Bactrocera ( Bactrocera ) moluccensis ( Perkins, 1939 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7300862 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A105F057-F2A4-4C14-B82E-14912B319D57 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D4F455-00BF-43A2-41BE-CAB52D2D3E10 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Bactrocera ( Bactrocera ) moluccensis ( Perkins, 1939 ) |
| status |
|
Bactrocera ( Bactrocera) moluccensis ( Perkins, 1939) View in CoL
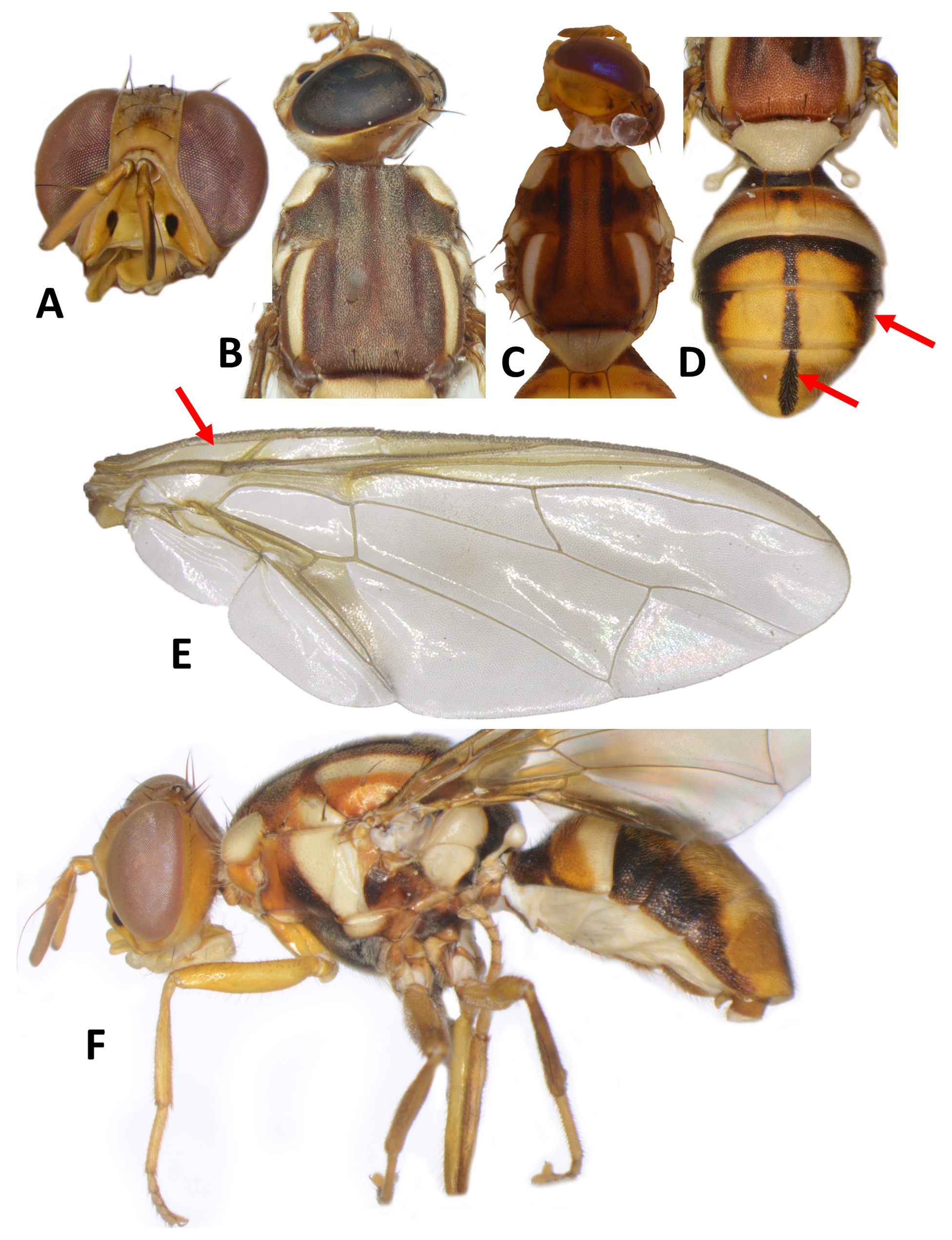
Figure 47 View Figure 47
Distribution. Indonesia ( Java, Sulawesi, Bali, Lombok, Moluccas). Papua New Guinea (mainland, New Britain, New Ireland, Bougainville). Solomon Islands (Shortland Group, Choiseul, Vella Lavella, Gizo, Kolombangara, New Georgia, Isabel, Russell, Florida, Guadalcanal, Malaita, San Cristobal, Rennell and Bellona, Santa Cruz).
Male lure. Cue-lure, zingerone (weak attraction) ( Royer et al. 2018).
Host plants. Category C pest ( Vargas et al. 2015). Host record in Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands: FABA- CEAE: Inocarpus fagifer .
Edible host common name: Tahitian chestnut.
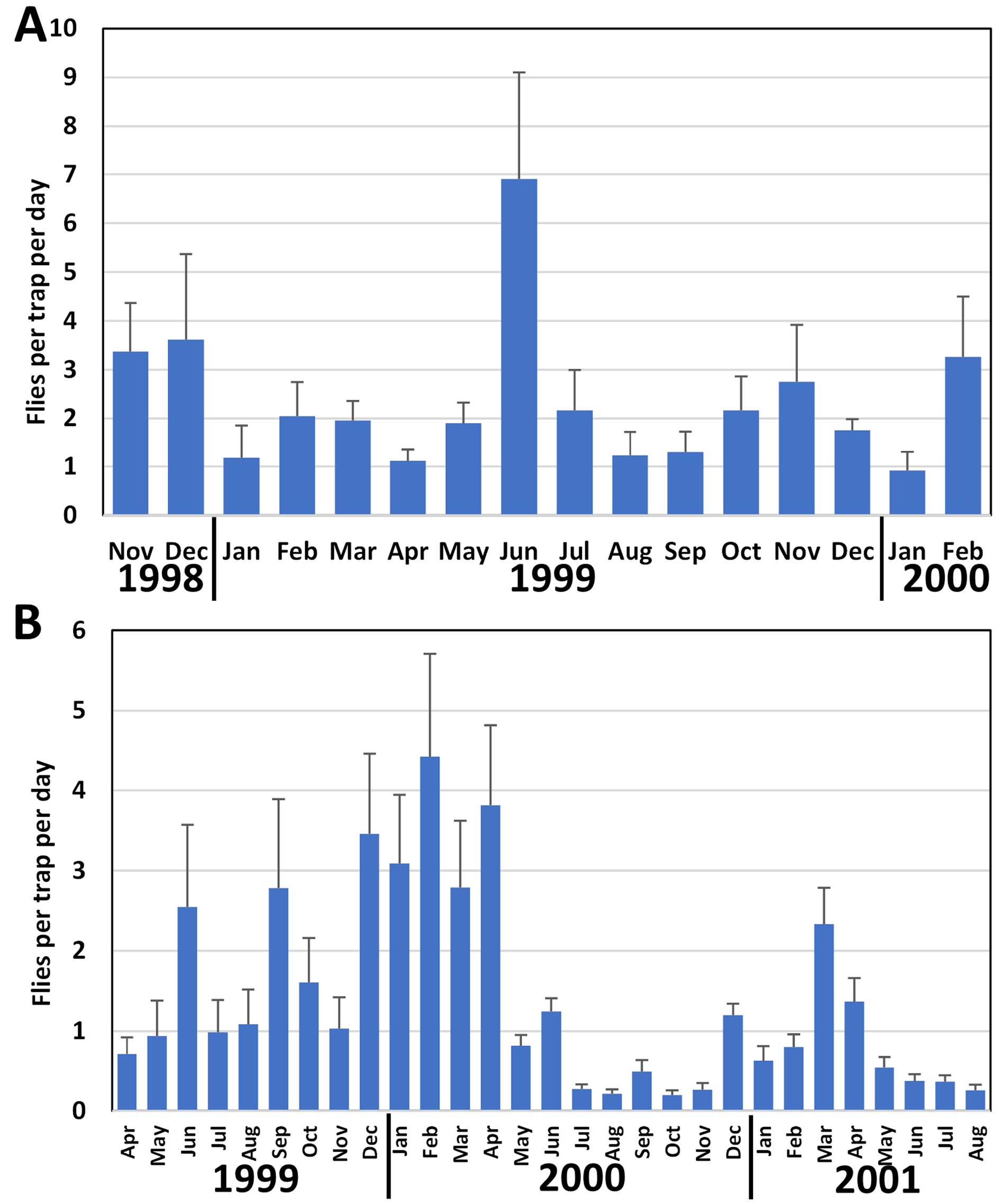
Biology. Contrary to other species that consume the outer fleshy part of Tahitian chestnut, B. moluccensis larvae damage the entire fruit, including the inner nut ( Leblanc et al. 2001a). Monthly trapping data illustrated on Figure 119 View Figure 119 .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |