Campodelphys seticoxus, Kim & Boxshall, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/megataxa.4.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5728105 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C487CB-ED06-386F-FF4D-F8BDFD45FDDD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Campodelphys seticoxus |
| status |
gen. et sp. nov. |
Campodelphys seticoxus gen. etsp. nov.
( Figs. 404 View FIGURE 404 , 405 View FIGURE 405 )
Type material. Holotype ♀ (dissected and mounted on a slide, MNHN-IU-2014-21435 ) from Eudistoma reginum Kott, 1991 (MNHN-IT-2008-4187 = MNHN A3/EUD/75), CRRFOCDN 1434-S, Manado, north Sulawesi, Indonesia, depth 60 m, 21 May 1993.
Etymology. The specific name refers to the presence of the inner seta on the coxa of leg 4.
Descriptionoffemale. Body ( Fig. 404A View FIGURE 404 ) slender, cylindrical, slightlycurvedventrally;bodylength2.10mm. Prosome unsegmented; anterior fifth tapering anteriorly and posterior third tapering posteriorly; anterior region from rostrum to level of leg 4 occupying about one-third of length of prosome. Cephalosome ( Fig. 404B View FIGURE 404 ) defined from metasome by weak lateral constriction, bearing prominent paired tubercles posterolaterally on ventral surface. Freeurosome ( Fig. 404C, D View FIGURE 404 ) 5-segmented, strongly curved ventrally. Genital somite narrower than anterior abdominal somites.Anal somite ornamented with row of spinules along posteroventral margin ( Fig. 404E View FIGURE 404 ). Caudal ramus ( Fig. 404E View FIGURE 404 ) as long as anal somite and twice as long as wide (45×22 μm): armed with 6 naked setae (1 outer lateral, 1 dorsal, and 4 distal) and ornamented with scattered stiff setules.
Rostrum ( Fig. 404B View FIGURE 404 ) directed anteroventrally, tipped with narrow tubercle. Antennule ( Fig. 404F View FIGURE 404 ) short and broad, 75 μm long, divisible into 5 segments by 4 partial articulations on posterior surface; first segment bearing 2 setae, setation of other segments not discernible due to dense packingof setae.Antenna ( Fig. 404G View FIGURE 404 ) 3-segmented, consisting of coxa, basis, and unsegmented endopod; basis about 1.7 timeslongerthan wide, unarmed; endopod about 2.3 times longer than wide (27×12 μm); armed with 8 smallsetae (arranged as 3, 2, and 3), plus terminal claw aslongas endopod.
Labrum missing. Mandible ( Fig. 404H View FIGURE 404 ) with narrow coxal gnathobase; medial margin of gnathobase pectinate, with 2 denticles distally (distal denticle much smaller than subdistal); palp armed with 1 setaon basis, 4 on exopod, and 1 and 4 on first and second endopodal segments, respectively; all setae naked. Maxillule ( Fig. 404I View FIGURE 404 ) as digitiform lobe bearing 7 pinnate setae (2 medial, 3 distal, and 2 outer). Maxilla ( Fig. 404J View FIGURE 404 ) as tapering lobe bearing 6 pinnate setae (3 medial, 2 distal, and 1 outer). Maxilliped ( Fig. 404K View FIGURE 404 ) unsegmented with 2 small, proximally-directed setae subapically.
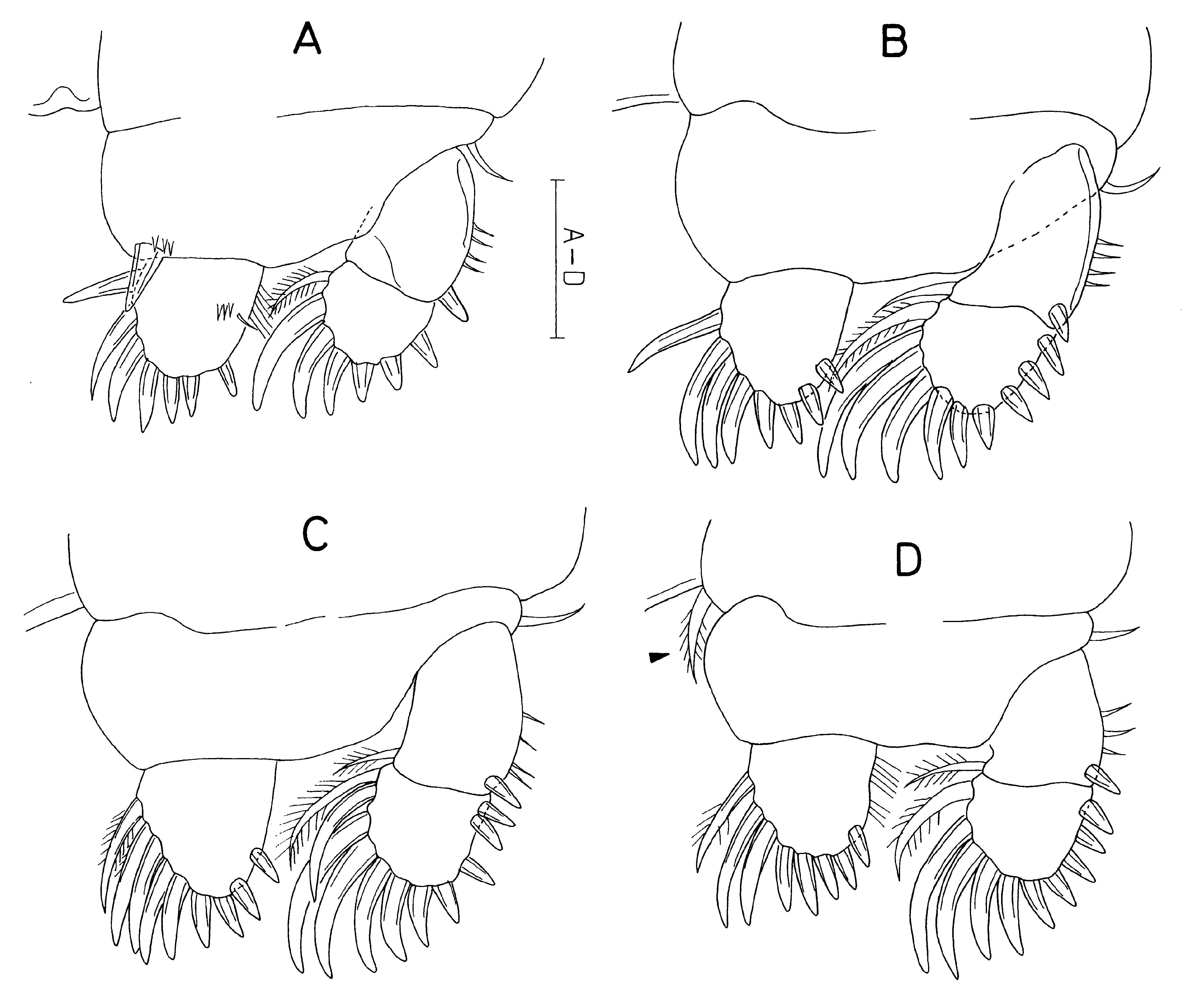
Legs 1–4 ( Fig. 405 View FIGURE 405 A-D) biramous, each with incompletely 2-segmented protopod, 2-segmented exopod, and unsegmented endopod. Coxa of leg 4 characteristically with inner seta (indicated by arrowhead in Fig. 405D View FIGURE 405 ). Basis of legs 1–4 with outer seta. Basis of leg 1 with spiniform inner distal seta. First exopodal segment of legs 1–4 with 3 or 4 thick setules on outer margin. Setae on rami spiniform and usually blunt, but 2 proximal setaeon exopods of legs 2–4 pinnate and attenuate. Armature formula for legs 1–4 as follows:
| Coxa | Basis | Exopod | Endopod | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leg 1 | 0-0 | 1-1 | 1-0; 7 | 6 (or 7) |
| Leg 2 | 0-0 | 1-0 | 1-1; 10 | 8 |
| Leg 3 | 0-0 | 1-0 | 1-1; 11 | 9 |
| Leg 4 | 0-1 | 1-0 | 1-1; 10 | 8 |
Leg 5 ( Fig. 404C, D View FIGURE 404 ) represented by 2 small setae on posteroventral surface of prosome.
Male. Unknown.
Remarks. Campodelphysseticoxus gen. etsp. nov. resembles C. ancylocephalus gen. et sp. nov. in having unsegmented endopods in all swimming legs and an inner distal seta on the basis of leg 1. However, they differ in the numbers of setaeon the maxillule, maxilla, maxilliped, and swimming legs. It is noteworthy that the presence of the inner seta on the coxa of leg 4 of C. seticoxus gen. et sp. nov. is a unique feature within the genus.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.