Muraenichthys Bleeker 1853
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4060.1.10 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0D7EB842-F5BB-4F6B-8461-14E9D1FB26A8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5692157 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E0523B-B976-FFDE-FF54-FF33FDEDE4A8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Muraenichthys Bleeker 1853 |
| status |
|
Genus Muraenichthys Bleeker 1853 View in CoL View at ENA
Muraenichthys Bleeker 1853:505 View in CoL ( type species: Muraena gymnopterus Bleeker 1853 ).
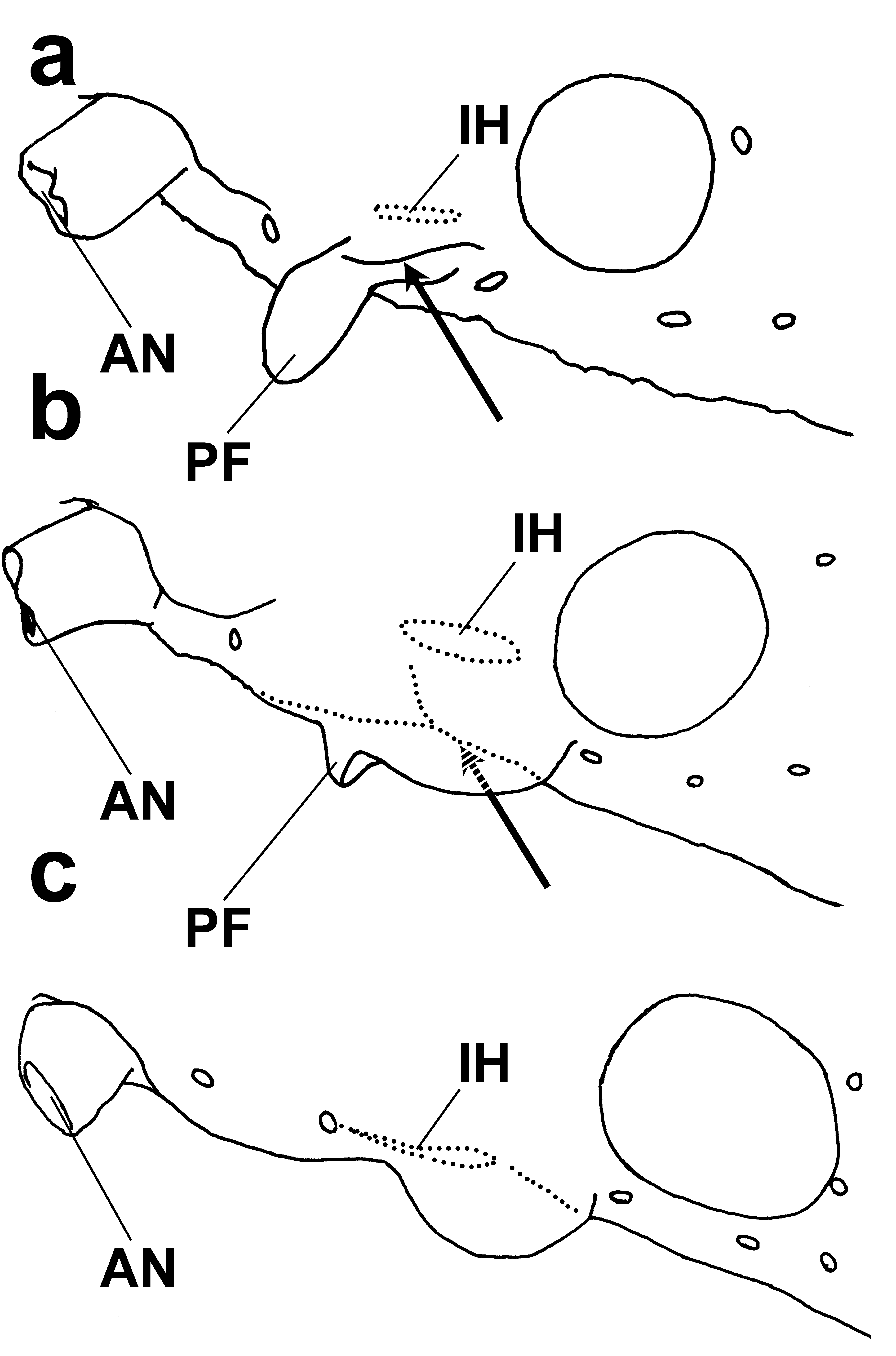
Diagnosis. A genus of the family Ophichthidae , subfamily Myrophinae , defined by the following combination of characters: eyes located anterior to mid-jaw; inner hole of posterior nostril above upper lip, and outer hole usually outside of mouth, with a prominent but short projected flap anteriorly ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 a, b); a single pore between anterior and posterior nostrils; three preopercular pores; teeth on jaws, vomer, and intermaxillary area; tooth shape variable, blunt to pointed but not distinctly recurved and tooth length equal or less than a half of eye diameter; teeth on jaws and vomer arranged in one to five rows; gill opening constricted, its height<170% of eye diameter; pectoral fins absent.
Description. Body elongate, cylindrical or subcylindrical, laterally compressed posteriorly. Snout usually broad and blunt; mouth inferior, distance from the tip of snout to tip of lower jaw usually almost equal to eye diameter; anterior nostril tubular; inner hole of posterior nostril above upper lip, and outer hole usually outside of mouth, with a prominent but short projected flap anteriorly; eyes located anterior half of mid-jaw; mouth large, rictus of mouth much behind posterior margin of eye; teeth on jaws, vomer, and intermaxillary area, its shape and arrangement variable; cephalic sensory pores small but conspicuous; supraorbital, infraorbital, preoperculomandibular, supratemporal, interorbital and mid-temporal pores present; lateral-line pores small but conspicuous, ending before posterior half of tail; gill opening constricted, opening ventrolaterally; median fins low, dorsal-fin origin located about mid-trunk to behind a vertical through mid-anus; caudal fin small but conspicuous, confluent with dorsal and anal fins; pectoral fins absent.
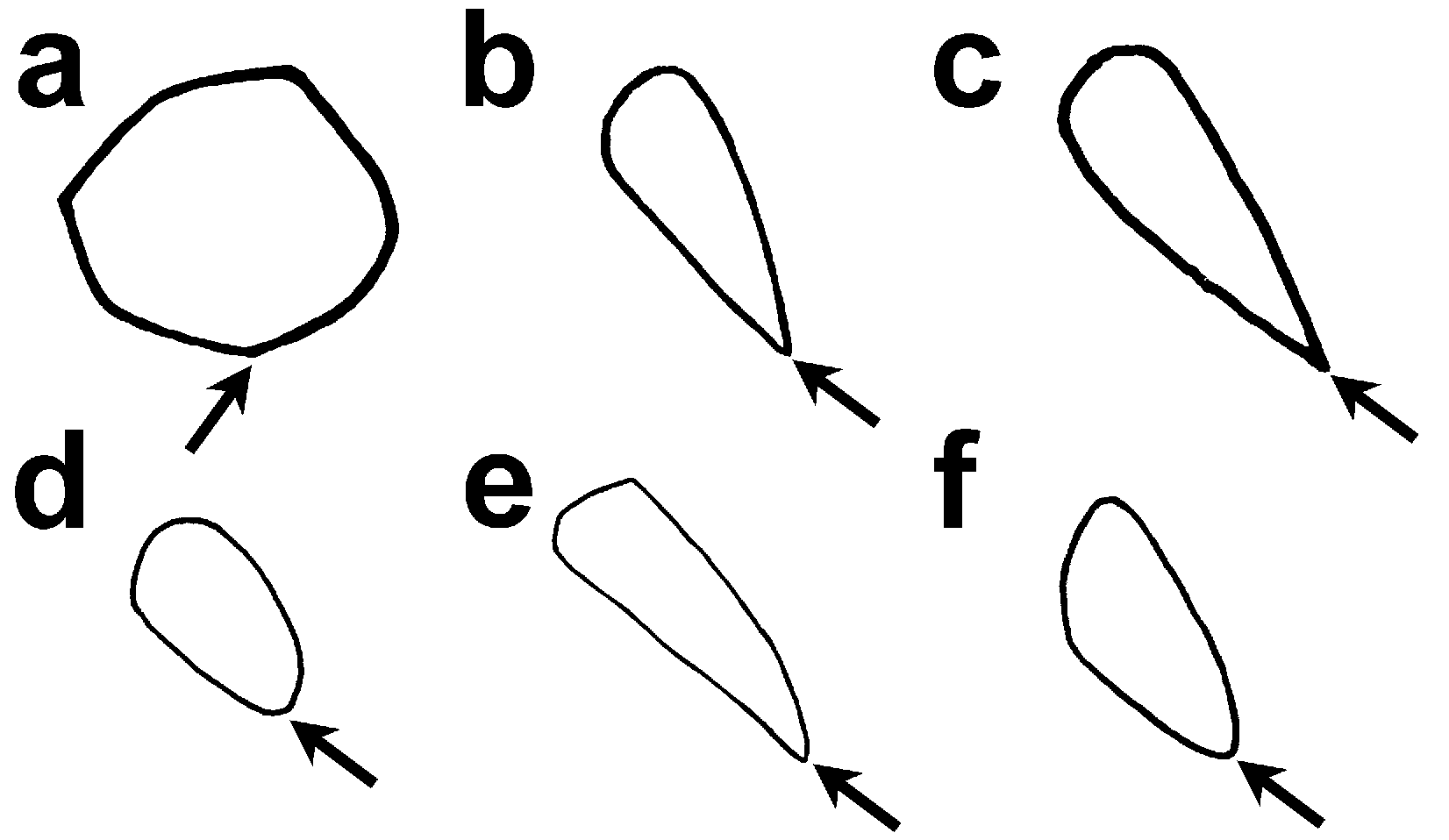
Remarks. Castle & McCosker (1999) divided Muraenichthys into Scolecenchelys and Muraenichthys and stated that Muraenichthys can be distinguished from two similar genera, Skythrenchelys and Scolecenchelys , by morphological characters including the shape and arrangement of teeth (blunt and multiserial in Muraenichthys ). Although M. gymnopterus and Muraenichthys hattae Jordan & Snyder 1901 have blunt and granular teeth, some species of Muraenichthys have pointed and conical teeth on their upper jaws ( Table 1; Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ). In addition, Muraenichthys philippinensis Schultz & Woods 1949 and Muraenichthys sibogae Weber & de Beaufort 1916 have uniserial teeth on their upper jaws. Consequently, we cannot regard the tooth morphology stated in Castle & McCosker (1999) as a synapomorphy or diagnosis of Muraenichthys . Castle & McCosker (1999) also defined that Muraenichthys has two or three preopercular sensory pores. In our examination, all currently valid species of the genus have three except for Muraenichthys macrostomus Bleeker 1864 has two. This species was transferred into Skythrenchelys by Hibino et al. (2013), such that all members of Muraenichthys have three preopercular sensory pores.
Muraenichthys can be distinguished from Scolecenchelys by the number of infraorbital sensory pores between the nostrils (one vs. two), the location of the eye (anterior to mid-jaw vs. posterior to mid-jaw), the shape and position of the posterior nostril (inner hole located above upper lip, outer hole usually opening outside of mouth with a projected flap anteriorly vs. inner hole located along upper lip or inside mouth, concealed by a dermal flap but without a prominent flap anteriorly) ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ); and from Skythrenchelys by the number of preopercular sensory pores (three vs. two), size and shape of teeth (length of largest tooth on upper jaw equal or less than a half of eye diameter and sometime weakly recurved vs. more than a half of eye diameter and strongly recurved), teeth on the maxilla (70% or less vs. 80% or more), shape and length of gill-opening (constricted vs. unconstricted; 170% of eye diameter or less vs. 200% or more).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Muraenichthys Bleeker 1853
| Hibino, Yusuke & Kimura, Seishi 2015 |
Muraenichthys
| Bleeker 1853: 505 |
Muraena gymnopterus
| Bleeker 1853 |