Decticus albifrons ( Fabricius, 1775 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4860.4.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:92E2564C-60AB-4759-AB06-F177CC6841DE |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4414345 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D587BE-FFEA-347E-2FA7-E8DCFC58FD56 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Decticus albifrons ( Fabricius, 1775 ) |
| status |
|
Decticus albifrons ( Fabricius, 1775) View in CoL
Locusta albifrons Fabricius, 1775 . Supplementum Entomologiae Systematicae 2: 86.
Conocephalus albifrons: Thunberg, 1815 . Mem. Acad. Imp. Sci. St. Peterburg 5:273.
Decticus albifrons: Fieber, 1854 . Lotos 4:220.
Decticus aeolicus Guarino, 1935 . Annu. Mus. zool. Univ. Napoli N.S. 6(16):3(syn.).
Material examined. See Table 1 View TABLE 1 and Table 2.
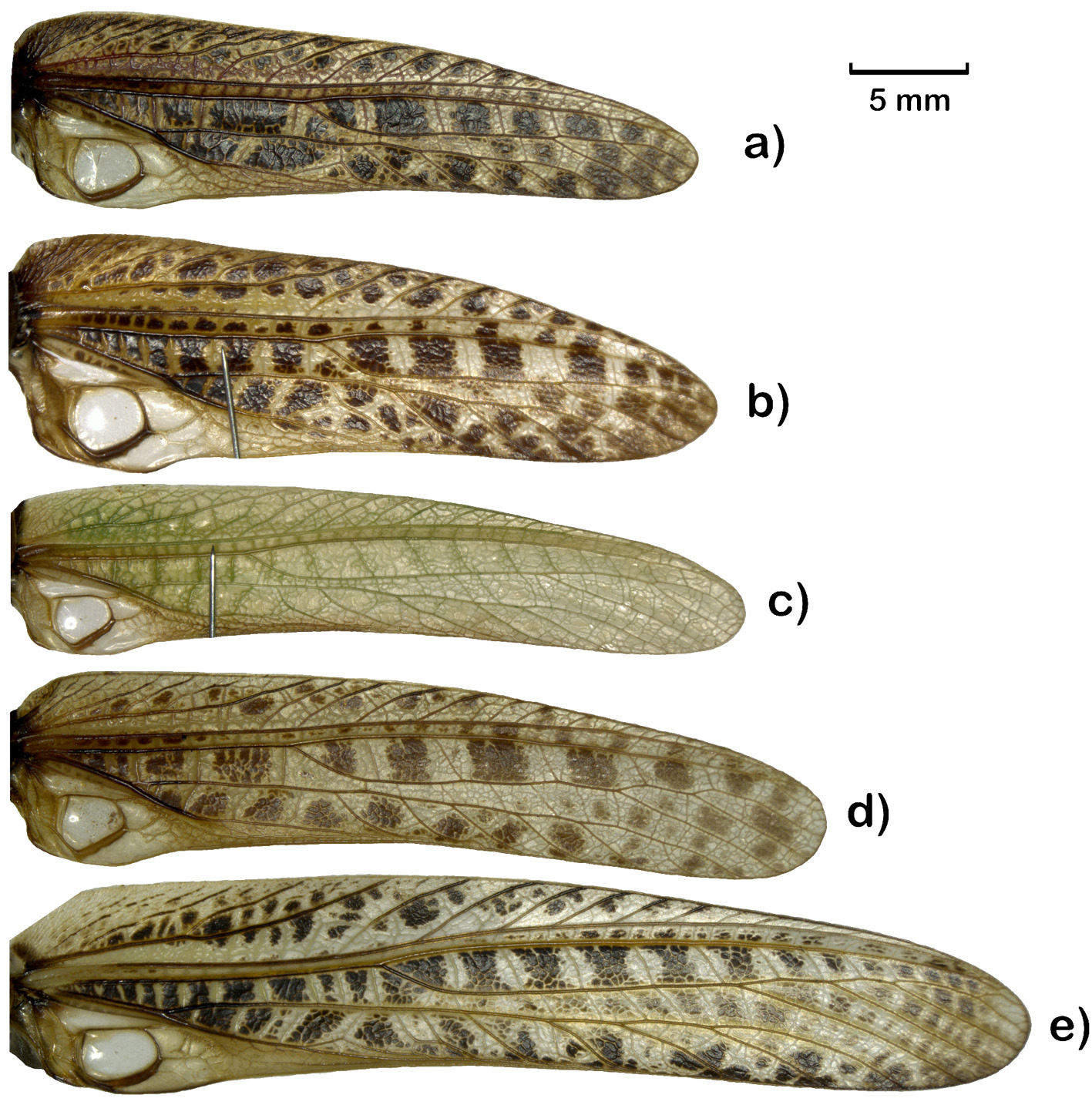
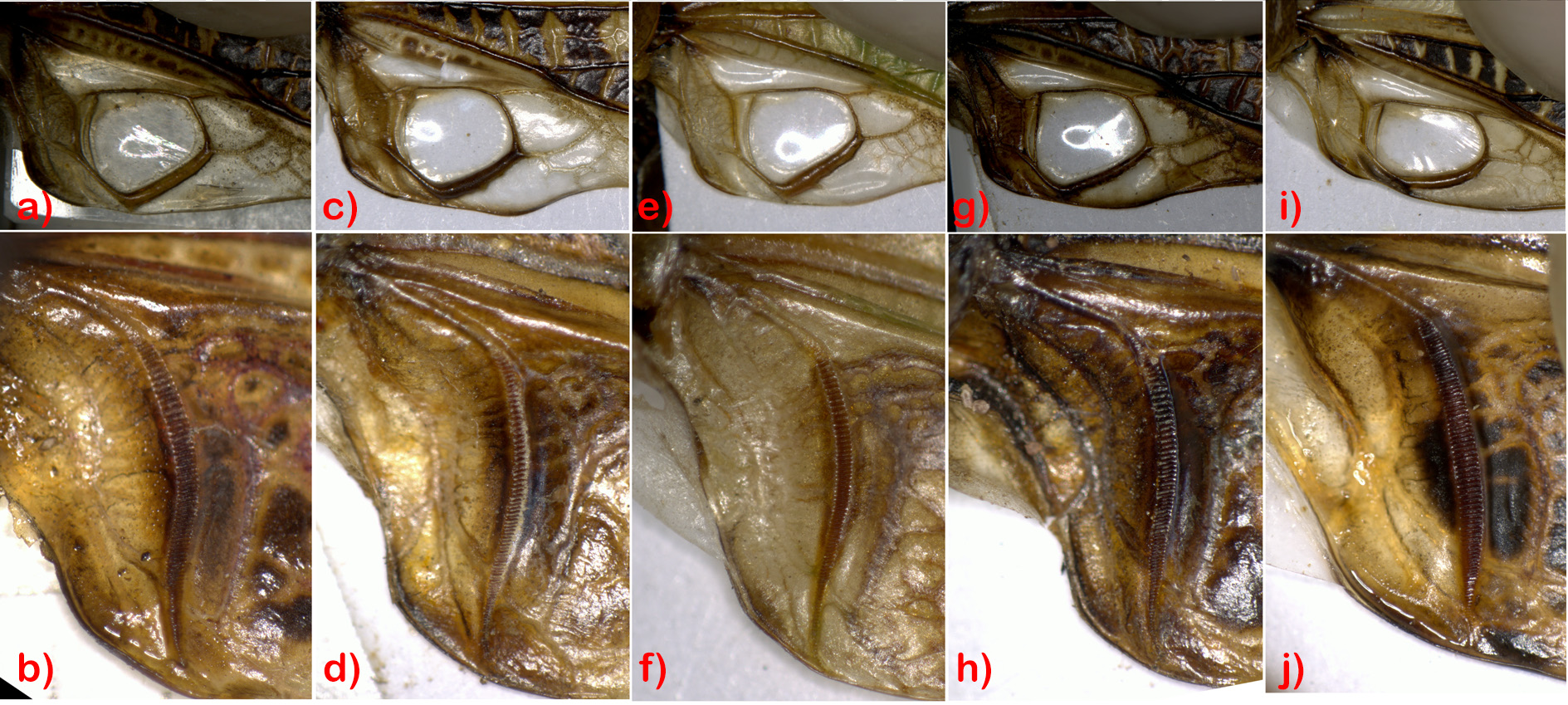
Diagnosis. Tegmen exceeding knee of hind femora, with narrow and rounded apices ( Fig. 5e View FIGURE 5 ). Male cercus conical, with a black inner tooth at base. Male subgenital plate with distinct lateral carina; cylindrical stylus slightly shorter than cercus, with sharp and black apex ( Fig. 4j & o View FIGURE 4 ). Female tegmen reaching or exceeding ovipositor apex. Female subgenital plate thick, with an acute-angled trianglar incision.
Redescription. Lateral lobe of pronotum about 1.5 times higher than wide; anterior margin inclining backward, posterior margin vertical, and ventral margin circular. Mirror irregular ellipse ( Fig. 6i View FIGURE 6 ). Stridulatory file with about 72–75 widely regularly-arranged pegs; pegs gradually becoming smaller towards both ends ( Fig. 6j View FIGURE 6 ). Male ninth abdominal tergum slightly extending backward with an obtuse angle. Male tenth abdominal tergum with an oval central concavity on dorsal surface; apex shrinking with a shuttle-shaped incision. Male epiproct covered by tenth abdominal tergum, bent down at an angle of 90° ( Fig. 4f View FIGURE 4 ). Male subgenital plate with distinct lateral carinae.
Generally brown, scattered with black and white spots. Face light purple, darkening to both sides. Clypeus pale yellow. Areas around eyes and antennal socket yellow. Occiput brown. Pronotum dark brown; center of pronotal lateral lobes dark brown, becoming black and yellow outwards. Tegmen creamy-brown, scattered with creamy-yellow and black spots. Hind femur black marbled on posterior surface, and brown on ventro-anterior surface. Yellow with the ventral of body.
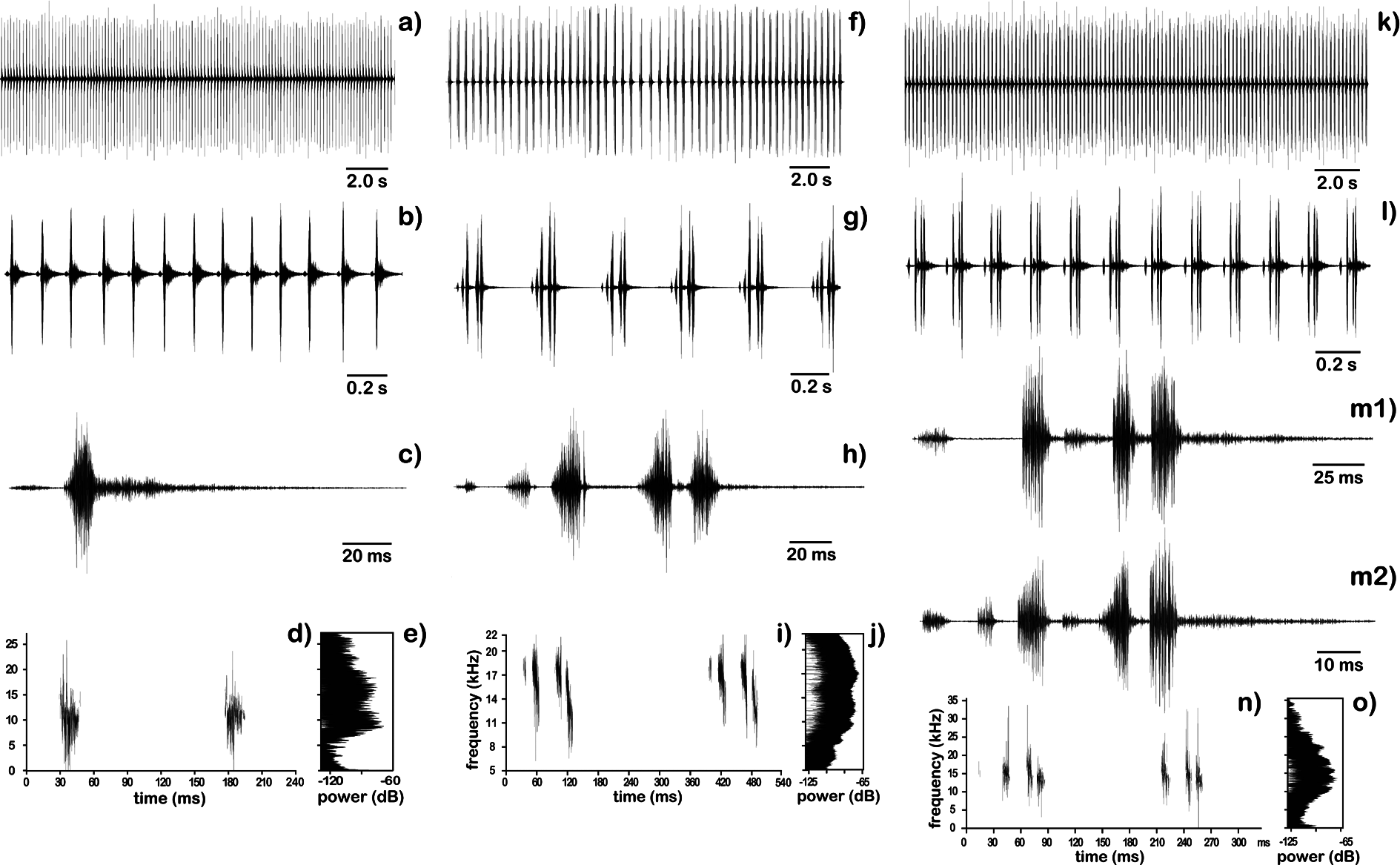
Song. The calling song consisted of stereotyped chirps with a regular period (147.47±6.75 ms) and duration (104.69±4.46 ms) ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 a–c). Each chirp was comprised of 2 syllable groups. Frequency ranges from 0 to 24 kHz, frequency of main peak is about 8.79 kHz, and that of second peak is not significant ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 d–e). The important parameters are listed ( Tab. 3 View TABLE 3 ).
Measurements (mm). See Table 6 View TABLE 6 and Table 7 View TABLE 7 .
Distribution. The distribution area includes the Canary Islands and Madeira and across the Mediterranean area (North Africa and Europe) up to southwesterm Asia ( Willemse et al. 2018).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Tettigoniinae |
|
Genus |
Decticus albifrons ( Fabricius, 1775 )
| Liu, Fei, Chen, Liusheng & Liu, Chunxiang 2020 |
Conocephalus albifrons :
| Thunberg 1815 |
Locusta albifrons
| Fabricius 1775 |