Symplectoscyphus cf. subarticulatus ( Coughtrey, 1875 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3852.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7DE3BCBA-E5F0-4F0D-B2FD-B5B59E4DAE51 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6143199 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D92A2C-474C-FFF0-FF51-87735D2CA4D2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Symplectoscyphus cf. subarticulatus ( Coughtrey, 1875 ) |
| status |
|
Symplectoscyphus cf. subarticulatus ( Coughtrey, 1875)
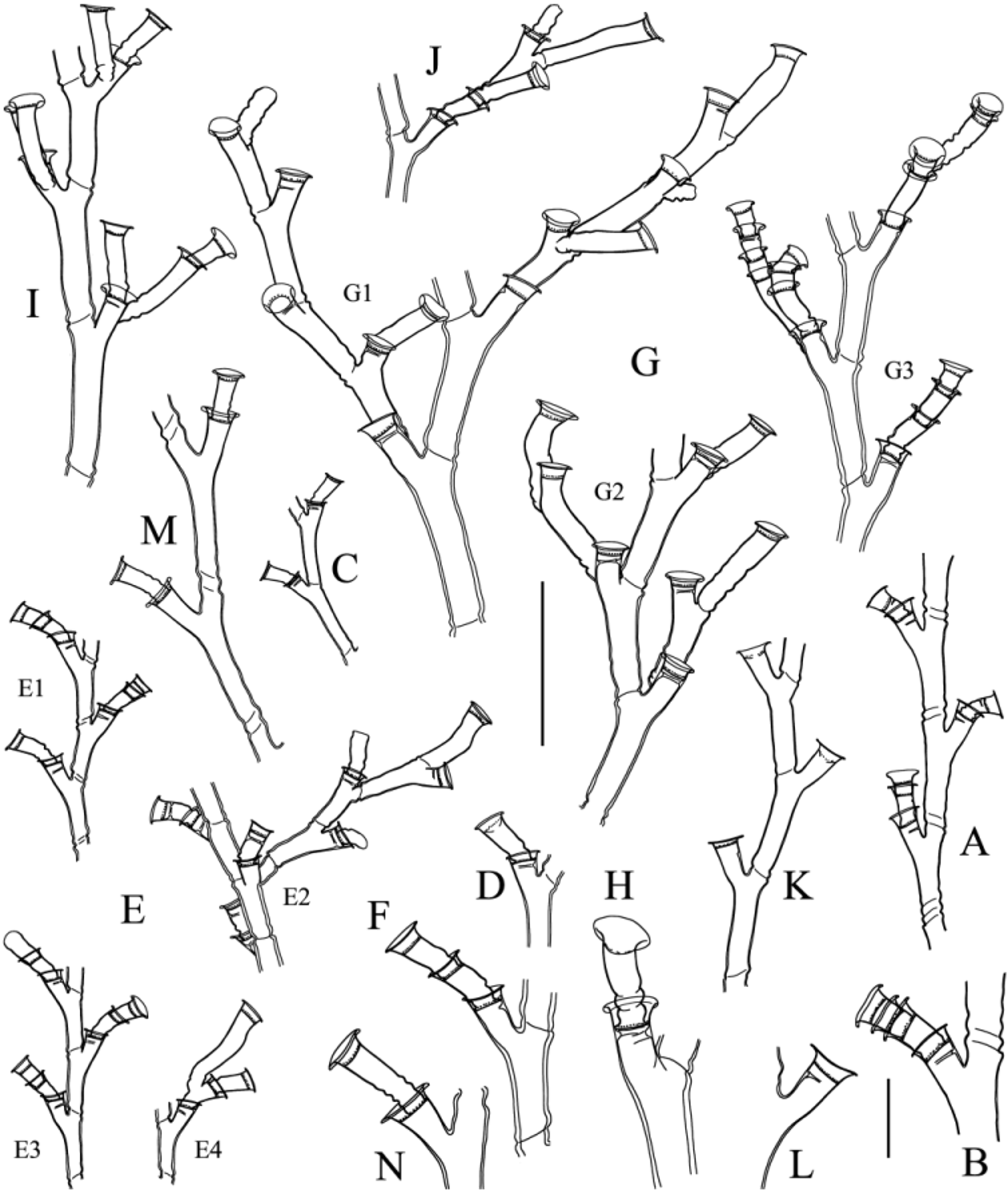
(Plate 3D; Fig. 7K–M; Table 10 View TABLE 10 )
Material examined. Corral, Chaihuin/Huiro, lat. -39.95000, long. -73.61667, 08.viii.2012, 14 m, sample 10: a few broken stems up to 2.2 cm high, some fragments bearing gonothecae (MHNG-INVE-86228).
Description. Colony coplanar; stems monosiphonic, geniculate (Pl. 3D), perisarc smooth or with up to 3 annulations above origin from stolon, followed by a portion bearing a few alternate hydrothecae; remainder of stem divided into internodes by oblique constrictions of the perisarc sloping alternately in opposite directions. Internodes of irregular length, composed of a succession of 2–20 subopposite hydrothecae, the last followed on the opposite side by a short apophysis supporting a cladium, and an axillar hydrotheca (Fig. 7K); number of hydrothecae per internode increasing generally from basal part of stems upwards, though exceptions occur towards their middle and upper parts. Cladia borne of corresponding stem apophyses, delimited from the latter by constrictions of the perisarc; straight, undivided into internodes, composed of a varied number of subopposite hydrothecae, more approximate than those of the stem; may occasionally rebranch once. Hydrothecae (Fig. 7L) tubular, immersed in the stem and cladia for about two-thirds their adaxial length, distally bent outwards; free adcauline wall almost straight, but tilted adaxially just below aperture; adnate part slightly curved; abcauline wall concave in middle; aperture with three pointed cusps separated by moderately deep embayments; operculum of three triangular flaps. Gonothecae, female in present material, given off from cladia, below the hydrothecal bases; ovoid in overall shape, back side flat to concave, being closely pressed against the cladium; walls with 8–9 independent, circular ribs with thickened free margin, not spirally arranged; distally, a small plateau giving rise in its centre to a short, trumpet shaped terminal neck, bearing an aperture distally (Fig. 7M).
Remarks. The present specimens are fragmentary and monosiphonic, and do not display neither the characteristic growth form illustrated by Trebilcock (1928, pl. 7 Fig. 7), nor the regularity in the structure of stem, as described and depicted by Ralph (1961), thus explaining the description given above.
The Patagonian S. divaricatus (Busk, 1852) , whose type was rediscovered by Totton (1930) and redescribed by Ralph (1961), somehow resemble the present species. According to the latter author, it is a less robust species, has smaller and more spaced hydrothecae, and their marginal cusps are more sharply pointed.
Distribution in Chile. Chiloé ( Leloup 1974) and Corral (present report).
World records. New Zealand ( Vervoort & Watson 2003), Lord Howe Island ( Briggs 1918), southern Australia ( Whitelegge 1899), Kerguelen ( Millard 1977).
TABLE 9. Comparison of Symplectoscyphus semper sp. nov. with congeners provided with transversely-ribbed gonothecae. The abbreviations used for the hydrotheca are as follows: Fad = free adaxial side, Aad = adnate adaxial side, Ab = abcauline side, Ap = diameter at aperture; and for the gonotheca: L = length, W = maximum width. All measurements are given in µm and, when not available, the abbreviation N.A. is used.
Colony, stem and Internodes (of both stem Hydrotheca Gonotheca Geographical Reference(s) Species branches/cladia and branches) Shape and size Terminal tube distribution bathyalis Colony likely coplanar, Long, slender, each Large, cylindrical, facing Pear-shaped, with ca. 7 Short, flaring distally Occurs in Vervoort Vervoort, stems monosiphonic, bearing a distal outward and slightly upward, annular ridges, L = 1350– scattered (1972, 1993) 1972 slender, cladia given hydrotheca, and adnate for less than 1/3rd, Fad = 1480, W = 1010–1150 localities in the
off irregularly occasionally a lateral 595–675, Aad = 285–310, Ab = Atlantic and
apophysis below 610–675, Ap = 350–375 Pacific
raised fluted frills,
measurements N.A.
exsertus Colony likely coplanar, Of varied length Long, tubular, facing upward, Ovoid, provided with ca. 7 Short, greatly Only known Allman Allman, stems monosiphonic, adnate for 1/3rd, measurements annular ridges, expanding distally from Heard (1888) 1888) ramified irregularly N.A. measurements N.A. Island
and subdichotomously
…….. Continued to the next page TABLE 9. ( Continued)
Species Colony, stem and Internodes (of both stem Hydrotheca Gonotheca Geographical Reference(s)
branches/cladia and branches) Shape and size Terminal tube distribution filiformis Colonies coplanar, in dense, Of varied length, though Tubular, facing outwards and Sexually dimorphic, female Short and wide in Scattered records Totton (1930), Allman, 1888 parallel assemblages, stems with generally 2–3 slightly upwards, nearly half usually with additional females, tubular and from various Galea (2007)
indistinct, monosiphonic, hydrothecae between adnate, Fad = 242–280, Aad = annulations and wider distal slender in males subantarctic
branching consecutive branches 247–269, Ab = 335–385, Ap = tube, L = 1213–1596 (♀), localities
pseudodichotomous 154–165 824–989 (♂); W = 740–894
(♀), 632–742 (♂)
alternate hydrothecae and a lateral 235, Aad = 335–380, Ab = 290– upturned flanges, L = 1815– to aperture
apophysis 315, Ap = 215–225 1975, W = 640–705
Colony coplanar, stems Short, comprising 3 Tubular, deeply immersed, for at Ovoid, narrowing basally, Up to 225 µm long, New Zealand, Ralph (1961), subarticulatus branched, polysiphonic, hydrothecae and a lateral least 2/3rd, Fad = 72–140, Aad = with 5–8 conspicuous widest distally in southern Australia, Vervoort & Coughtrey, cladia regularly alternate apophysis 350–390, Ab = 225–255, Ap = deeply flared annulations, L females Chile Watson (2003)) 170–175 = 1315–1475 (♀), 1150–
1230 (♂); W = 835–870
(♀), 900–985 (♂)
tricuspidatus Colonies coplanar, stems Short, geniculate, bearing Tubular, straight to slightly Ovoid, with 7–9 deep Short, gradually Circumpolar in Hincks (1868), Alder, 1856) monosiphonic, alternately a hydrotheca distally, curved outward, adnate for 1/3 rd transverse ridges, L = ca. expanding from base northern Atlantic Calder (1970),
branched or divided occasionally a lateral to 2/3 rd, Fad = 391–465, Aad = 1000, W = ca. 700 to aperture and Pacific Schuchert (2001)
dichotomously apophysis below 227–258, Ab = 492–565, Ap =
232–269
tuba Totton, Colonies straggling Varied in length, though Short, contracting from base to Ovoid, with 8–10 deep, 160–192 µm long, New Zealand, New Totton (1930),
multipinnate, stems mostly long, slender, margin, sometimes almost upturned flanges, L = 1120– trumpet-shaped, with Caledonia Watson (2003)
monosiphonic slightly geniculate, each tubular, directed upwards, almost 1200, W = 760–800 wide (240–280 µm)
bearing a hydrotheca, half adnate, sometimes free part aperture
occasionally a lateral shorter, Fad = 248–312, Aad =
apophysis below 296–360, Ab = 416–440, Ap =
192–216
Sertularia unilateralis Lamouroux, 1824: 615 View in CoL , pl. 90 Figs 1 View FIGURE 1. A, B –3.― Van Praët, 1979: 903, Fig. 55A, B.
Sertularella unilateralis ― Hartlaub, 1901b: 42, Fig. 20; 1905: 628, Fig. T3.― Billard, 1909a: 1065; 1909b: 315, Figs 3, 4; 1910: 36.
Sertularella pulchella Jäderholm, 1904 : viii; 1905: 30, pl. 12 Figs 4 View FIGURE 4. A ‒ F, M –7.
Sertularella macrogona Trebilcock, 1928: 11 View in CoL , pl. 1 Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4. A ‒ F, M ( syn.nov.).
Symplectoscyphus macrogonus View in CoL ― Millard, 1957: 219.― Ralph, 1961: 798, Fig. 14A, B.― Millard, 1964: 51; 1975: 316, Fig. 102D–G.― Gili et al., 1989: 105, Fig. 29B.― Vervoort & Watson, 2003: 264, Fig. 62A, B.
Sertularella rentoni Bartlett, 1907: 43 , Fig. ( syn.nov.)― Mulder & Trebilcock, 1914: 9, pl. 1 Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4. A ‒ F, M , pl. 3 Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1. A, B .― Bale, 1919: 337, pl. 16 Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2. A, B .― Trebilcock, 1928: 10, pl. 1 Fig. 3.
Symplectoscyphus rentoni ― Stechow, 1922: 148; 1923: 172.― Ralph, 1961: 804, Fig. 16A–C.― Vervoort & Watson, 2003: 227, Fig. 54A, B.
Symplectoscyphus sp. 2― Galea & Schories, 2012a: 56 View Cited Treatment , Fig. 7J.
Material examined. Corral, Chaihuin/Huiro, lat. -39.95000, long. -73.61667, 09.vii.2012, 5‒ 8 m, sample 10: male colony on seaweed, stems up to 7 mm high (MHNG-INVE-86238).
Remarks. The identification of the present material was facilitated thanks to the account by Billard (1909b), who re-examined the type of Sertularia unilateralis Lamouroux, 1824 . This species is characterized by the following features: 1) the stems are short, monosiphonic, unbranched or rarely branched, divided into very short internodes delimited by oblique nodes; 2) each internode bears a long, tubular hydrotheca, facing up- and outward; 3) there are generally three internal, well-developed, submarginal projections of perisarc; 4) the gonotheca is urnshaped in frontal view, flattened laterally, and bears a short, distal, tronconical tube provided with the aperture distally.
After a careful study of the relevant literature, it appears that the characteristic shape of the gonotheca is unique among the genus, and this feature could be exploited confidently to solve the taxonomy of several nominal species. However, the occurrence of submarginal cusps within the hydrotheca proves variable among specimens from various localities around the world. Unlike Vervoort & Watson (2003), who consider that S. macrogonus ( Trebilcock, 1928) is a species devoid of intrathecal cusps, we include it in the synonymy of the present species. In doing this, we follow the opinion expressed by Millard (1957, p. 220), who found that the occurrence of cusps “is apparently not a constant feature for the species, for although internal teeth are normally present, they may be absent in several hydrothecae on a stem, or even on a complete stem. It cannot therefore be used to establish a separate species”. It seems thus that the material from southern Africa [( Millard 1957, Gili et al. 1989)] represents a transition between the New Zealand form, not provided with intrathecal projections, and the specimens from around South America that exhibit this feature.
We also agree with Billard (1910) that the peculiar gonotheca, as well as the shape of the hydrotheca and the presence of submarginal cusps make the tricuspidate Sertularella pulchella Jäderholm, 1904 indistinguishable from S. unilateralis .
Bale (1919) noted obvious similarities between S. rentoni Bartlett, 1907 and S. unilateralis , but refrained from uniting them on the account of the presence of intrahydrothecal cusps in the latter. Based on the conclusions raised by Millard (1957), we now include S. rentoni in the synonymy of the present species.
Distribution in Chile. Only known from Chaihuin (present report); this is the first record for the country.
World records. New Zealand, Southeast Australia ( Vervoort & Watson 2003), South Africa ( Millard 1975), Namibia ( Gili et al. 1989), Falkland islands ( Lamouroux 1824, Jäderholm 1905).
TABLE 10. Measurements of Symplectoscyphus cf. subarticulatus (Coughtrey, 1875), in µm.
| Reference | Present study | Ralph (1961) | Vervoort & Watson (2003) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrotheca | |||
| - free adaxial side | 180–275 | 10–60 | 45–60 |
| - adnate adaxial side | 320–435 | 350–400 | 390–400 |
| - abcauline side | 340–365 | 270–350 | 275–285 |
| - base width | 185–220 | – | – |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Symplectoscyphus cf. subarticulatus ( Coughtrey, 1875 )
| Galea, Horia R., Schories, Dirk, Försterra, Günter & Häussermann, Verena 2014 |
Symplectoscyphus macrogonus
| Vervoort 2003: 264 |
| Gili 1989: 105 |
| Millard 1964: 51 |
| Ralph 1961: 798 |
| Millard 1957: 219 |
Sertularella macrogona
| Trebilcock 1928: 11 |
Symplectoscyphus rentoni
| Vervoort 2003: 227 |
| Ralph 1961: 804 |
| Stechow 1922: 148 |
Sertularella rentoni
| Trebilcock 1928: 10 |
| Bale 1919: 337 |
| Mulder 1914: 9 |
| Bartlett 1907: 43 |
Sertularella unilateralis
| Billard 1909: 1065 |
| Hartlaub 1901: 42 |
Sertularia unilateralis
| Van 1979: 903 |
| Lamouroux 1824: 615 |