Fittkauimyia mayumiae, Dantas, Galileu P. S. & Hamada, Neusa, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3681.5.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AED74FD0-05C5-4CB0-9CA6-E1F21CBA5390 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5629150 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E787AA-FF96-FFFA-FF38-FF3E783595B4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Fittkauimyia mayumiae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Fittkauimyia mayumiae new species
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 –3)
Type material. Holotype male, Brazil, Amazonas State, Novo Airão, Km 3 of the Ramal do Hotel Mercuri, 02º50'44,4"S, 60º54'56,9" W, 25/viii/2008, in decayed wood, G.P.S. Dantas, ( INPA, slide mounted in Euparal®). Paratypes: 1 male with pupal exuviae, as holotype except for 02/ix/2008; 1 male, as holotype except for 05/ix/ 2008; 1 female with pupal exuviae, as holotype except for 30/viii/2008.
Diagnosis. The male of F. mayumiae sp. n. can be distinguished from the other species of the genus by the combination of iridescent eyes; acrostichals confined from the anterior region to the scutal tubercle; antepronotum with 1 setae; scutellum with 9–11 setae; tibial comb on hind leg with 9–10; gonocoxite brown, gonostylus light brown and slightly covered with bristles in the 2/3 apical region. The pupae can be distinguished by the combination of anal lobe with fringe on both inner and outer border; 5 LS setae on segment VIII and all abdominal segments with shagreen.
Etymology. Named to honor Erika Mayumi Shimabukuro, a young biologist whose enthusiasm has made the work of the first author pleasant indeed.
Male (n = 3, except when otherwise stated).
Total length 4.43–4.60 mm. Wing length 1.97–2.10 mm. Total length/ wing length 2.12–2.25. Wing length/ length of profemur 1.89–1.95.
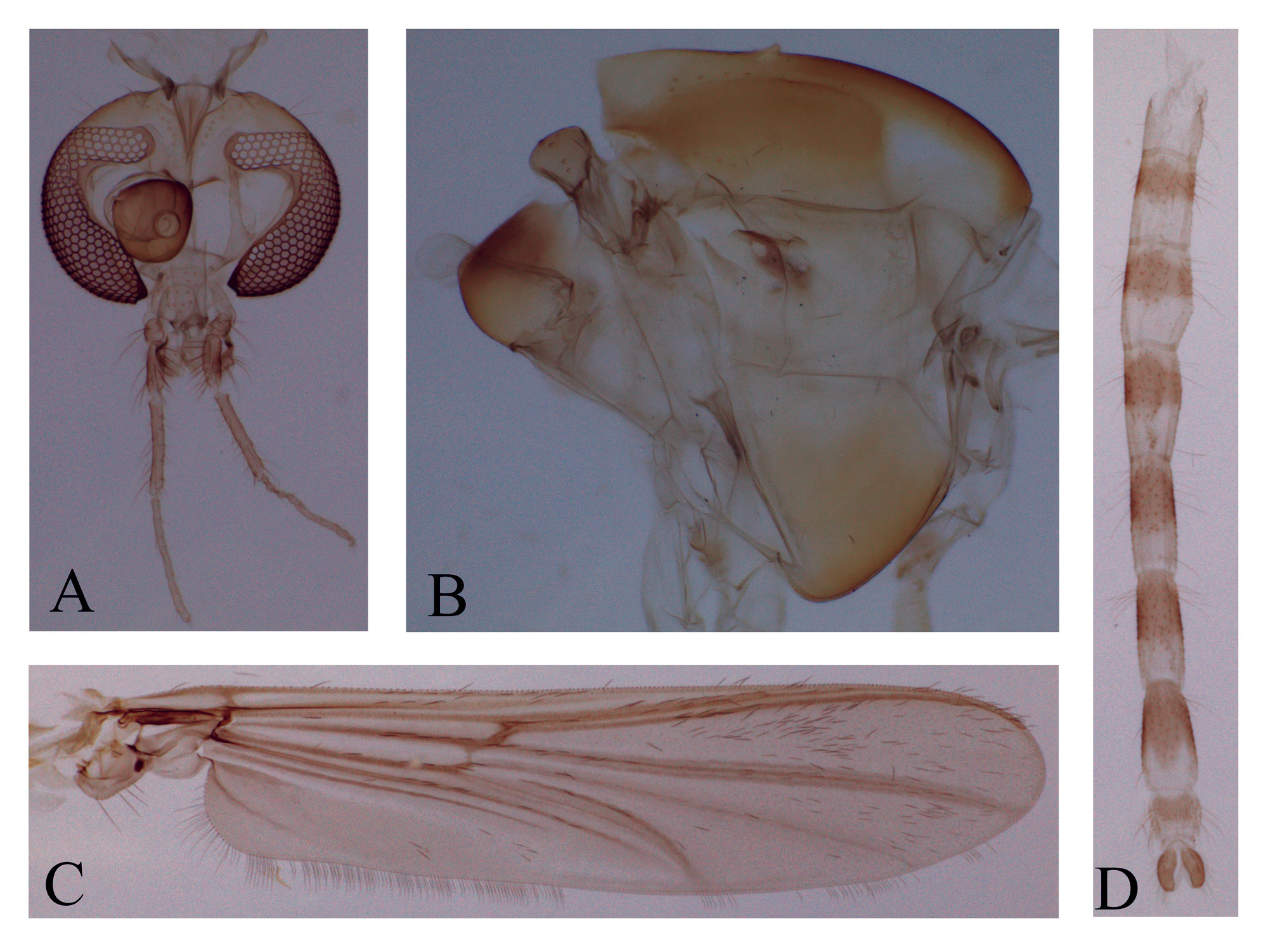
General coloration brownish. Eyes iridescent. Head, antennae, thorax, wings and legs brownish. Abdomen: T I pale, TII–TIV with anterior half brown, TV-TVII with anterior 2/3 brown, TVIII with anterior half brown, hypopygium brown ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D).
Head ( Fig 1 View FIGURE 1 A). AR 1.91–2.06. Thirteenth flagellomere 795–877 µm long. Apical flagellomere 81–96 µm long; 20–25 µm wide; with a subapical setae 55–61 µm long. Temporal setae 14. Clypeus with 15 setae. Tentorium 206 µm long; 45 µm wide at sieve pore; 17 µm wide at posterior tentorial pit. Palpomere lengths (1–5 in µm): 43–47; 49–55; 88–105; 178; 230.
Thorax ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B). Scutal tubercle present. Acrostichals 10–12, distributed between the anterior end of the scutum and the scutal tubercle; dorsocentrals 17, in a single irregular row; prealars 4–7, in a single row. Antepronotum with 1 setae. Scutellum with 9–11 setae, in two rows. Postnotum with 2 setae on posterior margin. Haltere with 12 setae.
Wing ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C). VR 0.92–0.96. Membrane with dense covering of macrotrichia except for cells r, m, r 2+3 and cu; C produced beyond apex of R4+5. Brachiolum with 3–4 setae. All veins with setae except for M–Cu. Squama with 16–18 setae.
Legs. Spur of fore tibia 55–60 µm long, with 16–18 teeth; spurs of middle tibia 50–54 µm long, with 11 teeth and 65–67 µm long, with 15–16 teeth; spurs of hind tibia 50–56 µm long, with 12–14 teeth and 58–62 µm long. Tibial comb on hind leg with 9–10 bristles, the lateral longer than the medial. Claws of fore and hind legs normal, sharply pointed; claws of middle leg spoon-shaped; pulvilli present. Lengths (in µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 1.
fe ti ta1 ta2 ta3 ta4
p1 1008–1118 1406–1483 1446–1497 630–578 468–524 311–363
p2 1301–1485 1473–1594 1442(1) 585(1) 347(1) 191(1)
p3 1170–1353 1700–1887 1516–1612 504–560 410–443 323–367 ta5 LR BV SV BR
p1 112–115 1.01–1.03 2.54–2.59 1.67–1.74 3.13(1)
p2 100(1) 0.98(1) 3.45(1) 1.92(1) 3.43(1)
p3 115–120 0.85–0.89 3.24–3.26 1.89–2.01 4.09(1) Hypopygium ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A). Gonocoxite elongated, subcylindrical and about 2.5 x as long as broad; 178–185 µm long; 68–69 µm wide. Gonostylus 95–108 µm long; basal 2/3 covered by hair, 2/3 apical slightly covered with bristles; megaseta 16–17 µm long. HR 1.71–1.87; HV 4.26–4.66.
Female (n =1). Total length 3.02 mm. Wing length 2.28 mm. Total length/ wing length 1.32. Wing length/ length of profemur 2.00. General coloration brownish. Eyes iridescent.
Head. AR 0.15. Apical flagellomere 114 µm long; 31 µm wide, with a pre-apical setae 66 µm long. Pedicel with 14 setae. Temporal setae 18. Clypeus with 18 setae. Palpomere lengths (1–3 in µm): 43; 54; 107.
Thorax. Scutal tubercle present. Acrostichals present; dorsocentrals 27, in two rows; prealars present. Scutellum with 17 setae, in two rows. Postnotum with 2 setae. Haltere with 12 setae.
Wing. VR 0.90. Wing membrane densely covered by macrotrichia except in cells r, m, r 2+3 and cu; C produced beyond apex of R4+5. Brachiolum with 11 setae and 20 sensilla campaniformia. All veins with setae except M-Cu. Squama with 17 setae.
Legs. Spur of fore tibia 67 µm long, with about 19 teeth; spurs of middle tibia 61 µm long, with 15 teeth and 74 µm long, with 19 teeth; spurs of hind tibia 61 µm long, with 16 teeth and 67 µm long, with about 13 teeth. Tibial comb with 10 bristles on hind leg. Claws of hind legs normal, sharply pointed, pulvilli present. Lengths (in µm) and proportions of legs are in Table 2 View TABLE 2 .
Genitalia ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B). Three spherical seminal capsules; spermathecal ducts separate for all of their length. T VIII with about 31 setae. Gonapophysis IX well developed; notum 141 µm long. Cercus 64 µm long and 28 µm wide.
Pupa (n = 1). Total length 5.58 mm. Coloration: cephalothorax and abdomen light brown. Cephalotorax. Thoracic horn (Fig. 3A) 413 µm long, maximum width 222 µm; plastron plate 65 µm long, 105 µm wide. Median suture granulose.
FIGURE 3. Fittkauimyia mayumiae sp. n. Pupa. A. Thoracic horn. B. Basal tubercle of D1-seta with sclerotized beak (left) and base of D2- and D3-setae (right) with large tubercles on tergite III. C. Abdomen, in dorsal view.
Abdomen (Fig. 3C). Tergite I–II with small field of very fine shagreen restricted to central area; tergite III–VIII with field of shagreen restricted to central posterior area; genital sac of male with shagreen on basal half. Tergite I with 4 pairs of D-setae, tergite II with 5 pairs of D-setae, all these setae short and taeniate. D1-setae somewhat taeniate on tergite III, 171 µm long; sclerotized and spiniform on tergite IV–VII, 74, 84, 90 and 96 µm long respectively, all arising from a more or less distinct tubercle; basal tubercle of D1-seta large with sclerotized beak on tergite III and IV (Fig.3B). D2- and D3-setae very long, about 2 times as long as the segment length and arising from large tubercles on tergite III and IV (Fig. 3B), short and not arising from tubercles on tergites V–VII, all taeniate. D4- and D5-setae short and taeniate on tergites III–VII. Segments I–VI with 2 pairs of taeniate L-setae, segment VII with 1 pair of taeniate L-setae, segment VIII with 5 pairs of taeniate L-setae. Lateral fringe with about 23 setae at the middle of segments II; with about 39 setae at the basal 2/3 of segment III; about 80–150 setae along each entire lateral margin of segments IV–VII; segment III with a single additional setae in posterolateral corner. Anal lobe 787 µm long and 339 µm wide; with fringe on both the outer and inner border. Male genital sac 182 µm long.
Larva unknown.
Systematic remarks. The male imago of F. mayumiae sp. n. resembles F. c r y p t a, since both have iridescent eyes and a similar coloration pattern, but can be differentiated by the distribution of the setae on gonostylus and the number of antepronotals and scutellar setae. The pupa of F. m a y u m i a e sp. n. resembles the pupa of F. nipponica by having all abdominal segments with shagreen and 5 LS setae on segment VIII, but in F. mayumiae sp. n. the anal lobe has fringe on both the outer and inner border, contrasting with F. nipponica that has fringe only on outer border.
Notes on species biology. The specimens of Fittkauimyia mayumiae sp. n. were obtained from decayed wood collected in small black water streams. Probably, larvae of the new species inhabit the surface of wood or in clefts in the bark, in which they are searching for or waiting for preys. The stream where the larvae were collected had an average width of 1.8 m, average depth of 0.14 m and average flow of 0.14 ms -1, and was characterized by acidic water (average pH = 4.74), low conductivity (average = 15 μScm -1), high concentration of dissolved oxygen (average = 6.45 mgL -1) and low temperature variation (average = 25.5 °C). The dominant substrate types in the stream beds were sand (average = 50%), coarse litter (average = 30%) and fine litter (average = 12%).
TABLE 2. Lengths (in µm) and proportions of leg segments of Fittkauimyia mayumiae sp. n. female (n = 1).
| te | ti | ta1 | ta2 | ta3 | ta4 | ta5 | LR | BV | SV | BR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 1189 | 1748 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| P2 1556 | 1909 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| P3 1438 | 2170 | 1739 | 643 | 500 | 192 | 70 | 0.80 | 3.81 | 2.07 | 4.04 |
| INPA |
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazonia |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |