Geranomyia maculata, Zhang, Xiao, Zhang, Zehua & Yang, Ding, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4154.2.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:54A803AA-1C58-4691-90A7-BCBD8DD72C99 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6091914 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D6AA0F-4216-FFC1-67E2-F9B72336CFA0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Geranomyia maculata |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Geranomyia maculata View in CoL sp. nov.
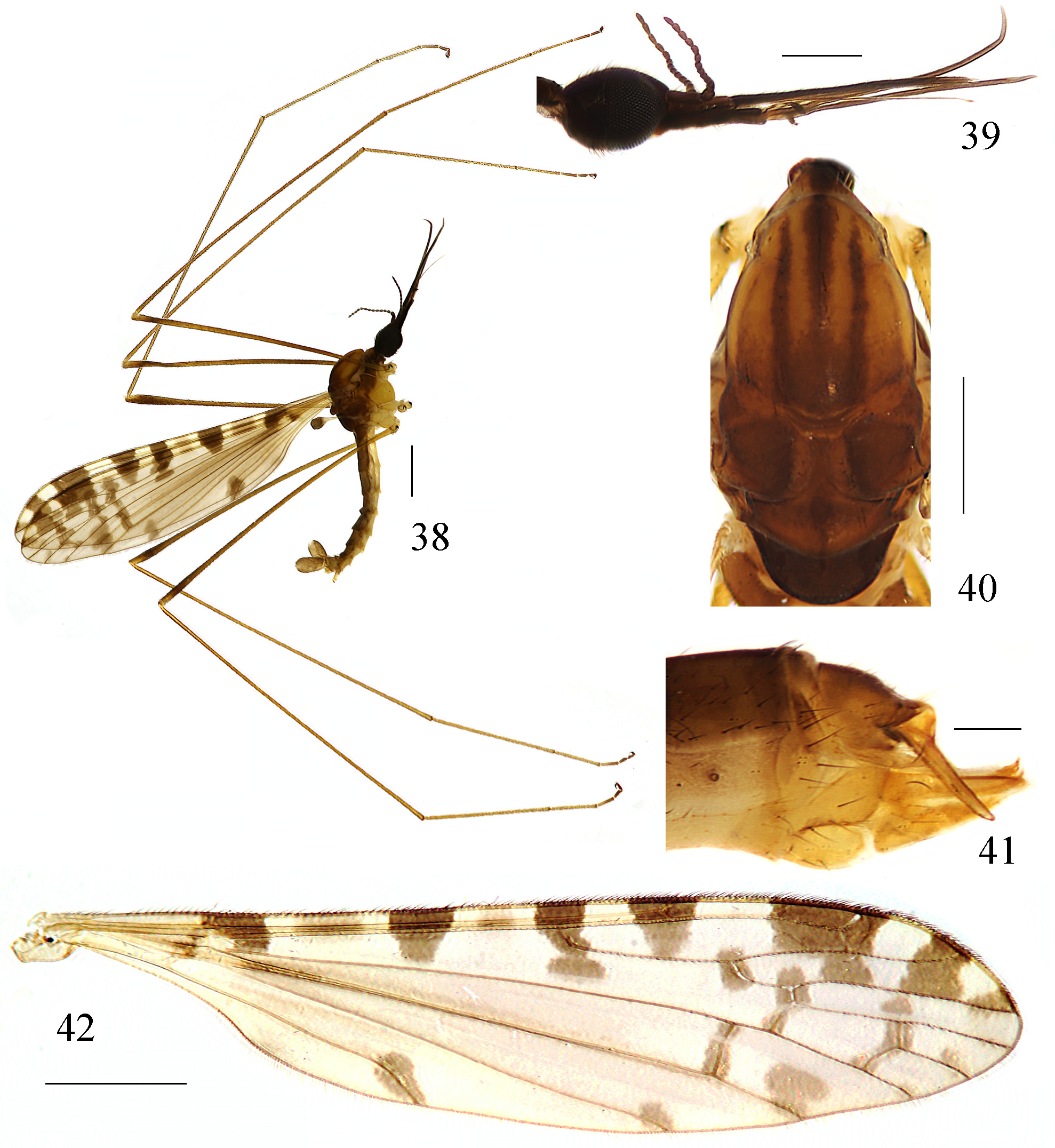
Figs. 38–44 View FIGURES 38 – 42 View FIGURES 43 – 44
Diagnosis. Prescutum brownish yellow to pale brown with three broad dark brown longitudinal stripes and a large posterior spot between lateral stripes. Pleuron yellow with a broad brown longitudinal stripe. Wing with nine large spots on costal region and a combined spot at middle area of cell CuA1 and tip of CuA2; Sc1 ending about opposite 2/3 of Rs, basal section of CuA1 about two-thirds its length before fork of M. Lobe of gonostylus with rostral prolongation small, middle with two long and slender spines arising from a small tubercle. Paramere with margin of mesal-apical lobe microscopically and irregularly toothed
Description. Male. Body length 6.0 mm, wing length 7.0 mm, mouthparts length 2.0 mm.
Head ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ). Black. Setae on head black. Antenna length 1.0 mm, black. Scape cylindrical. Pedicel nearly globose. Flagellomeres oval, terminal flagellomere with tip cuspate. Mouthparts black with black setae.
Thorax. Pronotum brownish yellow with a brown median stripe. Prescutum brownish yellow to pale brown with three broad dark brown longitudinal stripes and a large posterior spot between lateral stripes. Scutum dark brownish yellow with an ill-defined brown longitudinal stripe at middle area, each lobe with a large dark brown spot. Scutellum dark brownish yellow with middle area and borders brown. Mediotergite dark brown ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ). Pleuron ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ) yellow with a broad brown longitudinal stripe extending from cervical region to mediotergite. Setae on thorax brown. Coxae and trochanters yellow; femora brownish yellow with brown subterminal rings, bases paler; tibiae brownish yellow; tarsi brownish yellow with terminal segments darker. Setae on legs brown. Wing ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ) tinged pale brown with pale brown to brown pattern: nine large spots on costal region, second and fourth spots paler; seams along cord, m-m and basal section of M3; spots at fork of Rs, middle area of cell R4+5 and tips of A1 and A2; a combined spot at middle area of cell CuA1 and tip of CuA2; faint spots at tips of M3 and CuA1.
Veins brownish yellow, darker in clouded areas. Venation: Sc long, Sc1 ending about opposite 2/3 of Rs, Sc2 at its tip; basal section of CuA1 about two-thirds its length before fork of M. Haltere length 0.8 mm, yellow with knob pale brown.
Abdomen ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ). Tergites brownish yellow. Sternites yellow. Setae on abdomen brown.
Hypopygium ( Figs. 43–44 View FIGURES 43 – 44 ). Posterior margin of tergite nine slightly emarginate. Gonocoxite with a relatively small and simple ventromesal lobe. Clasper of gonostylus arched at 1/2 length, abruptly narrowed to apical spine. Lobe of gonostylus large; rostral prolongation small, middle with two long and slender spines arising from a small tubercle. Paramere with mesal-apical lobe slender and short, margin microscopically and irregularly toothed, tip relatively blunt.
Female. Body length 6.5 mm, wing length 7.2 mm, mouthparts length 2.0 mm. Similar to male. Cercus brownish yellow. Hypogynial valve pale brownish yellow. Tip of hypogynial valve and cercus nearly aligned ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ).
Type material. Holotype male ( CAU), China : Taiwan, Hualian, Bilvshenmu ( 24°10'48"N, 121°24'01"E, 2200 m), 2013. VI.6, Wenliang Li ( light trap). Paratype: 1 female ( CAU), same data as holotype GoogleMaps .
Distribution. China ( Taiwan).
Etymology. The specific name (from Latin maculatus (adj., meaning"spotted”)) refers to the combined spot at the middle area of cell CuA1 and tip of CuA2.
Remarks. This new species is somewhat similar to G. i m m o b i l i s ( Alexander, 1932) in having the similar venation of wing and structure of male hypopygium. It can be distinguished by the wing with nine large spots on costal region ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ) and the tubercle on rostral prolongation of lobe of gonostylus less than one-third of the rostral prolongation ( Figs. 43–44 View FIGURES 43 – 44 ), whereas in G. immobilis , the wing has seven spots on costal region and the tubercle slightly shorter than rostral prolongation ( Alexander 1932). This new species is also somewhat similar to G. tenuispinosa (Alexander, 1929) in having the similar venation of wing, but can be easily distinguished from the latter by the wing with a combined spot at middle area of cell CuA1 and tip of CuA2 ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 38 – 42 ), and lobe of gonostylus of male hypopygium with a small rostral prolongation and two spines arising from a small tubercle ( Figs. 43–44 View FIGURES 43 – 44 ). In G. tenuispinosa , the wing has no spot at the middle area of cell CuA1 or tip of CuA2 ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 2 – 17 ), the lobe of gonostylus has a long and slender rostral prolongation and two spines of which one arises from a small tubercle and the other arises from the rostral prolongation directly ( Alexander 1929a).
| CAU |
China Agricultural University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |