Rapisma gaoligongensis, Liu & Li & Yang, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4531.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:56BE37A6-16B7-4608-BAF6-8BB529DD2924 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5977317 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CE87E5-B42C-FFC4-FF1E-FD15FAE9FDEC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rapisma gaoligongensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Rapisma gaoligongensis sp. nov.
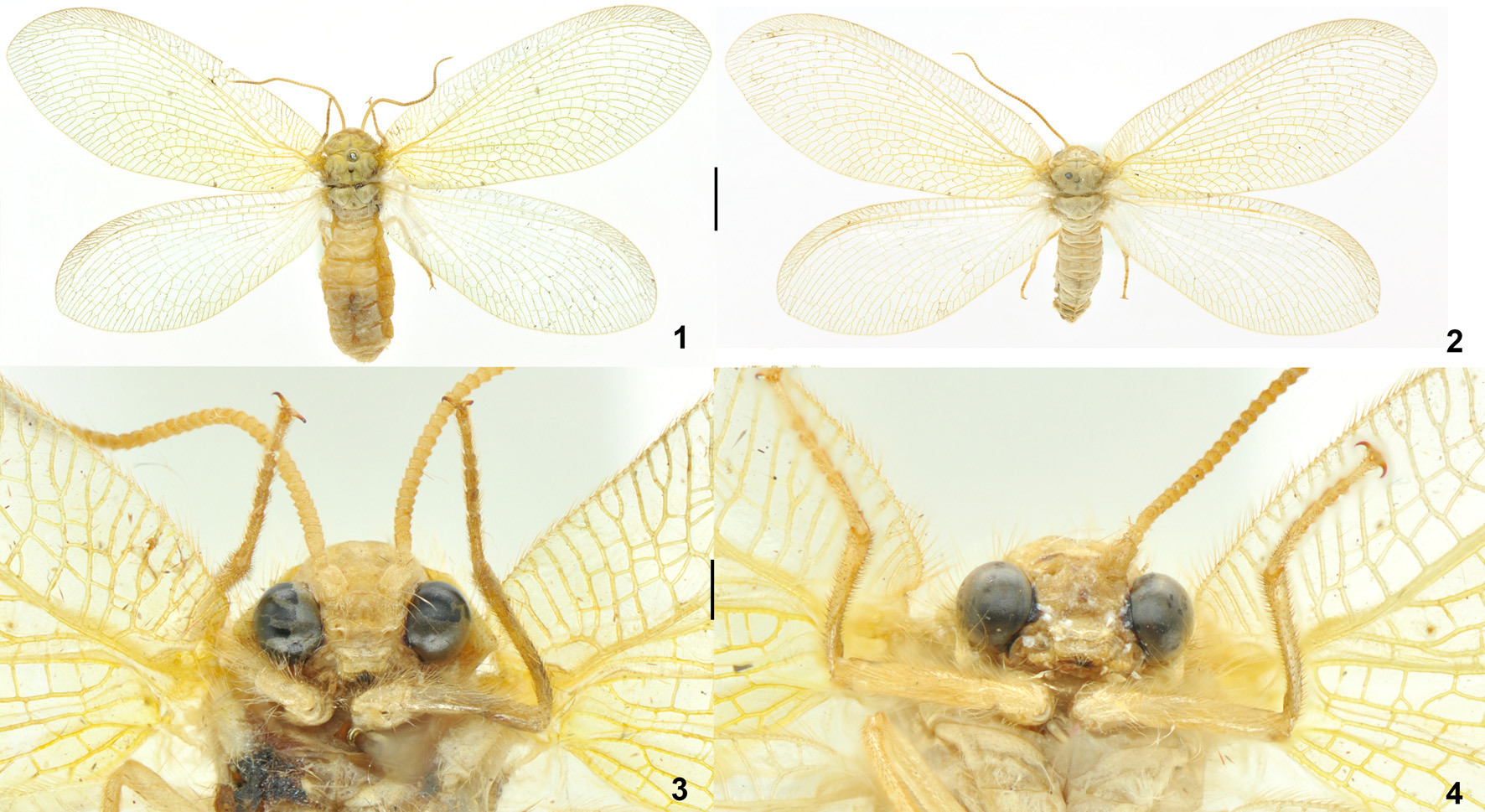
( Figs. 1–8 View FIGURES 1–4 View FIGURES 5–8 )
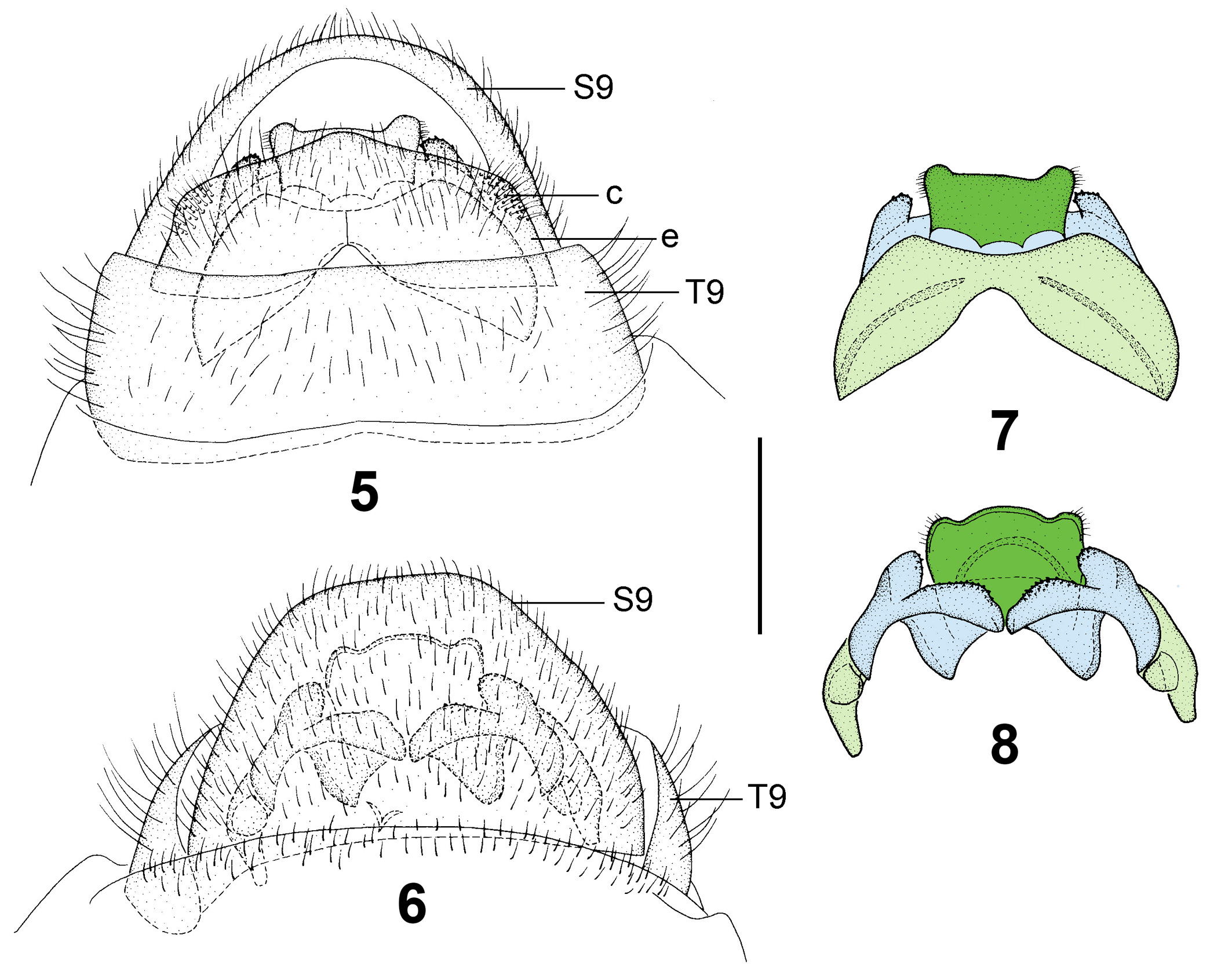
Diagnosis. Body and forewings generally yellowish green. Forewing with sparse small grayish spots. Male head immaculate. Antenna subserrate, ~1/2× forewing length. Male gonocoxites 9 paired, covered with many short spines; each with a banana-shaped lobe, which laterally bears a short, ovoid projection and dorsally bears a flat, subtriangular accessory lobe, and with a short, arcuately curved lateral arm; fused gonocoxites 11 generally arched, in dorsal view anteromedially strongly concaved, leaving a pair of broadly foliate lobes, posteromedially slightly concaved; gonostyli 11 fused, subquadrate, bearing short setae, laterally with a pair of obtuse processes.
Description. Male. Body length 16.7–20.0 mm; forewing length 27.2–27.6 mm, hindwing length 23.5–24.2 mm.
Head nearly semiglobular, largely retracted under prothorax, invisible in dorsal view. Head yellowish throughout. Compound eyes blackish brown; EI ratio 0.80–0.88. Antenna subserrate, 12.3–13.1 mm long, with 56–60 flagellomeres; yellowish, but flagellomeres on distal half of flagellum slightly darker. Mandibles with tips black.
Thorax yellowish; meso- and metanotum each laterally with two pairs of pale grayish markings on scutum and a pale grayish spot on scutellum. Legs yellowish; pretarsal claws reddish brown, proximally slightly produced.
Forewing yellowish green, with sparse small grayish spots. Trichosors present only along costal margin. A proximal nygma present between RP+MA and MP, grayish. RP with 8–10 pectinate branches. Hindwing much paler than forewing, immaculate. A proximal nygma present between RP+MA and MP, grayish. RP with 5–6 pectinate branches.
Abdomen yellowish throughout. Tergum 9 nearly rectangular, moderately setose. Sternum 9 about twice as long as but narrower than tergum 9, subtrapezoidal. Ectoprocts slightly shorter and much narrower than tergum 9, medially slightly prominent in dorsal view; callus cerci present, somewhat prominent. Gonocoxites 9 paired, covered with many short spines; each with a banana-shaped lobe, which laterally bears a short ovoid projection and dorsally bears a flat subtriangular accessory lobe, and with a short, arcuately curved lateral arm. Fused gonocoxites 11 generally arched, in dorsal view anteromedially strongly concaved, leaving a pair of broadly foliate lobes, and posteromedially slightly concaved. Gonostyli 11 fused, subquadrate, bearing short setae, laterally with a pair of obtuse processes. Hypandrium internum very small, arrow-shaped, with slender lateral lobes.
Female. Unknown.
Material examined. Holotype male, CHINA, “ Dian [= Yunnan], Baoshan City, Longyang District , Gaoligongshan , Nankang ; habitat: tropical rain forest; method: light trap; N: 24°50’03.0’’ E: 98°46’10.9’’; Alt. 2097 m, 2014-VII-25, YANG Zizhong et al. leg.” ( CAU) . Paratype: 1 male, CHINA, “ Dian [= Yunnan], Baoshan City, Longyang District , Gaoligongshan , Nankang Wild Station , 2014-VII-24, FENG Rui et al. leg.” ( CAU) .
Etymology. The new species is named after its type locality, i.e. Mt. Gaoligongshan, which is one of the hot spots of biodiversity in China.
Distribution. China (Yunnan).
Remarks. The new species appears to be closely related to Rapisma daianum Yang, 1993 from southern Yunnan, China, and Rapisma corundum Barnard, 1981 from eastern Myanmar in having the following shared characteristics: head immaculate and similar configuration of male gonocoxite 9. However, the new species can be distinguished from the latter species in detailed features of male gonocoxite 9 and the fused male gonostyli 11. In R. gaoligongensis sp. nov. the medially directed part of gonocoxite 9 is feebly prominent posteriad and is not strongly narrowed at tip, and the fused gonostyli 11 is distinctly prominent laterally as a pair of obtuse processes. But, in R. daianum and R. corundum the medially directed part of gonocoxite 9 is distinctly prominent posteriad and is strongly narrowed and curved anteriorly; and in addition, the fused gonostyli 11 lacks lateral processes (see Liu 2018: fig. 5; Barnard 1981: fig. 21). Moreover, the hypandrium internum in R. gaoligongensis sp. nov. is much smaller than that in R. daianum and R. corundum , which also may be a diagnostic character of the new species, however, the variation in this genital sclerite among individuals of same species of Rapisma is poorly known.
| CAU |
China Agricultural University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |