Thysanozoon brocchii (Risso, 1818) Grube, 1840
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.37828/em.2016.9.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8033349 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CD8799-FFC0-E573-FF2C-FC0C464FF8E1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Thysanozoon brocchii (Risso, 1818) Grube, 1840 |
| status |
|
Thysanozoon brocchii (Risso, 1818) Grube, 1840 View in CoL View at ENA
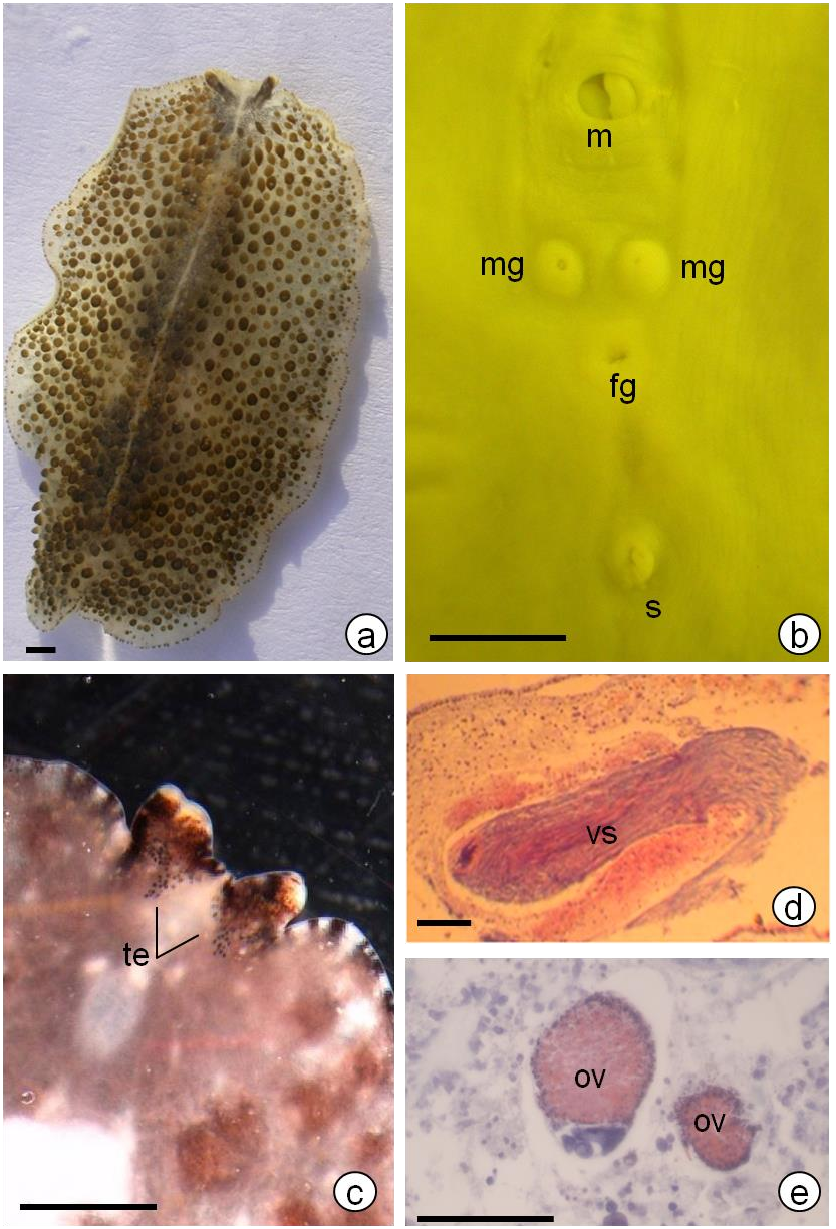
General features. This polyclad is broadly oval shaped. It uses undulations of its body margins to swim actively. The dorsal face is cream to brownish and provided with several black papillae. The number and size of papillae decrease going from median region to the marginal zone ( Fig. 4a View Figure 4 ). Some papillae are provided with a white spots. Tentacles are developed and appear as expansion of anterior margin. They contain two clusters of marginal eyes ( Fig. 4c View Figure 4 ). Behind marginal eyes, are located in the median region, the two semicircular clusters of cerebral eyes. The ventral surface is whitish and transparent and shows a ruffled pharynx located in the first third of body. In ventral surface of fixed specimens, different prominent structures are located in the anterior half of body ( Fig. 4b View Figure 4 ). The mouth opens in the posterior part of pharyngeal cavity. Two symmetric male gonopores are situated in the same horizontal level and in both side of median line of body. A unique female gonopore lies behind the two male gonopores. Posteriorly, is located a developed sucker characteristic of cotylea sub-order ( Fig. 4b View Figure 4 ).
Reproductive apparatus. The testes follicles are numerous and located more in the ventral parenchyma then in dorsal one. The ovaries are less numerous and bigger in size than testes ( Fig. 4e View Figure 4 ). They are located in the dorsal and median parenchyma. There are two male copulatory apparatus. Each male gonopore leads to a male atrium in which is projected a penis papillae armed with stylet. The penis papillae are surrounded by a penis sheath. The ejaculatory duct leads to elongated seminal vesicle filled usually with sperm ( Fig. 4d View Figure 4 ). A free prostatic vesicle is connected to the ejaculatory duct via a narrow prostatic canal. The eosinophilous secretions are detected in the two prostatic canals and in male atrium. The single female apparatus comprise a narrow female atrium that extends vertically to form a widened chamber corresponding to cement pouch characteristic of cotylea sub-order. The vagina curve then anteriorly where is located the entrance of oviducts to form a section oriented anteriorly.
Habitat. The two specimens of Thysanozoon brochhii were collected from a depth of 16 m among a dense sea grass meadows of of Posidonia oceanica (Linnaeus) Delile extended in rocky substrate. These flatworms were found associated with the sponge Dysidea tupha , the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus , the crustacean Achaeus cranchii Leach, 1817 and the bryozoans Electra posidoniae Gautier, 1954 . Thysanozoon brocchii is a good swimmer. It move using undulations of its flat body.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |