Arpactophilus futuna, Breitkreuz, Laura C. V., Ohl, Michael & Engel, Michael S., 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4063.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:80401ED8-C6BA-4420-9109-854C5CC1E88D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6088309 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E4FF4A-FF8E-FFD4-3FB9-FF00C316F9C3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Arpactophilus futuna |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Arpactophilus futuna View in CoL sp. nov.
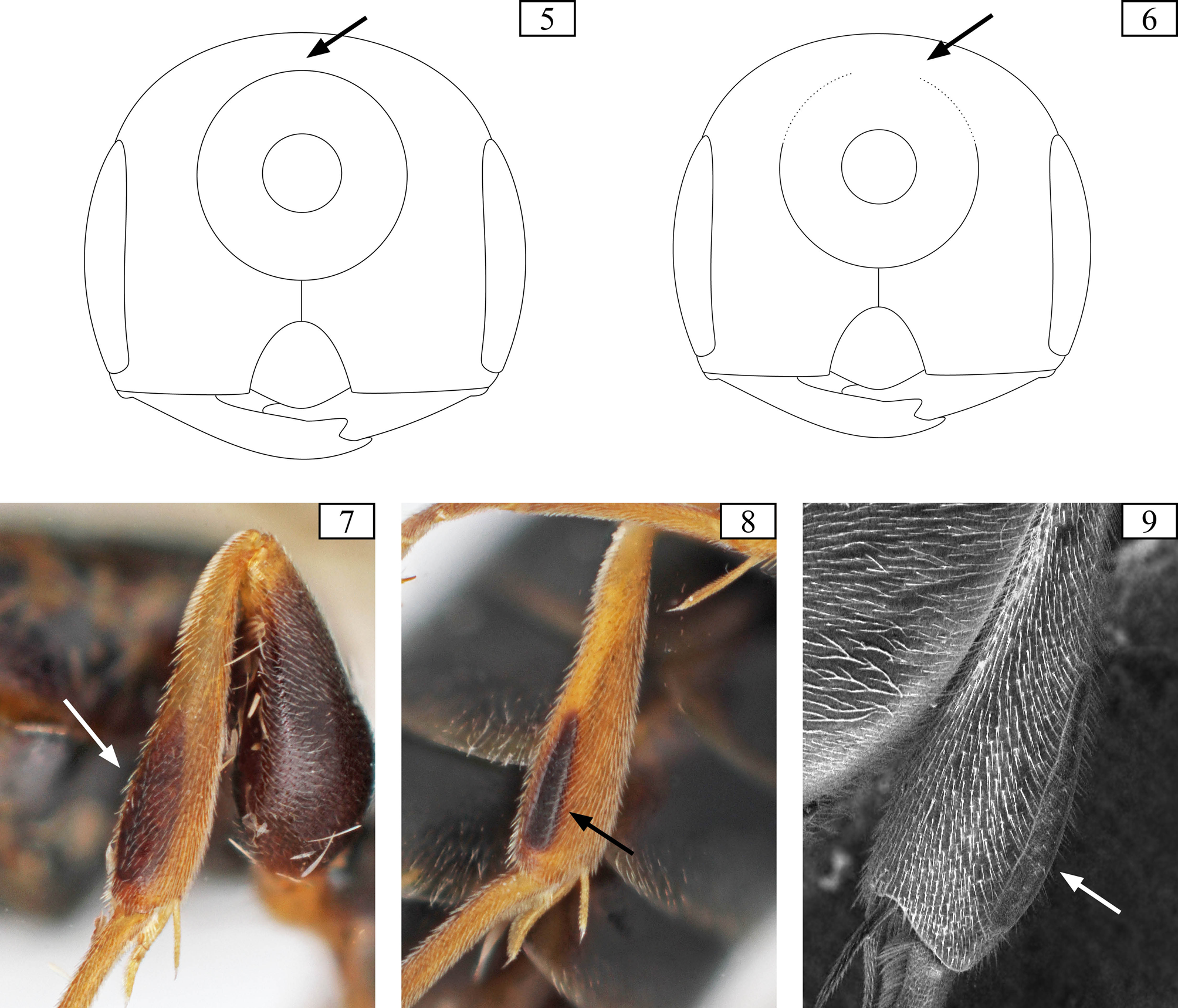
( Figs. 13 View FIGURES 10 – 15 , 53–54 View FIGURES 53 – 58 )
Diagnosis. Arpactophilus futuna is the only New Caledonian species in the genus with a thin, acutely rounded genal spine ( Figs. 13 View FIGURES 10 – 15 , 54 View FIGURES 53 – 58 ). Especially among the group of species with a reddish metasoma, a genal structure is unique.
Description. FEMALE: Total length 4.2 mm; forewing length 2.6 mm.
Body black and reddish-brown, with areas of yellow and brown. Yellow: mandible laterally at base; palpi; tegula; trochanters; femora partially; tibiae, except apical area on metatibia; tarsi. Brown: most of mandible (slightly reddish); anterior pronotal margin; pronotal lobe; coxae; femora partially; apical area on metatibia. Antenna light brown. Metasoma reddish brown ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 53 – 58 ). Wings hyaline; pterostigma light brown.
Head about 1.1 × as long as wide in frontal view. Apical margin of clypeus strongly projecting medially in a nearly straight line ( Fig. 53 View FIGURES 53 – 58 ). Apical margin of labrum slightly bilobed. Ventral mandibular tooth about ¼–1/5 of total mandibular length, not reaching opposite mandibular base. Palpal formula 5:4. Frons finely reticulate with dense punctation and short setae. Frontal carina present from median ocellus almost to apical margin of clypeus, forming small point at basal clypeal margin and a sharp, elevated ridge on apical half of clypeus. Scape 3.5 × as long as wide. Ocellar triangle anterior of tangent between upper posterior orbits of compound eyes, lateral ocelli anterior of tangent by less than their diameter. Occipital carina interrupted dorsally ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 5 – 9 ). Gena imbricate with sparse punctation and sparse setae; with a single thin, acutely rounded genal spine on either side ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 10 – 15 ). Hypostomal midventral line posteriorly carinate with bordering short transverse carinulae on hypostomal integument, slightly angulate medially.
Mesosoma about 1.7 × as long as wide in dorsal view. Propodeum about 0.8 × as long as wide in dorsal view. Mesosoma dorsally densely punctured, laterally carinulate ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 53 – 58 ), except on propodeum; lateral surface of propodeum transversely carinulate; dorsal surface of propodeum intermediately reticulate (similar to pattern in Fig. 19 View FIGURES 16 – 22 ). Pitted sulcus present posterior to mesoscuto-mesoscutellar sulcus. Hypersternal sulcus absent. Metafemur 2.7 × as long as wide. Metatibia with a light brown area apically. Pretarsal claws without teeth. Forewing with two submarginal cells; anterior border of submarginal cell II much shorter than posterior border, almost triangular shape. Hind wing with five distal hamuli.
Metasoma polished, punctation and associated setae sparse ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 53 – 58 ). Metasomal sternum II without bulge (as in Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 4 ). Pygidium with narrow row of silk setae.
MALE: Difference from female aside from genitalic structures: antenna and mandible lighter brown; metatibia without differently colored area apically. Metasomal sternum VIII narrow.
Remarks. Arpactophilus futuna can easily be identified by the presence of the genal spine, a feature unique among all known species of Arpactophilus . Interestingly, such genal tubercles in Apoidea are often found in macrocephalic individuals and yet the present series do not have heads that are disproportionately enlarged relative to other species or their own body sizes. Arpactophilus futuna is somewhat similar in body size and coloration to A. fagauvea but the mentioned genal spine is not present in the latter.
Material examined. HOLOTYPE ♀: “Nouvelle Calédonie, Pinda 30m, 18.IV.1995, Réc. Chazeau & Jourdan [ MNHN].
PARATYPES 2♂: “Nouvelle Calédonie, Pinda 30m, 18.IV.1995, Réc. Chazeau & Jourdan [ CAS, MNHN].
Etymology. The specific epithet is taken from the name Futuna , one of the New Caledonian native languages. It is treated as a noun in apposition.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |