Belém waterworks), Pará, Brazil GoogleMaps .
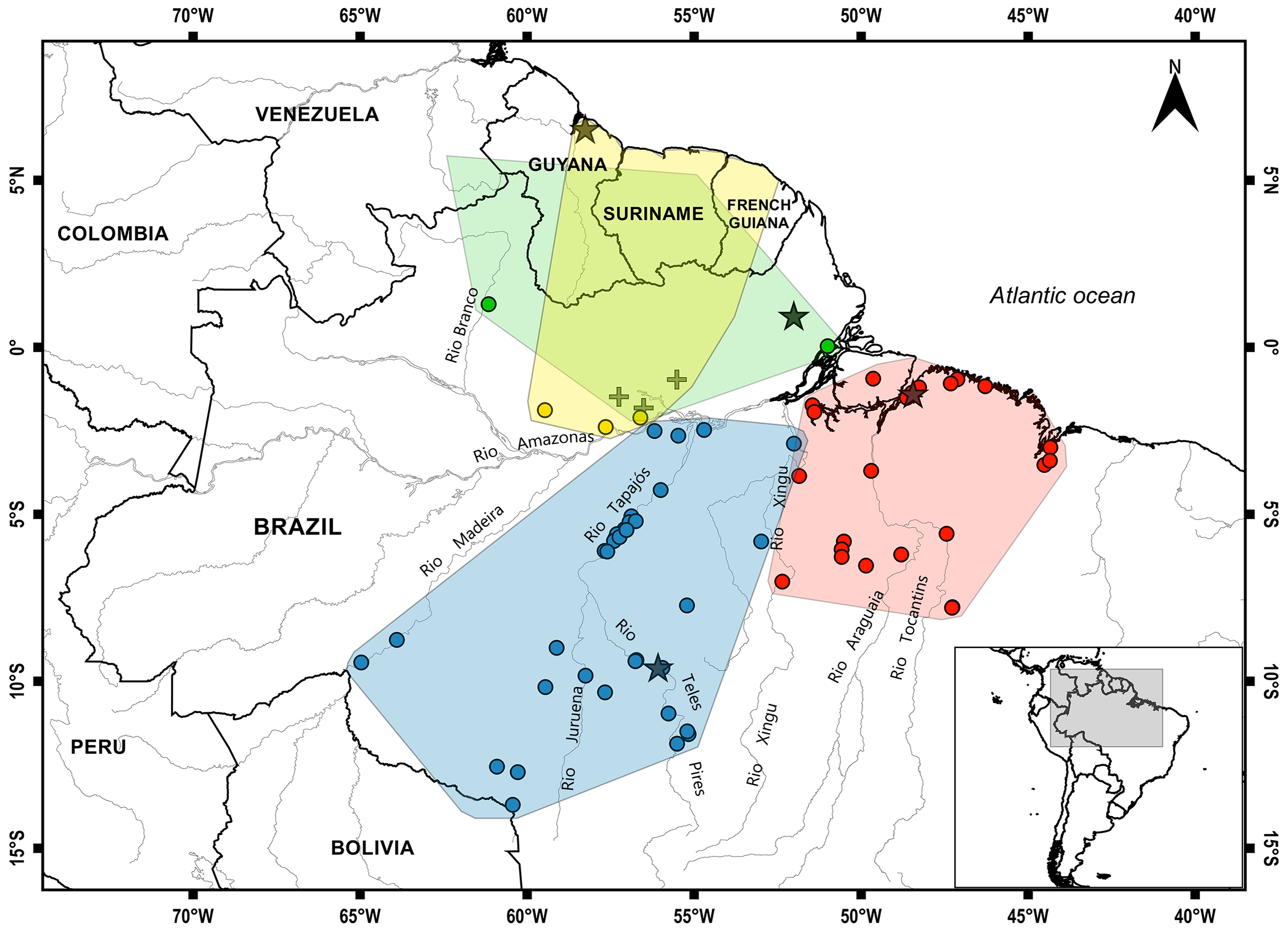
Geographic distribution. It occurs on the right bank of the Xingu River , including the Marajó Island in the state of Pará, extending east to the state of Maranhão and south to the state of Tocantins, Brazil ( Figure 5 View FIGURE 5 ) .
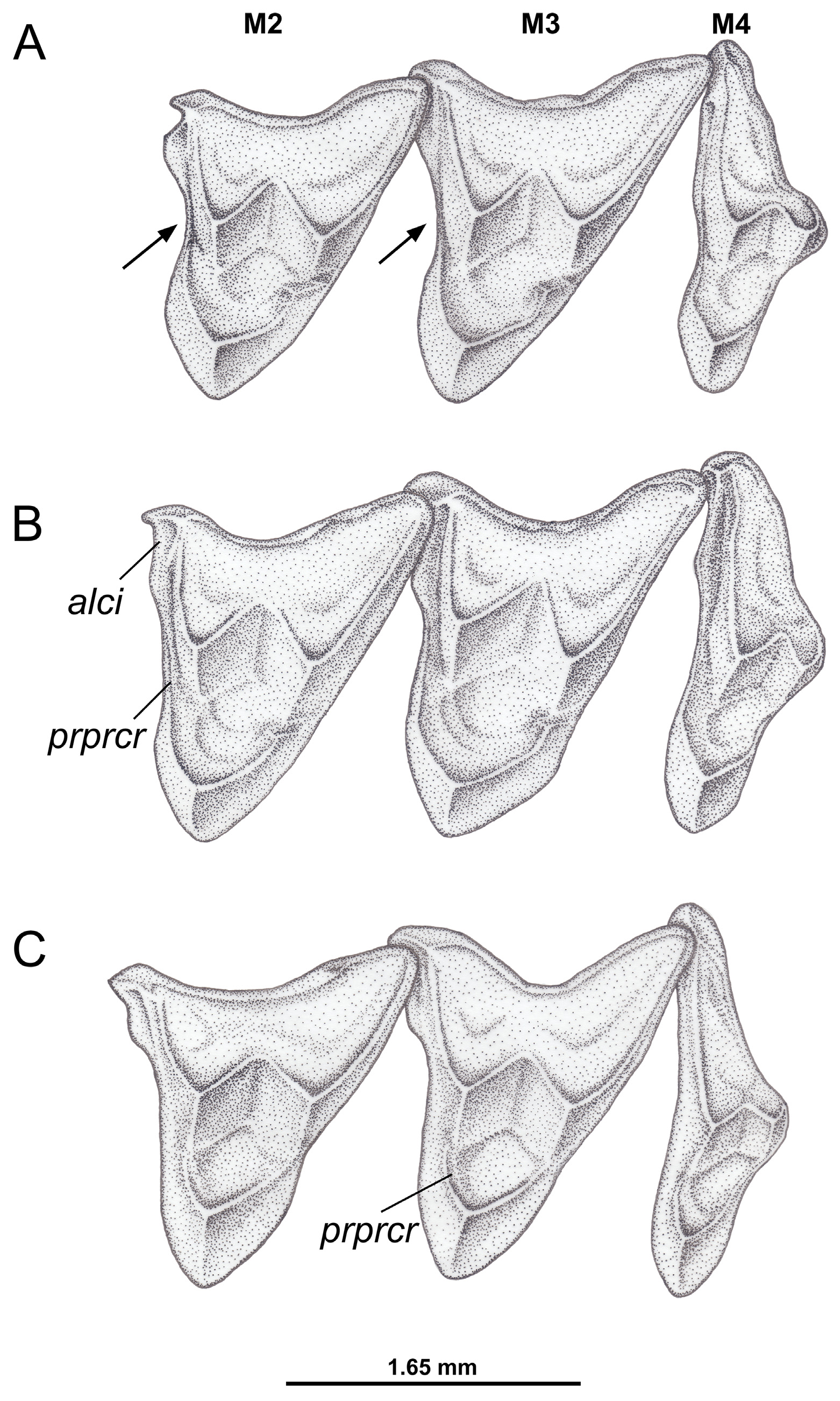
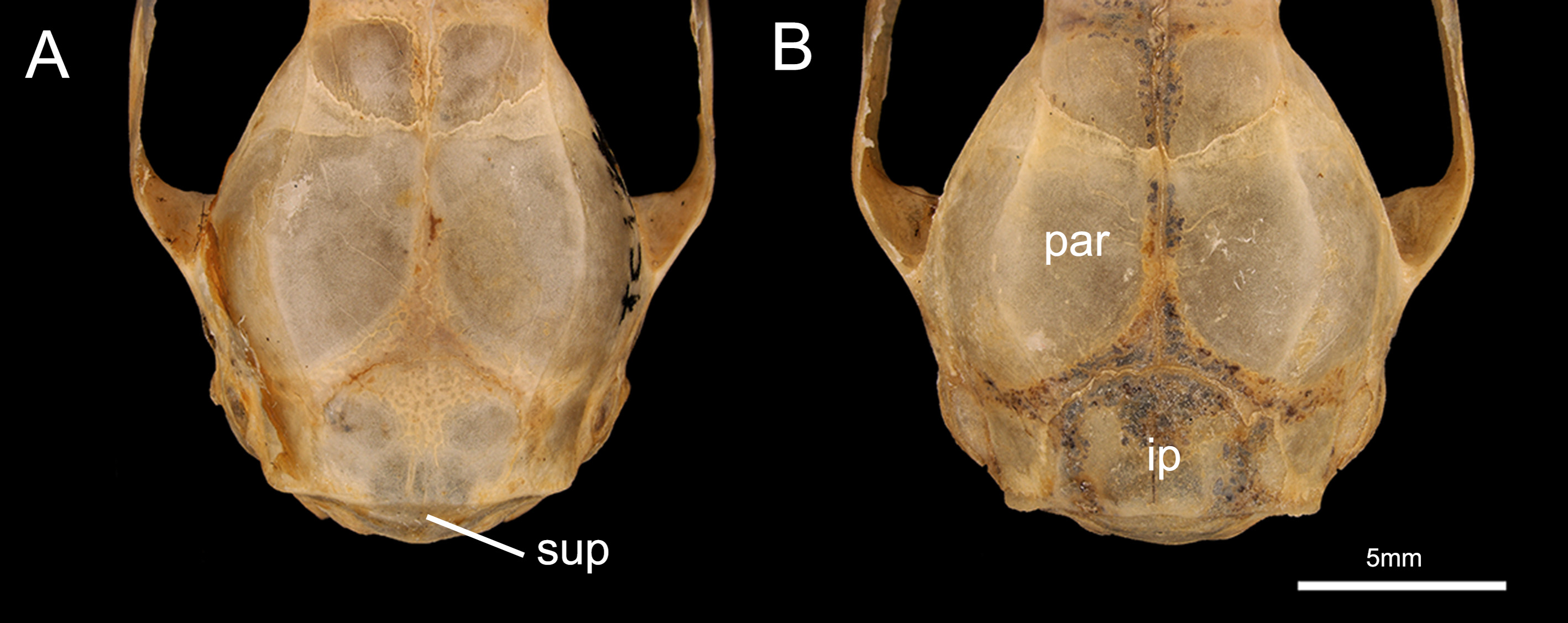
Amended diagnosis. Dorsal coloration usually dark brown; tail length (LT: 92–158 mm) relatively longer in relation to head and body length ( HBL: 70–120 mm); ventral coloration white, with narrow lateral bands of graybased and white-tipped hairs arranged irregularly, which may or may not join on the throat and/or mid-chest and usually do not extend to the inner surface of the hind limbs; supraoccipital rounded in dorsal view (due to its con-vex shape); M3 with posterior portion of the stylar shelf more labially designed than the anterior portion (occlusal view); upper molars with preprotocrista and anterolabial cingulum seperated, not forming a continuous shelf along the anterior margin of the tooth crown; metaconule of the upper molars undeveloped; and talonid of the m4 usually tricuspid.
Morphological description. Marmosops woodalli has head body size ranging from 70 to 120 mm and a longer tail (LT: 92–158 mm; Tables 4 View TABLE 4 and 5 View TABLE 5 ); dorsal hairs 6–9 mm long; dorsal fur smooth, usually dark brown, being slightly lighter laterally; rostrum lighter than the top of the head, presenting grayish brown coloration, with some gray hairs; mask around the eyes blackish, with conspicuous posterior portion (except in UFMT 3975; UFPA-M 371, 384; MPEG 40177, 40178, 40181); cheeks with both white hairs and gray-based and white-tipped hairs; hands covered dorsally with whitish hairs; tail bicolor, brown dark (54%, n=79) or grayish-brown (46%, n=79); tail scales arranged in a spiral, each with three hairs inserted in the posterior margin; the central hair of the triplet clearly thick-er and more pigmented than the lateral ones; white venter, with narrow lateral bands of gray-based and white-tipped hairs arranged irregularly, which may or may not join on the throat and/or mid-chest and usually do not extend to the inner surface of the hind limbs (83.3%, n=88); hands with lateral spoon shaped carpal tubercle in adult males.
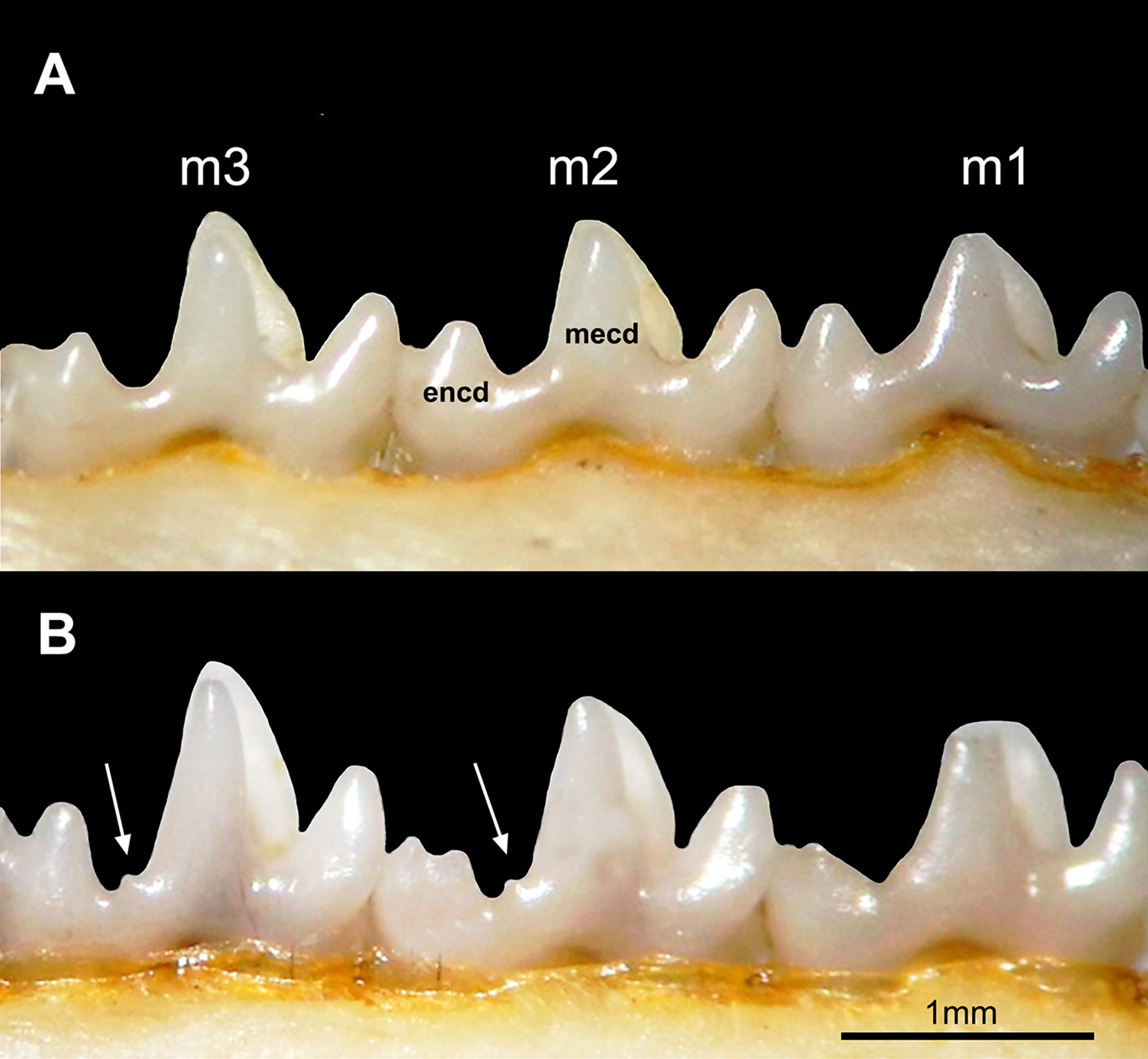
Craniodentally, M. woodalli exhibits zygomatic process of the squamosal widely overlapped dorsally by the jugal; lacrimal foramina may be exposed or not exposed in lateral view (less common); supraorbital margin slightly rounded with non-prominent crest; long nasal bones (extending slightly behind the lacrimal) and generally wider posteriorly than anteriorly (71.4%, n=49); supraoccipital with rounded shape in dorsal view, due to its markedly convex shape; paraoccipital process long and narrow; tympanic process of the alisphenoid with ventral surface oval or globose; cochlear fenestrae exposed in ventral view (except in UFMT 1251, 1258; MZUSP: AS 30; MPEG 40183, MPEG: SBER 02, 11, 15); palatine fenestrae absent, but diminutive perforations are present in the palatine and/or maxillary bones in 45% of the specimens (n=70); C1 with anterior and posterior accessory cusps in males and females; M3 with posterior portion of the stylar shelf more labially projected than the anterior portion (in oc-clusal view); upper molars with preprotocrista and anterolabial cingulum separated, not forming a continuous shelf along the anterior margin of the tooth crown (except in UFPA-M 376; MPEG 40167, 40296, MPEG: CAX 098, 293, MAR 428); metaconule of upper molars slightly developed; lower canine (c1) premolariform, (with posterior accessory cusps) subequal in height with first lower premolar (p1) (except in UFMT 3719, 3718, 3966; MZUSP: AS 30; MPEG: MAR 222, 428, 485, 1294; in which c1 is slightly higher than p1); m2 paraconid usually higher than the entoconid of m1 (70%, n=70); and talonid of the m4 usually tricuspid (83%, n=70; except in UFPA-M 382, 429; MNRJ 75117, 75121, 75122, 75139; UFMT 765; MPEG 40378, 40380; MPEG: CAX 293, MAR 589, PEB 12).
Geographic variation. Specimens of M. woodalli from the Cerrado biome (states of Maranhão and Tocantins) exhibit lighter dorsal fur (reddish brown) than specimens from forested areas (dark brown). In addition, specimens from the right margin of the Tocantins River have larger body size ( HBL = 110.1 ±17.8 mm) than those from the left bank ( HBL = 102.8±17.6 mm), and Student´s t tests showed that females from the right margin exhibit larger CBL, PL, MTR, UMS, WM4, BRC, BRJ, LMS, Lm4, and smaller TBO, while males exhibit larger PL, MTR, UMS, PPB, WET, POC, LMS, and Lm4 ( Table S5 View TABLE 5 ).
Comparisons with M. parvidens and other species of the “Parvidens” group ( Table 6). Comparisons between M. woodalli , M. marina and M. pinheiroi ( s.s.) are provided above. Marmosops woodalli can be discriminated from M. parvidens by exhibiting dark brown dorsal coloration (versus slightly reddish brown); white (versus cream) ventral fur; lateral bands of gray-based hairs on the venter narrow and irregularly arranged, joining or not on the throat and/or mid-chest (versus usually absent, never joining together; Figure 4A and D View FIGURE 4 ); rounded supraoc-cipital ( Figure 9A View FIGURE 9 ), due to its markedly convex shape in dorsal view (versus slightly convex); tympanic process of the alisphenoid with ventral surface oval or globose (versus usually globose); posterior portion of the stylar shelf of the M3 more labially projected than the anterior portion (versus anterior and posterior portions equally projected labially); preprotocrista and anterolabial cingulum separated, not forming a continuous shelf on the anterior margin of crown of the upper molars (versus united, forming a continuous shelf on the anterior margin of crown the upper molars; Figures 7 View FIGURE 7 B-C); and small accessory cusp between the metaconid and the entoconid of lower molars absent ( Figure 8 View FIGURE 8 A-B).
Habitats and sympatry. Marmosops woodalli is geographically distributed in the Babaçu Forests of Maranhão, Xingu/Tocantins-Araguaia Humid Forests, Tocantins-Araguaia/ Maranhão Humid Forests, Marajó Várzea Forests, and Tropical Dry Forests ecoregions ( sensu Olson et al. 2001). One specimen collected in Itapecuru Mirim, state of Maranhão, Brazil ( MPEG 45528), was associated to disturbed forest (secondary vegetation) according to its tag information. There is no record of sympatry between M. woodalli and other Marmosops species.
Natural history data. Mammary formula 4–1–4 = 9. Pregnant females were recorded in October, in Primavera, state of Pará, Brazil. In this locality, M. Aragona captured four specimens in live-traps (Sherman), three of which set on the ground (three individuals – UFMT 3975, 3978, and UFMT: TC 189) and one in the understory ( UFMT 3966); two other individuals were captured in pitfall-traps.
Specimens examined (n=165). BRAZIL - Maranhão: Bacabeira , 3°0’S, 44°19’W, 1 F, 1 M ( UFPA-M 966 , 980 ) GoogleMaps ; Ferrovia Norte Sul , 5°35’S, 47°26’W, 1 M ( MZUSP: AS 30 ) GoogleMaps ; Itapecuru Mirim , 3°24’S, 44°21’W, 1 M ( MPEG 45528 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Miranda do Norte , 3°31’38”S, 44°30’46”W, 1 M ( UFPA: EFC 08-03 ) GoogleMaps . Pará: Barcarena , 1°30’S, 48°37’W, 12 M, 2 F ( UFPA-M 345 , 368 , 369 , 371-374 , 376 , 377 , 379 , 380 , 381 , 382 , 384 ) GoogleMaps ; Belém, Agropalma , 1°19’S, 48°28’W, 4 F, 2 M ( MPEG: AGPM 06 , 11 View Materials , 33 View Materials , 38 View Materials , 109 View Materials , 152 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Canaã dos Carajás , 6°32’S, 49°51’W, 1 M ( MZUSP: CA 20 ) GoogleMaps ; Caxiuanã , 1°55’S, 51°22’W, 9 M, 3 F, 4? ( MPEG 40167 View Materials , 40169 View Materials , 40171 View Materials , 40172 View Materials , 40298 View Materials ; MPEG: MAR 222 View Materials , 428 View Materials , 589 View Materials , 683 View Materials , 1294 View Materials ; CAX 098, 186, 209, 293, 360, 407) GoogleMaps ; Estrada de Ferro Carajás , 6°16’S, 50°34’W, 7 M (UFPA-M 423, 426, 429, 458, 459, 487, 521) GoogleMaps ; Chaves, Fazenda Tauari, Ilha de Marajó , 0°39’S, 50°11’W, 5 M, 2 F ( MPEG 40388 View Materials , 40389 View Materials , 40390 View Materials ou 40392 (double), 40391, 40393, 40394, 40395) GoogleMaps ; Linha de Transmissão do Tucurui-Xingu (Jurupari), 3°42’0”S, 49°41’59”W, 2 M, 1 F ( MZUSP: LTBM 02 , 09 View Materials ; LTC 24 ) GoogleMaps ; Marabá , 5 M, 3 F ( UFPA-M 257 , 347 , 355 , 356 , 358 , 382 , 1824 , 1907 ) ; Marabá, Flona Tapirapé , 5°49’0”S, 50°30’60”W, 3 F, 7 M, 7? ( MPEG 40174- 40179 View Materials , 40181 View Materials , 40183 View Materials ; MPEG: PSA 065 View Materials , 087 View Materials , 154 View Materials ; UFMT 1241, 1245, 1247, 1251, 1252, 1258) GoogleMaps ; Melgaço, Estação Científica Ferreira Penna , 1°41’33”S, 50°28’43”W, 5 M, 4 F, 4? ( MPEG 40375-40378 View Materials , 40380 View Materials , 40381-40384 View Materials , 40385- 40387 View Materials ; MPEG: EPM 095 ) GoogleMaps ; Parauapebas , 6°4’S, 49°54’W, 1 M ( MPEG 38941 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Peixe-boi , 01º05’53”S 47º19’54”W, 2 F, 1 M ( MPEG: PEB 06 , 12 View Materials , 25 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Primavera , 0°57’S, 47°6’W, 7 M, 6 F, 2? ( UFMT 765 , 3703 , 3704 , 3716 , 3718 , 3719 , 3964 , 3966 , 3975 , 3977-3979 , 3981 ; UFMT: TC 178 , 189 ) GoogleMaps ; São Felix do Xingu , 7°1’S, 52°21’W, 5 M, 3 F ( MPEG 42460 View Materials , 42721 View Materials , 42723 View Materials , 42725 View Materials , 42726 View Materials , 42728 View Materials , 42730 View Materials , 42793 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Santa Barbara , 1°12’26”S, 48°16’14”W, 6 M, 1 F ( MPEG: SBER 01 , 02 View Materials , 07 View Materials , 11 View Materials , 15 View Materials , 17 View Materials , 32 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; São Geraldo do Araguaia 6°23’S, 48°33’W, 2 M ( MNRJ 75242 View Materials , 75244 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Senador José Porfírio , 3°51’S, 51°51’W, 6 M ( MPEG 41851 View Materials , 41862 View Materials , 42447 View Materials , 42458 View Materials , 42459 View Materials , 42460 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Tucu-ruí, 3°42’S, 49°42’W, 1 F, 1 M ( MPEG 12296 View Materials , 12297 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Nova Área Experimental, Utinga, Belém , 1º27’S, 48º29’W, 1 F ( USNM 393532 About USNM , photograph of the holotype) GoogleMaps ; Utinga, Parque Ambiental de Belém , 1°25’33”S, 48°26’39”W, 6 M, 9 F, 1? ( MPEG 8787 View Materials , 12701 View Materials , 12960 View Materials , 15257 View Materials , 38654 View Materials , 38657 View Materials , 38658 View Materials , 38666 View Materials , 38667 View Materials , 38669 View Materials , 38671 View Materials , 39695 View Materials , 39697 View Materials , 39698 View Materials , 39706 View Materials ; MPEG: PAB 017 ) GoogleMaps ; Viseu , 1°10’58”S, 46°17’32”W, 1 M ( MPEG: VIS 45 ) GoogleMaps . Tocantins: Goiatins , 7°47’53”S, 47°16’40”W, 2 M, 1 F ( MNRJ 75121 View Materials , 75122 View Materials , 75136 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Ribeiro Gonçalves , 7°47’48”S, 47°16’47”W, 1 M, 2 F ( MNRJ 75117 View Materials , 75139 View Materials , 75140 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .
Others specimens examined: Marmosops parvidens ( n=34). BRASIL - Amazonas: Balbina , 1º53’S 59º28’W, 2 F ( MZUSP 22940 View Materials ; MPEG 22141 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Urucará , 2º23’S, 57º38’W, 2 M ( MPEG 40065 View Materials , 40068 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . Pará: Floresta Estadual Faro ( Flota Faro), left bank of Rio Nhamundá , 1°16’44”S, 58°2’24”W, 2 F, 4 M, 1? ( MPEG 39959 View Materials , 39963 View Materials , 30075 View Materials , 39976 View Materials , 39982 View Materials , 39984 View Materials ; MPEG: CN 080 ) GoogleMaps ; Óbidos, Flota Trombetas, 0°58’S, 55°31’W, 3 M, 4? ( MPEG 40401 View Materials , 40403 View Materials , 40404 View Materials ; MPEG: CN 182 , 186 View Materials , 207 View Materials , 210 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Oriximiná, Porto Trombetas , 1º49’S 56º30’W, 6 M, 6 F ( MPEG 39802 View Materials , 39807 View Materials , 40070 View Materials , 40074 View Materials , 42404 View Materials , 42422 View Materials , 42364 View Materials , 42372 View Materials , 42405 View Materials , 42424 View Materials , 42437 View Materials , 42441 View Materials ) GoogleMaps ; Terra Santa , 2°6’S, 56°29’W, 2 M, 1 F ( MPEG 40081-40083 View Materials ) GoogleMaps . GUYNA: “Hyde Park, 30 miles up the Demarara River,” Demerara-Mahaica ( FMNH 18545 About FMNH , photograph of the holotype) .
| UFMT |
Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso |
| MPEG |
Museu Paraense Emilio Goeldi |
| MZUSP |
Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo |
| MAR |
Grasslands Rhizobium Collection |
| MNRJ |
Museu Nacional/Universidade Federal de Rio de Janeiro |
| PL |
Západoceské muzeum v Plzni |
| UMS |
Universiti Malaysia Sabah |
| BRC |
Botanical Record Club |
| LMS |
Carolina Biological Supply Company |
| WET |
Wartburg College |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Marmosops ( Sciophanes ) woodalli ( Pine, 1981 )
| Ferreira, Claudilívia, Oliveira, Ana Cristina Mendes De, Lima-Silva, Luan Gabriel & Rossi, Rogério Vieira 2020 |
Marmosops pinheiroi :
| Voss, R. S. & Lunde, D. P. & Simmons, N. B. 2001: 49 |
Marmosa parvidens woodalli
| Pine, R. H. 1981: 62 |