Jatropha curcas, L. Stem
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5252/adansonia2022v44a10 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6390572 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E087F9-FF83-FF8A-FCB5-F9E9FB6E2D41 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Jatropha curcas |
| status |
|
JATROPHA CURCAS L. View in CoL
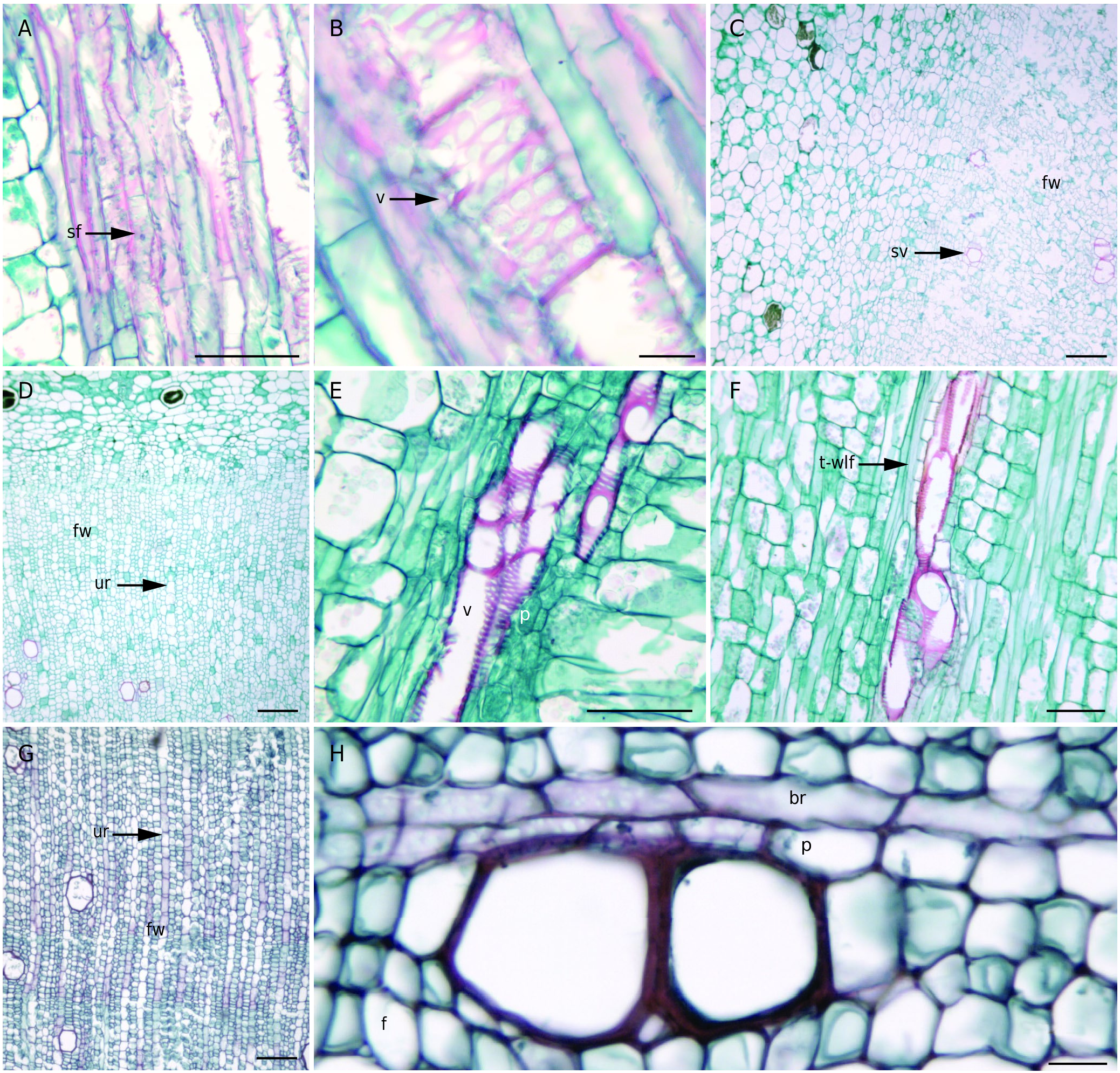
Stem cortex has scattered laticifers. Wood is just formed. Vascular cambium occurs in the entire circumference Some phloem is visible. Pith has some amyloplasts.
Caudex cortex is chlorenchymatous and it has druses and scattered laticifers. Wood is diffused fibrous. The axial matrix is formed by solitary or two vessels with circular bordered pits ( Fig. 2 View FIG C-E), also it has thin secondary wall libriform fibers ( Fig. 2F View FIG ) and apotracheal unilateral parenchyma with abundant amyloplasts. Ray system is uniseriate with abundant amyloplasts ( Fig. 2F View FIG ). Secondary phloem ray parenchyma has begun to dilatate. Laticifers run parallel to the secondary phloem. Primary phloem fibers are above secondary phloem, these fibers are gelatinous fibers and have formed an incomplete ring around caudex circumference.Pith has large parenchyma cells with abundant amyloplasts.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |