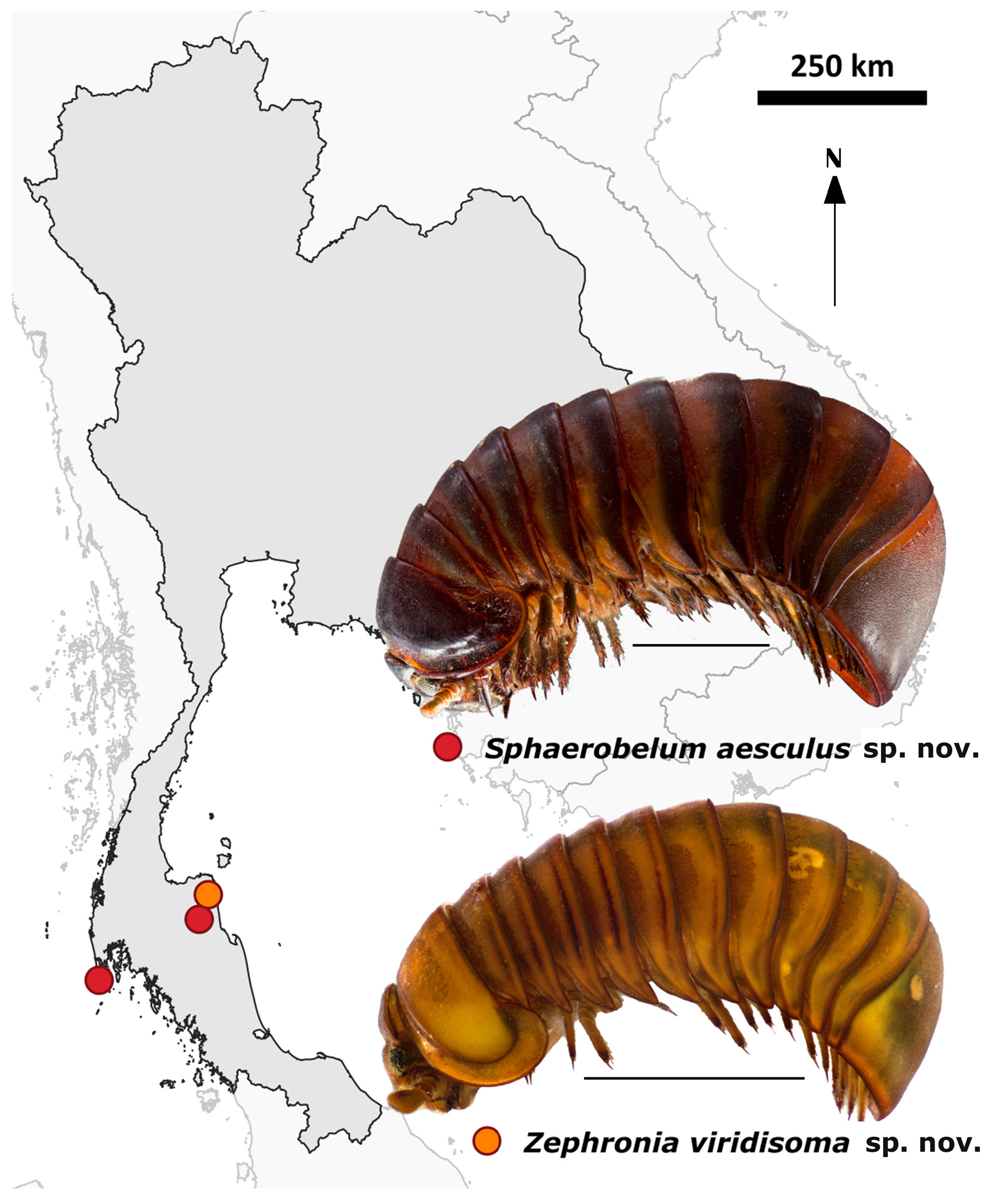
Zephronia viridisoma Rosenmejer & Wesener, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2021.762.1457 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:253B791F-78FF-42AC-8047-E92449BA4E47 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5213033 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/272E06C8-2DE5-4722-A7D5-D85002D68424 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:272E06C8-2DE5-4722-A7D5-D85002D68424 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Zephronia viridisoma Rosenmejer & Wesener |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Zephronia viridisoma Rosenmejer & Wesener View in CoL sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:272E06C8-2DE5-4722-A7D5-D85002D68424
Figs 2B View Fig , 6B View Fig – 12 View Fig
Diagnosis
Posterior telopod typical for the genus, not differing from those of other Zephronia species. Small (25– 28 mm long) green species ( Fig. 2B View Fig ), surface appearing glabrous, dull, with a single medium sized locking carina at the anal shield and a strongly projecting pleurite 1 ( Fig. 9A View Fig ). One of the few Zephronia species with just a single apical spine on the legs ( Fig. 9B View Fig ), differing in this character from all other described Thai Zephronia species which have 2–5 apical tarsal spines. Male antennomere 6 swollen ( Fig. 7A View Fig ) but not axe-shaped, with <50 apical cones. Endotergum with three dense rows of long marginal setae ( Fig. 6B View Fig ). Palpi of gnathochilarium with sensory cones arranged in clusters ( Fig. 8C–D View Fig ). Anterior telopod podomere 3 with an elevated process at posterior side carrying sclerotized teeth. Podomere 4 short and narrow.
Derivatio nominis
Named after the overall green colour of living individuals of the species, noun in apposition.
Material examined
Holotype THAILAND • ♂; Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, Sichon District, Khao Lark Waterfall ; 9°03′6″ N, 99°47′24″ E; 25 Aug. 2007; Chulalongkorn University expedition of millipede workshop leg.; dense jungle on limestone; NHMD 621695 . GoogleMaps
Paratypes THAILAND • 2 ♂♂, 4 ♀♀; same collection data as for holotype; NHMD 621696 GoogleMaps • 1 ♂; same collection data as for holotype; ZFMK MYR8786 About ZFMK GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; same collection data as for holotype; CT scan voucher; ZFMK MYR8787 About ZFMK GoogleMaps .
Description (based on holotype)
SIZE. Length 25.6 mm. Width of thoracic shield 12.1 mm, of widest segment (8) 13 mm. Height of thoracic shield 7.1 mm, of highest segment (8) 7.7 mm.
COLOUR. Head medium brown, faded from green. Antennae medium brown. Legs medium brown, tarsal claws apically dark brown. Tergites light brown, faded green medially, with darker brown posterior margin. Paratergite tips medium brown with darker edges. Anal shield dark green, edges faded to brown ( Fig. 2B View Fig ).
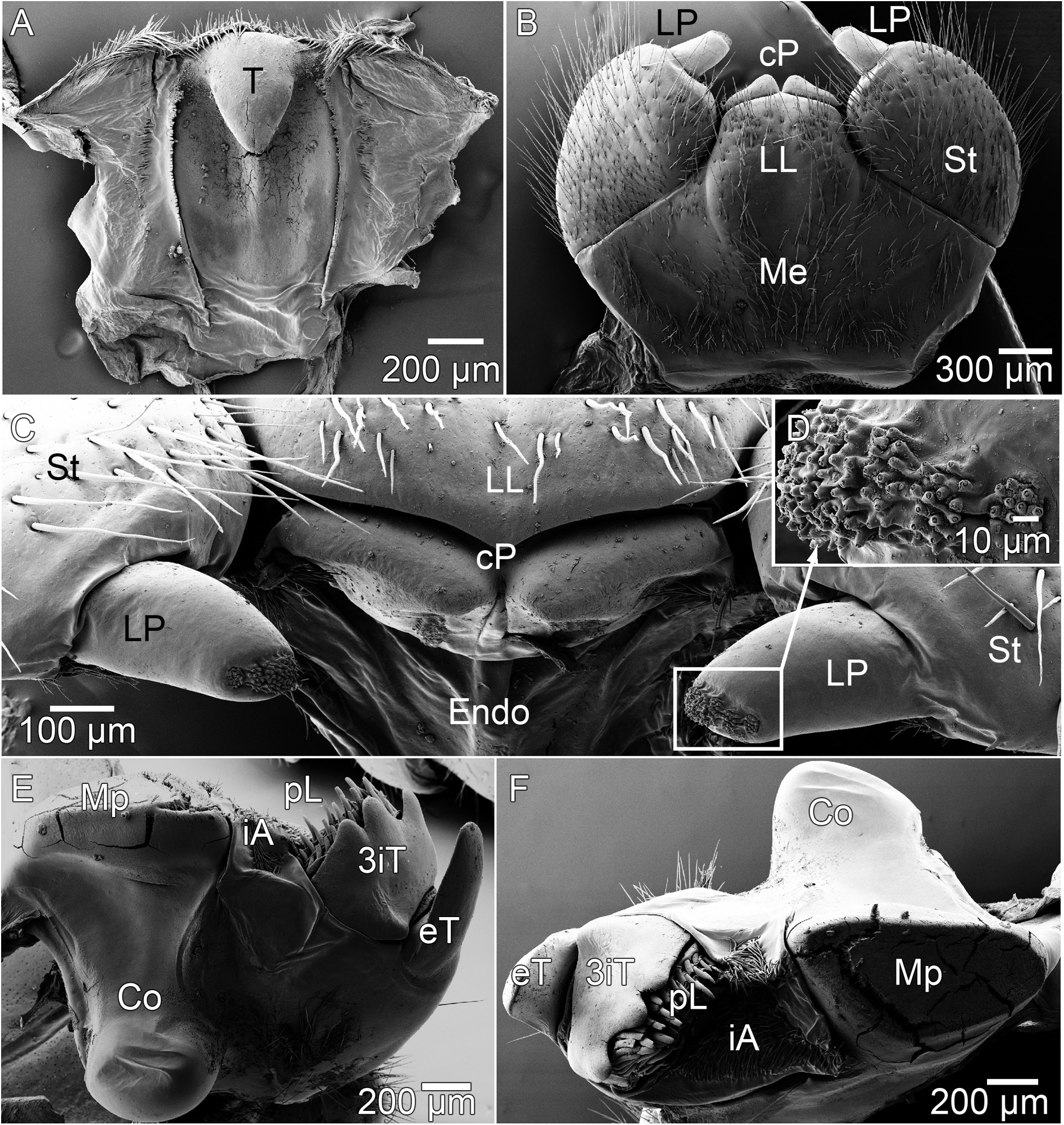
HEAD ( Fig. 7A–C View Fig ). Number of ommatidia 50 ( Fig. 7B View Fig ). Organ of Tömösváry placed midway between ocelli and antennal groove ( Fig. 7A View Fig ), with its typical coral-like inner structure ( Fig. 7C View Fig ).
ANTENNAE ( Fig.7A,D View Fig ). Reaching leg pair3,6visible antennomeres.Antennomere lengths:6>1>2=3>4=5. Antennomere 6 apically swollen, number of apical cones 32/44.
EPIPHARYNX ( Fig. 8A View Fig ). With an extraordinarily large inner tooth.
MANDIBLE ( Fig. 8E–F View Fig ). Inner tooth 3-cusped. Pectinate lamellae with 6 or 7 rows of teeth. Condylus at anterior margin with two ridges.
GNATHOCHILARIUM ( Fig. 8B–D View Fig ). Lamellae linguales with numerous long setae, medially glabrous. Stipes and mentum with numerous long setae in a regular patter. Sensory cones on gnathochilarium palps in clusters ( Fig. 8D View Fig ).
COLLUM. With short setation, evenly distributed across surface.
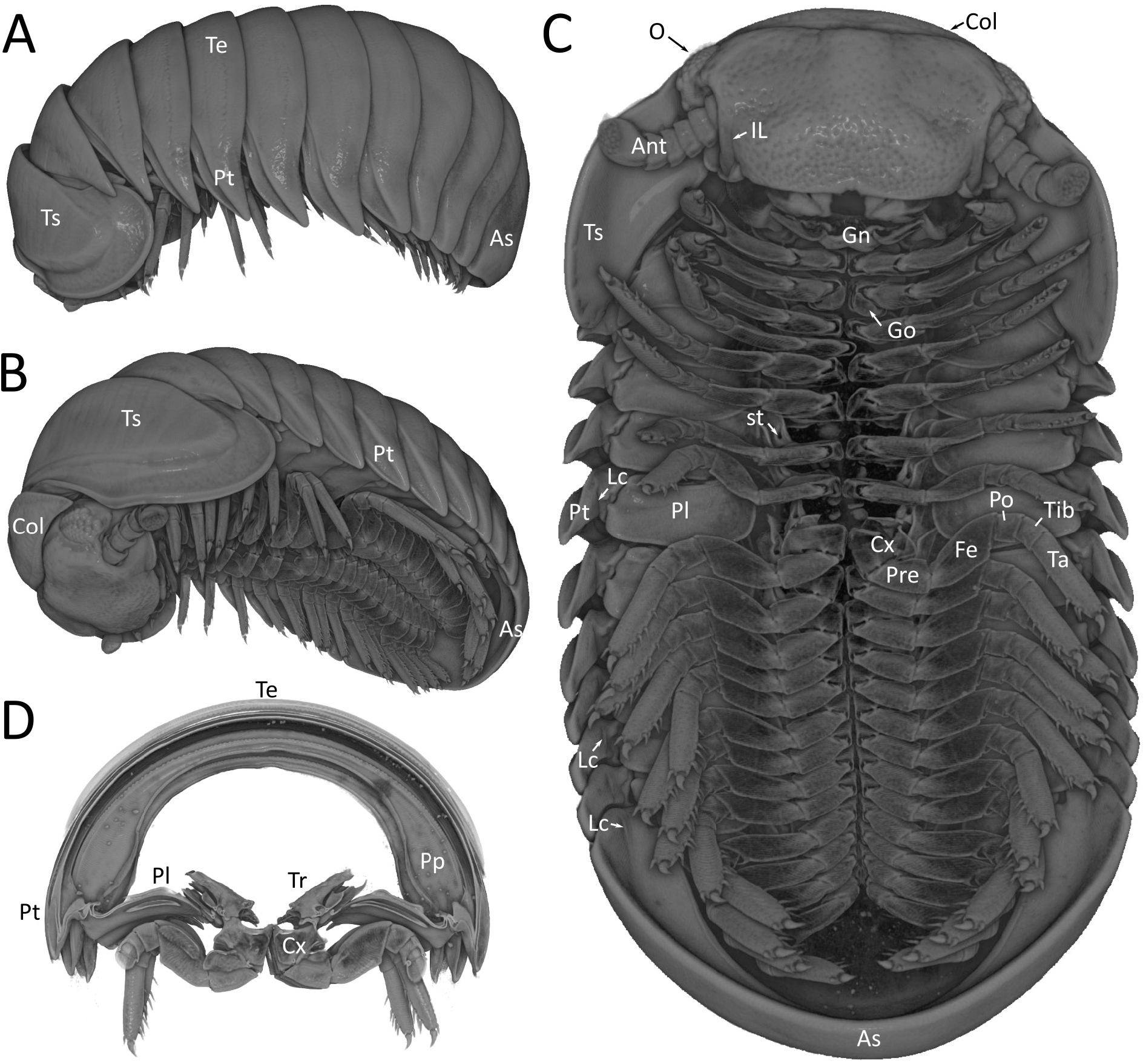
THORACIC SHIELD. Thoracic shield grooves wide and deep, with 9 sclerotized ledges along inner ridge of grooves.
TERGITES ( Fig. 9D View Fig ). Tergites glabrous, with dull orange skin like surface. At high magnification tiny setae and knobs become visible. Paratergite tips on posterior half projecting backwards ( Fig. 12A–B View Fig ).
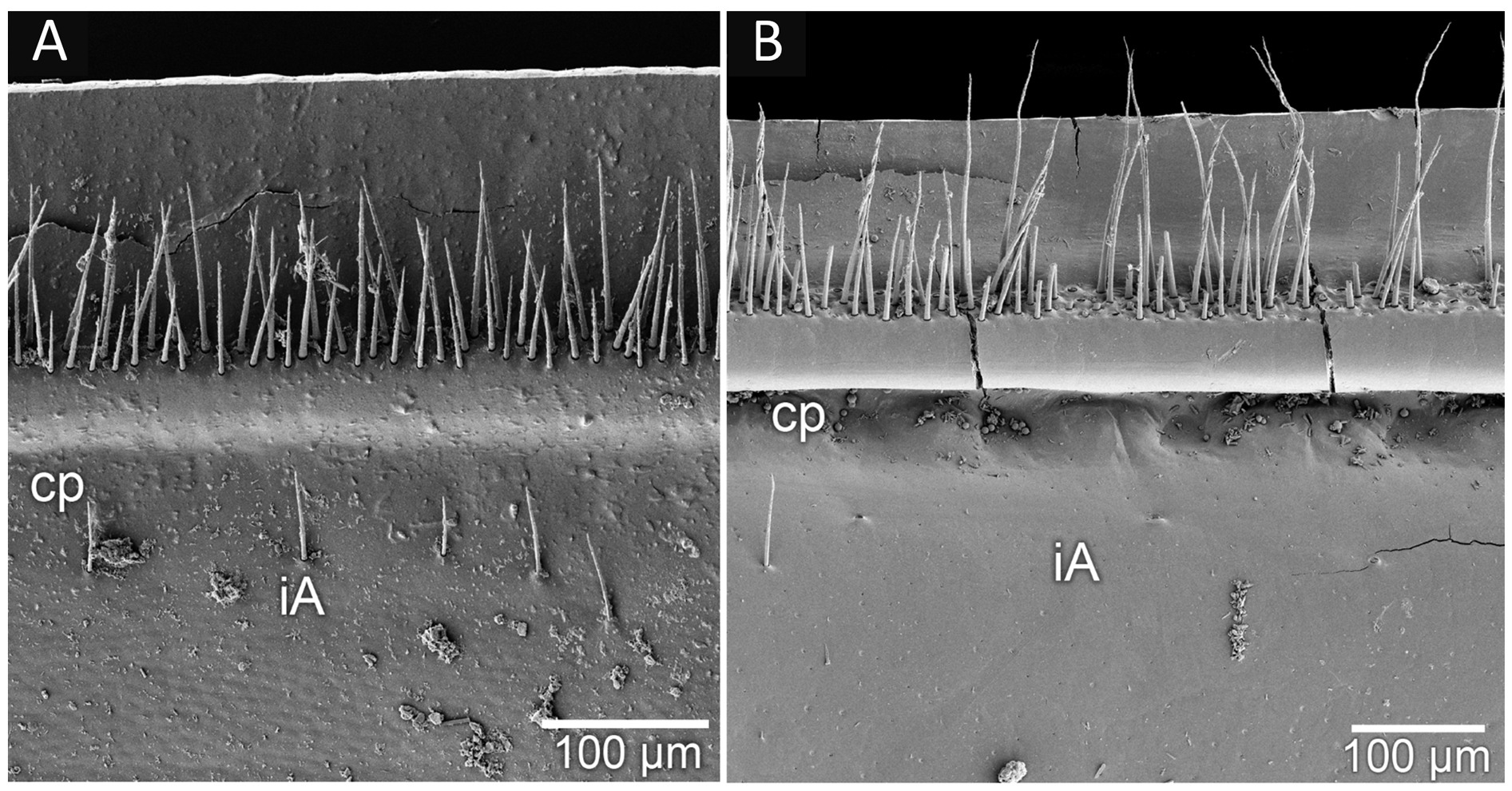
ENDOTERGUM ( Fig. 6B View Fig ). With a regular flat margin. Outer zone with three dense rows of irregular marginal setae, some of them extending beyond posterior margin. A single row of rounded cuticular impressions present next to marginal ridge. Intersegmental membrane smooth, without cones and with very few setae.
STIGMATIC PLATE ( Fig. 10A View Fig ). First plate with a rounded sub-triangular apex. More posterior plates similar to those of other representatives of the family, half-covered by the pleurites ( Fig. 12C View Fig ).
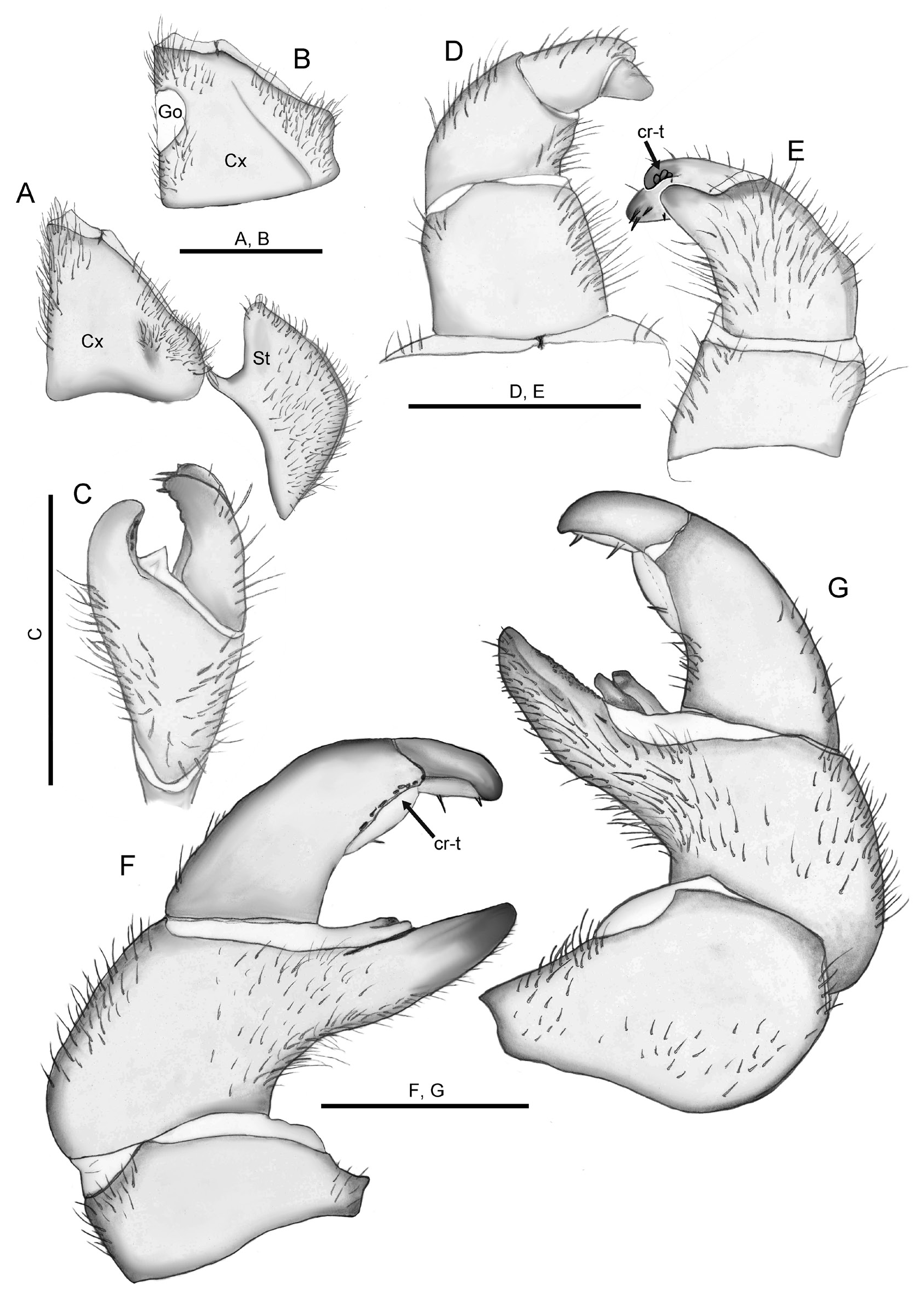
PLEURITES ( Figs 9A View Fig , 12D View Fig ). Pleurite 1 projecting strongly, with sharp apex. Pleurite 2 projecting slightly less than 1 and with more rounded apex ( Fig. 12D View Fig ). Projection absent from pleurite 3 ( Fig. 12D View Fig ).
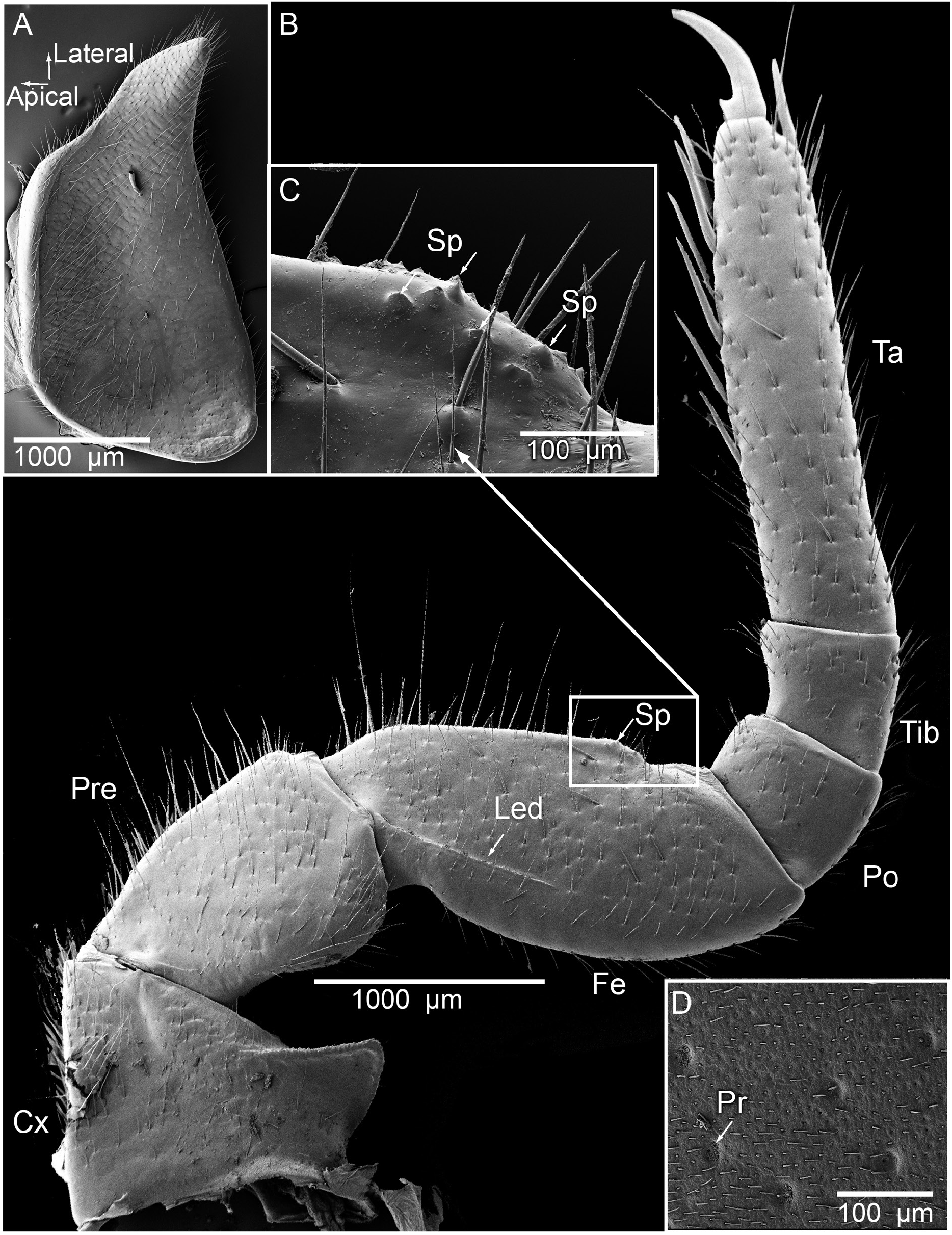
LEGS. Ventral spines on leg 1 1/1, on leg 2 3/2, on leg 3 4/4. Apical spine on leg 3 absent. A single apical spine and 5 or 6 ventral spines on midbody legs ( Fig. 9B View Fig ). Femur regularly shaped, 2.2 times longer than wide, sclerotized ledge of medium length, inner margin apically with 5 or 6 small rounded triangular spines on ventral side ( Fig. 9B–C View Fig ). Tarsus 4.2 times longer than wide.
ANAL SHIELD. Well-rounded and glabrous. Ventral side with dark coloured. A medium-sized locking carina placed slightly closer to pleurite than margin ( Fig. 12D View Fig ).
MALE GONOPORE ( Fig. 10B View Fig ). Inconspicuous, consisting of large membranous opening located directly at mesal margin.
ANTERIOR TELOPODS ( Fig. 10C–E View Fig ). With long setae medially on the first 2 podomeres, covering posterior part on podomere 2. Podomere 1 rectangular, as long as wide. Podomere 2 in anterior view as wide as but slightly narrower than podomere 1. Immovable finger barely visible in anterior view ( Fig. 10D View Fig ), short, not protruding up to podomere 4 ( Fig. 10C View Fig ). Podomere 3 long and wide, with rounded projection on posterior side, bearing 3 crenulated teeth. Podomere 4 very narrow and short, with 3 large spines near apex, and a smaller spine near edge to podomere 3.
POSTERIOR TELOPODS ( Fig. 10F–G View Fig ). Podomere 2 setose, immovable finger straight, apically tapering, with rows of small circular sclerotized spots. Membranous lobe between podomere 3 and 4 bearing 2 elongated processes, fused at base. Podomere 3 with 8 or 9 small crenulated teeth on posterior side. Membranous lobe on podomere 3 with single spine. Podomere 4 slightly curved towards immovable finger, membranous lobe with 2 spines. Setation on podomere 2 primarily on anterior side.
Description of female paratype
Length 25.6 mm. Width of thoracic shield 12.3 mm, of widest tergite (8) 13.7 mm. Height of thoracic shield: 8.4 mm, of highest tergite (8) 9.3 mm. Antennae reaching leg pair 3. Apical cones left/right:
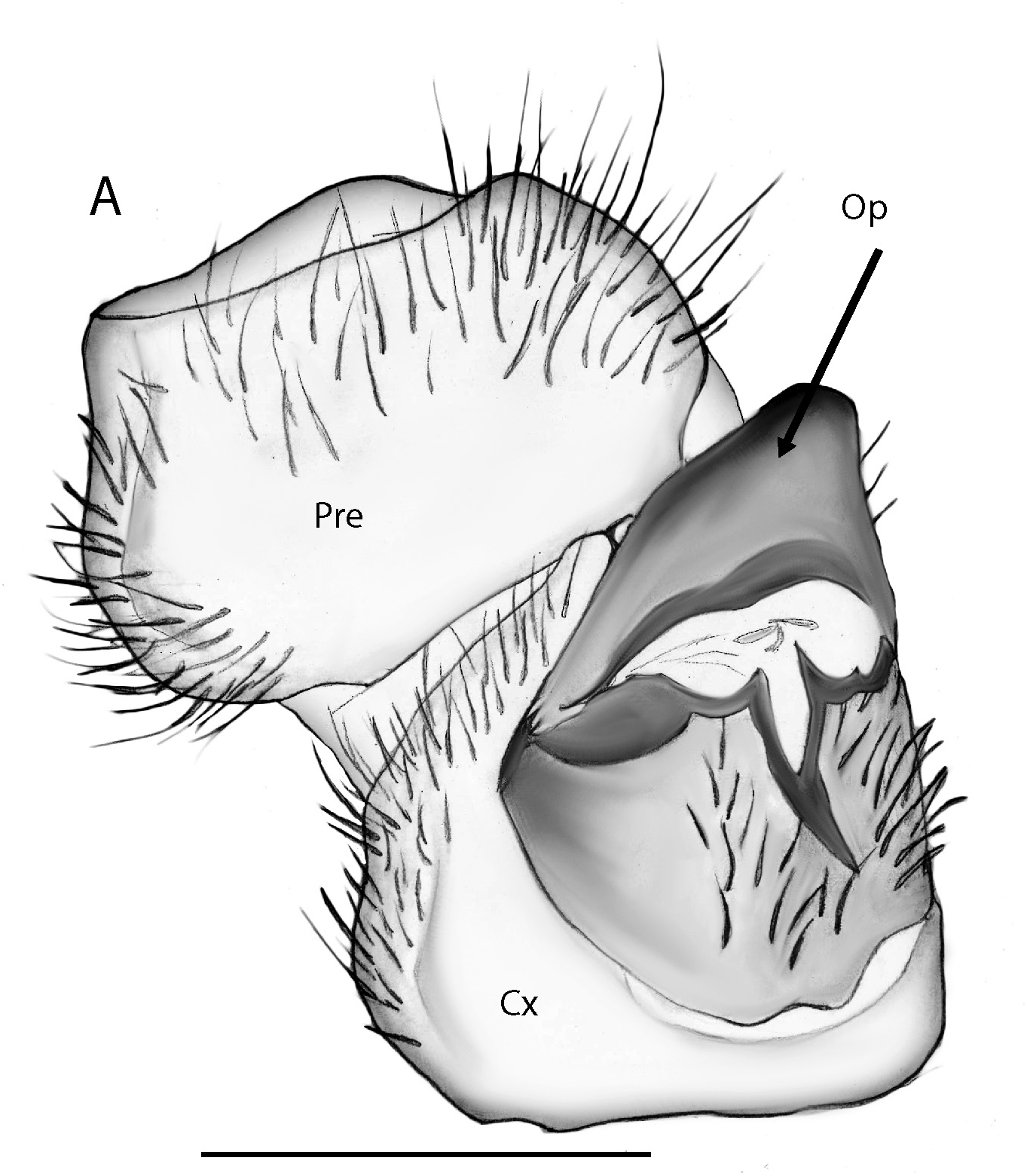
25/25. Subanal plate well rounded. Vulvae ( Fig. 11 View Fig ): with a large pointed operculum (Op). External lateral plate (EP) and inner mesal plate (IP) fused at bottom.
Another female paratype was used for microcomputed tomography. The resulting volume rendering is shown in Fig. 12 View Fig . While this approach revaled no significant additional details it serves to illustrate morphology of the specimen in an excellent way, much better than any photograph.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |