Dryocosmus liui Pang, Su et Zhu, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4403.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:80438F5A-0097-464B-BB62-B06DA9A1792D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5950126 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C41F4E-8A22-F934-FF32-F97D1B71DAAF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Dryocosmus liui Pang, Su et Zhu |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Dryocosmus liui Pang, Su et Zhu , new species
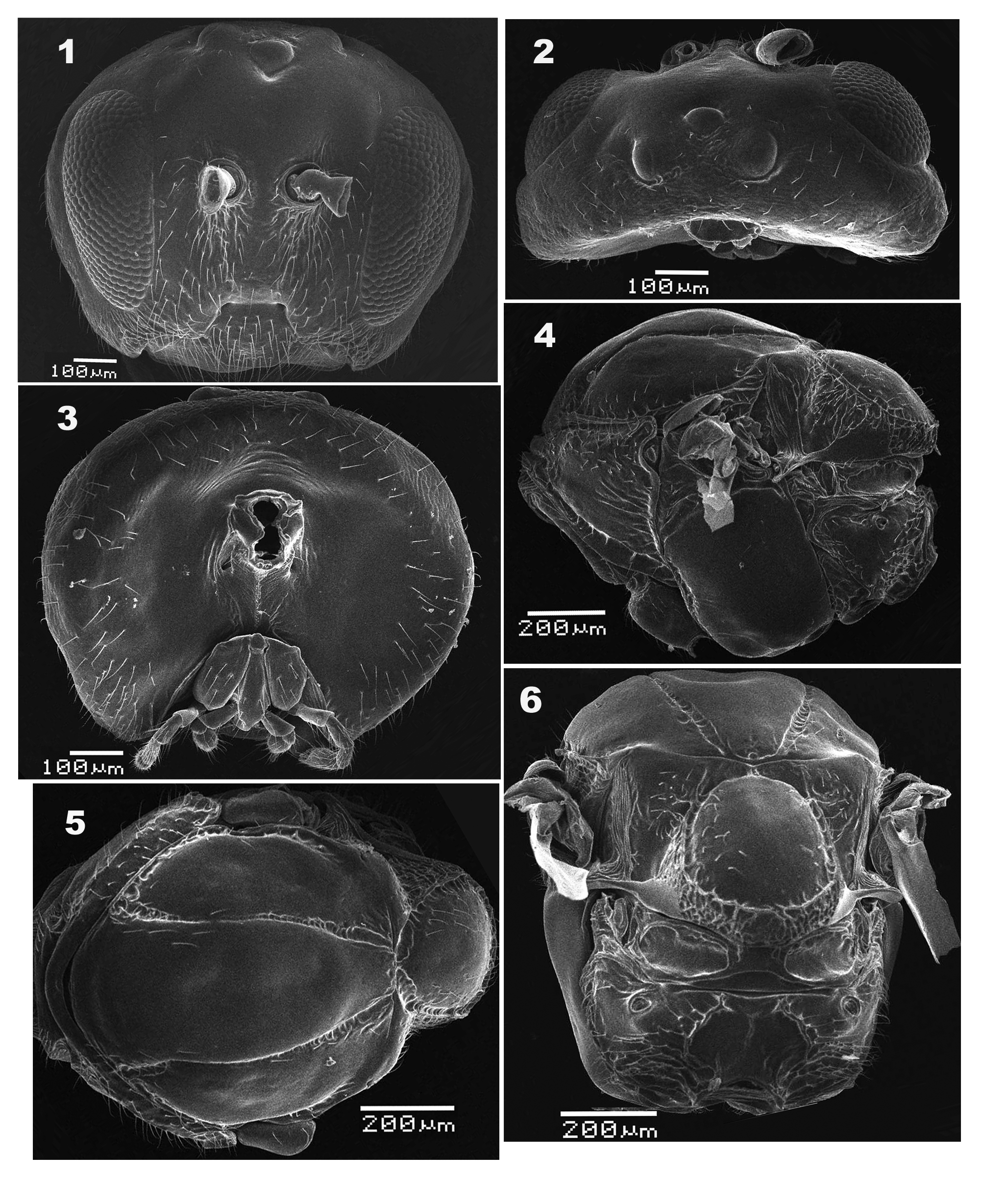
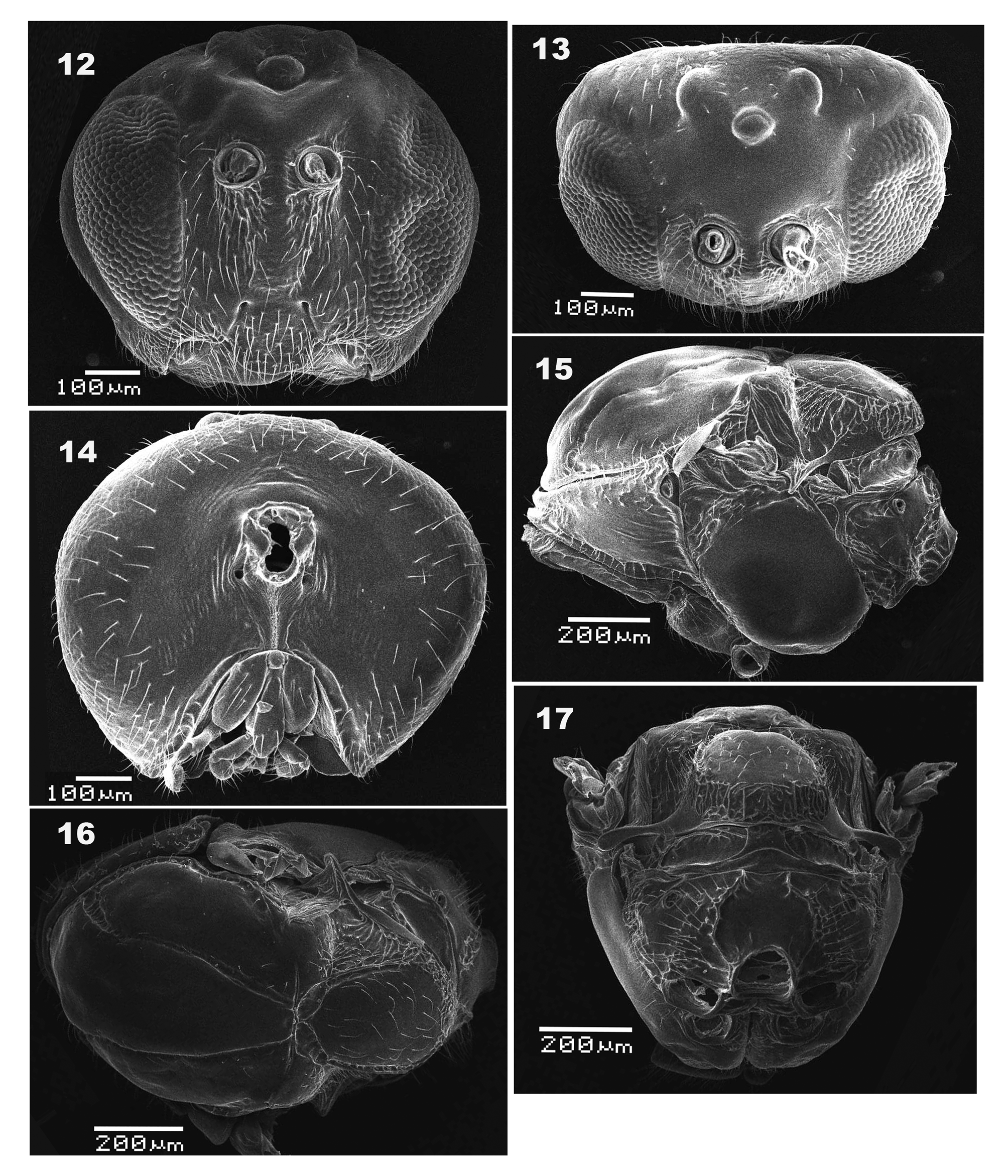
( Figures 1–17 View FIGURES 1-6 View FIGURES 7–11 View FIGURES12–17 )
Type materials. Holotype: ♀ Paratypes: 10♀♀, 10♂♂. CHINA, Hunan Province, Yanling County, 2017-III- 11 ~20, leg. Han-Qing Hou, Gao-Zhi Zhao, deposited in Insect Collection, Central South University of Forestry and Technology ( CSUFT), Changsha, Hunan .
Etymology. The species is named after Dr. Zhiwei Liu for his kind help and encouragement during this study, and for his significant contributions to the studies on systematics and evolution of Cynipoidea .
Diagnosis. The new species is most similar to Dryocosmus sefuriensis Ide , wachi et Abe, 2013, but can be easily distinguished from the latter by the following features. Firstly, radiating striae in lower face in the new species is mostly absent, traceable only between lower margin of compound eyes and clypeus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1-6 ), whereas in D. sefuriensis , radiating striae in lower face reach to lower margin of compound eye and antennal sockets ( Ide et al. 2013: Fig. 1a View FIGURES 1-6 ). Secondly, setae on lower face sparse and unevenly distributed, forming a denser band between antennal socket and tentorial pits in the new species ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1-6 ), but much denser and evenly distributed in D. sefuriensis ( Ide et al. 2013: Fig. 1a View FIGURES 1-6 ). Thirdly, clypeus is prominent and ventrally projected into a sub-rectangular lobe in the new species ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1-6 ), but not as prominent, ventrally forming a smoothly curved, short, and inverted trapeZoid projection in D. sefuriensis ( Ide et al. 2013: Fig. 1a View FIGURES 1-6 ). Lastly, in the new species, lateral propodeal carinae are distinct in anterior half and posteriorly indistinct, merged with the rugosity of propodeum, median propodeal carina is obsolete, and median propodeal area is glabrous, lacking submedian longitudinal carinae ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1-6 ). In comparison, D. sefuriensis has percurrent lateral and median propodeal carinae, as well as several submedian subparallel longitudinal carinae distinct posteriorly on dorsal propodeal area ( Ide et al. 2013: Fig. 1d View FIGURES 1-6 ).
Description. Female ( Figs. 1–10 View FIGURES 1-6 View FIGURES 7–11 ):
Body length 2.0– 2.1mm (n=10).
Head completely black. Antenna uniformly black, except for scape, pedicel and F1 dark brown and F2 dark brown at basal half and dark apically ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Mandible reddish brown, maxillar and labial palpi dark brown. Front legs with basal half of coxa, tibia, tarsomeres 1 and 5, and claw of front leg dark, and end of coxa, femur and tarsomeres 2–4 reddish brown; the other legs uniformly reddish brown, except dark tarsomere 5 and claw. Mesosoma black; metasoma mostly dark and ventrally reddish brown; ventral spine of hypopygium light yellow.
wing with distinct veins R+Sc, R1+Sc, R1, M, M+Cu1, Cu1, Cu1b, Cu1a, 2 r and Rs +M; areolet distinct and large; radial cell 4.3 times as long as wide; all visible veins dark brown ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7–11 ).
Head 1.25 times as wide as high, broader than mesosoma in front view and twice as broad as long in dorsal view. Gena slightly broadened behind eye in anterior view. Height of eye longer than length of malar space. Frons glabrate; lower face laterally with very weak striae radiating from clypeus to lower level of eyes; malar space glabrate. Lower face, malar space and clypeus somewhat setose. Clypeus distinct and impressed, ventrally projected into a sub-rectangular lobe; epistomal sulcus indistinct, indicated by a very subtle depression bordering ventral margin of central area of lower face; anterior tentorial pits small, but distinct; clypeo-pleurostomal line distinct. Transfacial distance longer than height of eye; distance between inner margin of eye and outer rim of antennal torulus slightly longer than distance between antennal toruli, but longer than diameter of torulus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1-6 ). Posterior ocelli separated from each other narrowly, ratios of POL/OOL, POL/LOL, and LOL/OOL 1.25, 3.13 and 0.4, respectively; in dorsal view, posterior margin of anterior ocellus almost aligned with anterior margin of posterior ocelli ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1-6 ). Vertex and interocellar area coriarious to finely reticulate; vertex and gena coriarious, with scattered setae behind eye ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1-6 ); postgena mostly glabrate with scattered setae; occiput very finely imbricate; occipital carina distinctly present below level of middle of occipital foremen. Gular sulci distinct; posterior tentorial pits distinct. Area around occipital foramen impressed and glabrous ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1-6 ). Antenna filiform with 12 flagellomeres, slightly tapering toward apex; pedicel 1.62 times as long as broad; relative lengths of scape, pedicel and F1–F12: 7:13:20:25:18:12:15:15:14:13:13:13:12:20; placoid sensillae distinctly visible on F2–F12.
Mesosoma longer than high in lateral view. Pronotum median length is one eighth of length of outer lateral margin. Anterior plate of pronotum glabrate medially and sparsely setose laterally; lateral pronotal carina distinct and present only in posterior half area ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1-6 ). Mesoscutum longer than width measured at anterior tip of tegulae, surface mostly distinctly strigate-rugose in posterior half, with some small foveae and setae; notauli distinct and complete, slightly broader anteriorly than posteriorly. Mesoscutellum broader than long, with a row of foveae along lateral margin. Scutellar foveae deeply impressed and glabrous, separated by a median carina. Mesopleuron smooth and glabrate; mesopleural triangle rugulose. Metapleural sulcus reaching mesopleuron in upper 2/3 of its height; metapleuron glabrate medially, with sparse setae and some foveae along margins ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1-6 ). Dorsellum glabrous, as long as ventral impressed area. Propodeum with sparse appressed setae; lateral propodeal carinae distinct anteriorly and indisctict posteriorly, median propodeal carina obsolete; median propodeal areas glabrate, lateral propodeal areas with sparse appressed setae and irregular wrinkles posteriorly ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1-6 ). Nucha short, 3.3 times as wide as long in lateral view, and sulcate ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1-6 ).
Metasoma 1.2 times as long as high in lateral view; abdominal tergite II 1.9 times as high as long in lateral view, laterally with a median row of long setae; tergite VIII posteriorly with long setae. Prominent part of hypopygium slender, distally not pointed, 3.5 times as long as basal width, and ventrally with a row of long setae ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7–11 ).
Male ( Figs. 11–17 View FIGURES 7–11 View FIGURES12–17 ). Similar to female, but different as below. Antenna with 13 flagellomeres, length of scape 2.8 times as long as wide; pedicel 1.5 times as long as broad. F1 strongly curved medially, 2.5 times as long as pedicel and as same long as F2; length of scape including constricted base, pedicel, and F1– F13:11:6:15:15:12:12:11:11:11:11:11:11:10:9:8. Placoid sensillae distinctly visible on F2–F13, increasing in number per segment distally.
Biology. Bisexual, with sex ratio of adults=1: 1 (n> 400). All specimens were emerged from galls collected from Castanopsis tibetana . The elliptic to globular and multi-chambered galls are formed on young branches and twigs, and are highly lignified ( Figs. 18, 19 View FIGURES 18–19 ). Gall siZe: about 15–45 mm in width by 18–55 mm in length. Adults were reared in mid-March from galls collected in early March.
Distribution. Currently known only from Yanling County, Hunan Province, China.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |