Pseudomaevia cognata Rainbow, 1920
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3811.3.10 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:09B993A9-EC44-4BAE-9B17-EB82470C0CA5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6135333 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D88787-D24E-7C51-FF5B-FC2A8692FECC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pseudomaevia cognata Rainbow, 1920 |
| status |
|
Pseudomaevia cognata Rainbow, 1920 View in CoL
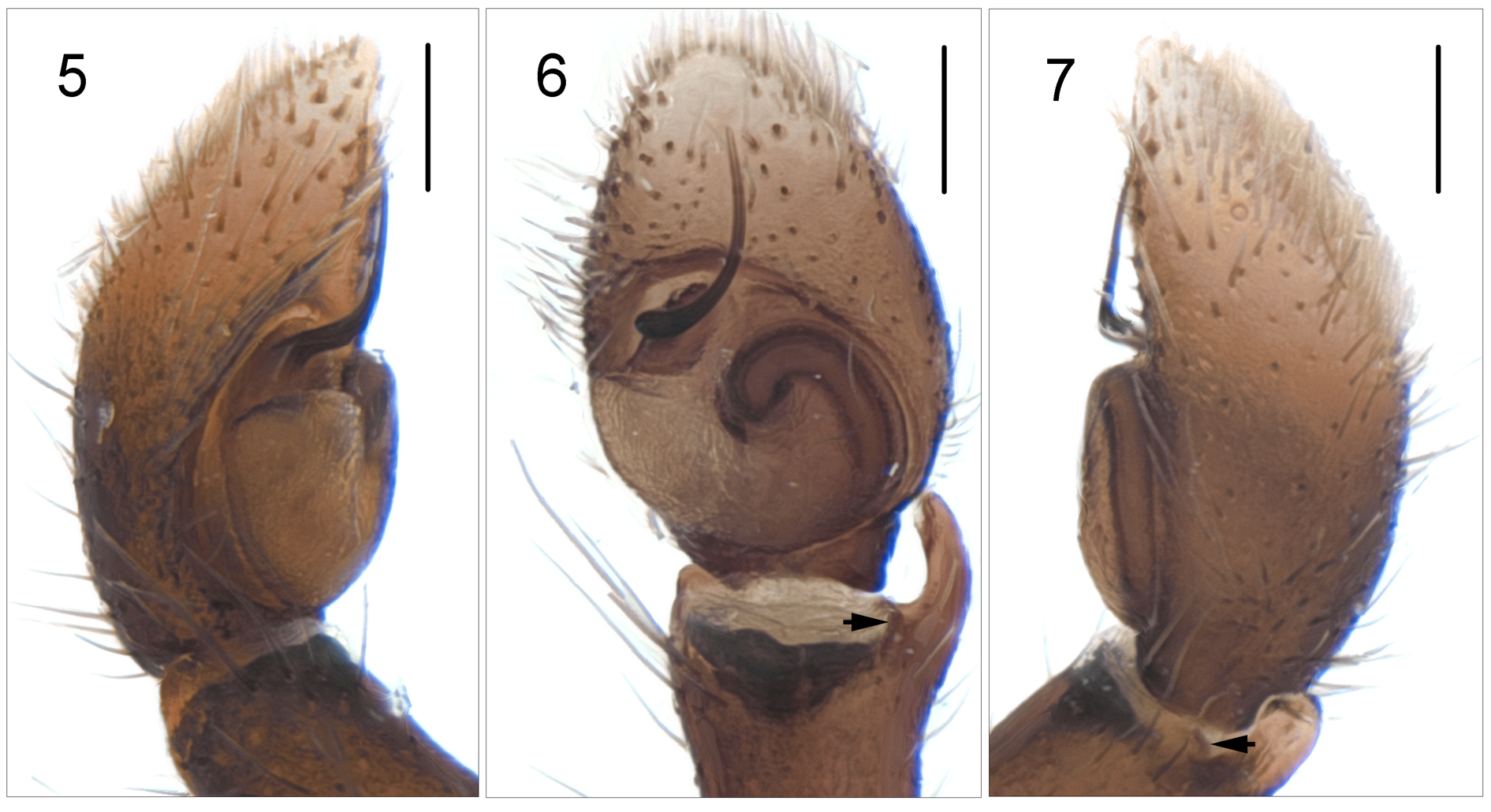
Figs 1–15 View FIGURES 1 – 4 View FIGURES 5 – 7 View FIGURES 8 – 11 View FIGURES 12 – 15
Pseudomaevia cognata Rainbow 1920: 269 View in CoL , Pl XXXI, figs 123–127.
Type material. Holotype ♂, Lord Howe Island, 31.50°S, 159.03°E, Australia, XII.1915, A.M. Lea ( SAMA NN 305 [N1981366]).
Other material examined. AUSTRALIA, Lord Howe Island: 1♀, Stn 3, North Bay, grassy area along track, 31.52°S, 159.03°E, 30.I.1971, M. Gray (AM, KS22224); 1♂, 1♀, Stn 40, near top of Goat House Track, 31.55°S, 159.08°E, 2.X.1971, M. Gray (AM, KS22225); 1 imm., 31.55°S, 159.08°E, 1.I.1928, G. Troughton (AM, KS22217); 1♀, Erskine Valley, 31.55°S, 159.08°E, 1.II.1971, M. Gray (AM, KS22223); 1♂, Erskine Valley, 31.57°S, 159.07°E, 29.I.1979, T. Kingston (AM, KS86867); 1♀, Stn 42, foot of saddle rise, Erskine Valley, 31.57°S, 159.07°E, 15.II.1971, M. Gray (AM, KS22222); 1♂, Mt Gower, 390m, site G3, 31.57°S, 159.08°E, 20.XI.2004, N. Velez (AM, KS 122111); 1 imm., Stn 45, NE area of Mt Gower Summit, 31.58°S, 159.07°E, 15.II.1971, M. Gray (AM, KS22221); 1♂, Mt Gower Summit, 31.58°S, 159.08°E, 19.VIII.2000, D. Michael (AM, KS68266); 1♂, Mt Gower, 230m, site G9, 31.58°S, 159.08°E, 20.XI.2004, N. Velez (AM, KS 122110); 1♂, Mt Gower, 690m, site G27, 31.58°S, 159.08°E, 29.X.2005, N. Velez (AM, KS 122070); 1♀, Mt Gower, 360m, site G14, 31.58°S, 159.10°E, 1.IV.2006, N. Velez (AM, KS 122087); 1♀, Mt Gower, 390m, site G15, 31.58°S, 159.10°E, 29.X.2009, N. Velez (AM, KS 122036); 1♂, Mt Gower, bottom of gulley, 18.XI.2001, C. Reid (AM, KS90265); 1♂, Mt Gower, 800m, site G32, 31.62°S, 159.08°E, 1.IV.2006, N. Velez (AM, KS 122112).
Description. Male: Holotype: Cephalothorax long and very flat, mid to dark orange with scattered pennate grey hairs around the eyes and along the sides. Surrounds of ALE, PME and PLE, black with scattered grey hairs. Clypeus tiny, without a fringe of hairs ( Figs 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Chelicerae mid to dark orange, straight, with fangs folded a little backwards towards a tapering inner surface ( Figs 3–4 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Two, well separated, medium sized promarginal teeth and one medium sized, fissident, retromarginal tooth with two large terminal and a variable pattern of one or two small intermediate cusps ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 12 – 15 ). Endites and labium orange grading to yellow distally. Sternum orange. Abdomen long and narrow, dorsal surface yellow with a pair of longitudinal brown stripes (more recently collected males are not so faded and all show a pattern of brown and yellow bands grading to solid brown laterally down the sides of the abdomen (as in Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8 – 11 ). Spinnerets small, yellow. Ventral abdomen light orange. Legs mid to dark orange. L1 more robust and larger than other legs, with grey fringe on tarsus and metatarsus. Strong spines on the patella, tibia and tarsus of L1; all other spines tiny or missing. Palp: light orange, with one short ( Figs 6–7 View FIGURES 5 – 7 ) and one medium sized blunt tibial apophysis. Cymbium short, rounded. Tegulum rounded, without lobe. Embolus arises from a distinct mound on the prolateral distal edge of the tegulum and moves away from the tegulum before forming an anti-clockwise quarter circle. Dimensions: CL 3.90, EFL 1.55, CW 2.54, AEW 1.92, AMEW 1.24, PEW 2.17, AL 4.64, P1+T1 3.22, L1 7.49 (2.23+1.24+1.98+1.42+0.62), L2 4.02 (1.23+068+0.93+0.74+0.43), L3 4.27 (1.36+0.68+0.93+0.87+0.43), L4 6.01 (1.80+0.93+1.61+1.18+0.50).
Female. As for the male, except animal much larger. Epigynum : median facing, ‘C-shaped’, guides and copulatory openings indistinct. Insemination ducts first move vertically a short distance (not apparent in figures). The ducts then move in a posterior direction with small lateral diverticula, and finally curve laterally and move forward again to end in the fertilization ducts ( Figs 11–14 View FIGURES 8 – 11 View FIGURES 12 – 15 ). There is no obvious shape differentiation of a spermatheca, however it may be that the vertical section is the insemination duct, the first two thirds of the horizontal section (orange coloured, Fig. 14 View FIGURES 12 – 15 ) is the spermatheca and the final third the fertilization duct. Dimensions: CL 5.15, EFL 1.92, CW 3.47, AEW 2.48, AMEW 1.55, PEW 2.79, AL 8.61, P1+T1 4.46, L1 10.4 (2.97+1.85+2.72+2.04+0.80), L2 6.93 (2.17+1.24+1.73+1.30+0.50), L3 5.94 (1.92+0.99+1.24+1.24+0.56), L4 8.17 (2.35+1.24+2.35+1.61+0.62).
Distribution and biology. The species is known only from Lord Howe Island, an Australian administered island 700km north-east of Sydney in the Tasman Sea. It has been collected on foliage and in pitfall traps.
| SAMA |
South Australia Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Pseudomaevia cognata Rainbow, 1920
| Richardson, Barry J. 2014 |
Pseudomaevia cognata
| Rainbow 1920: 269 |