MONACHULINA
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.158400 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6272775 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E8879E-9505-FFF5-FEE0-878F801CF97E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
MONACHULINA |
| status |
|
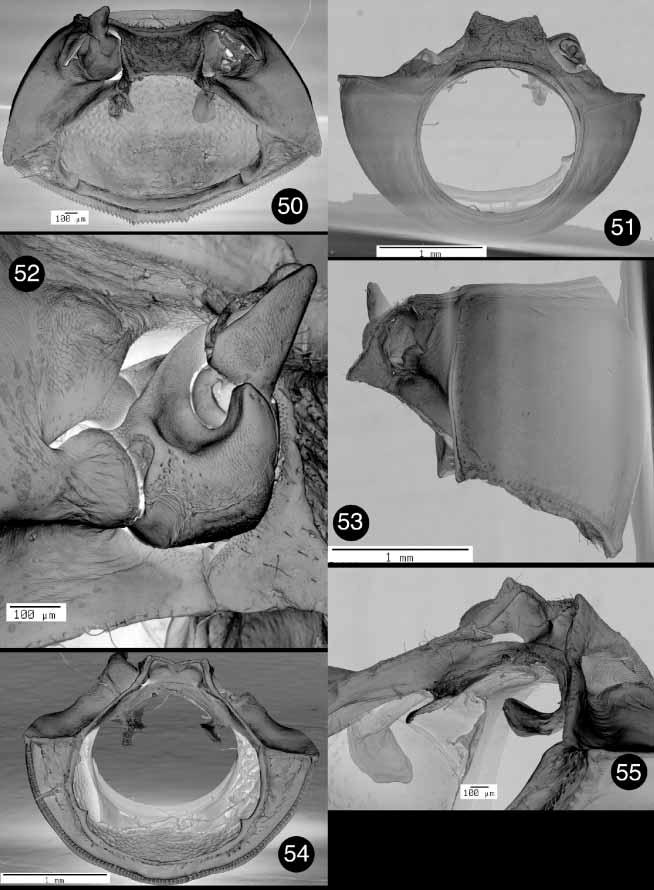
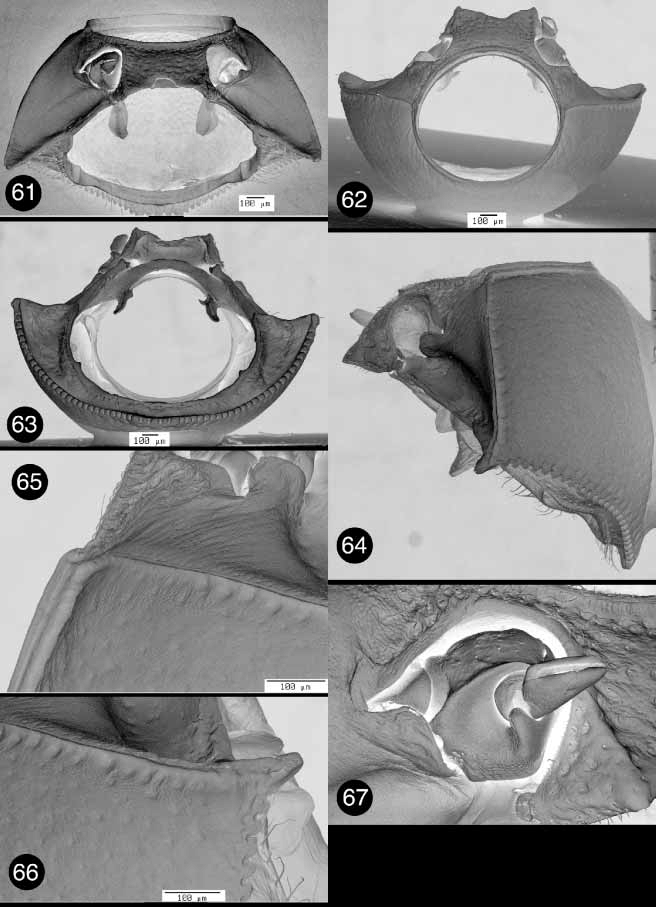
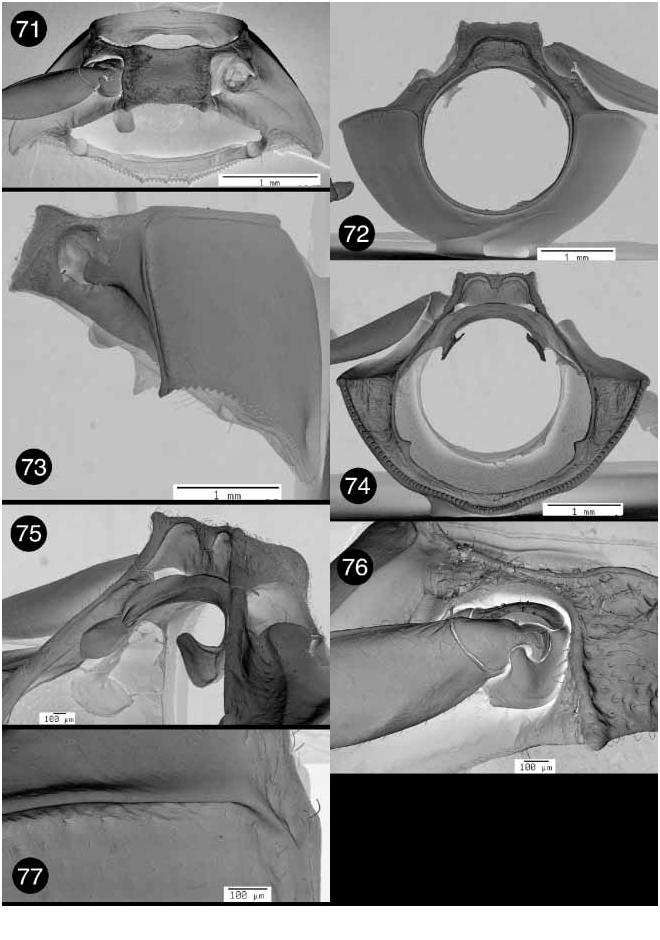
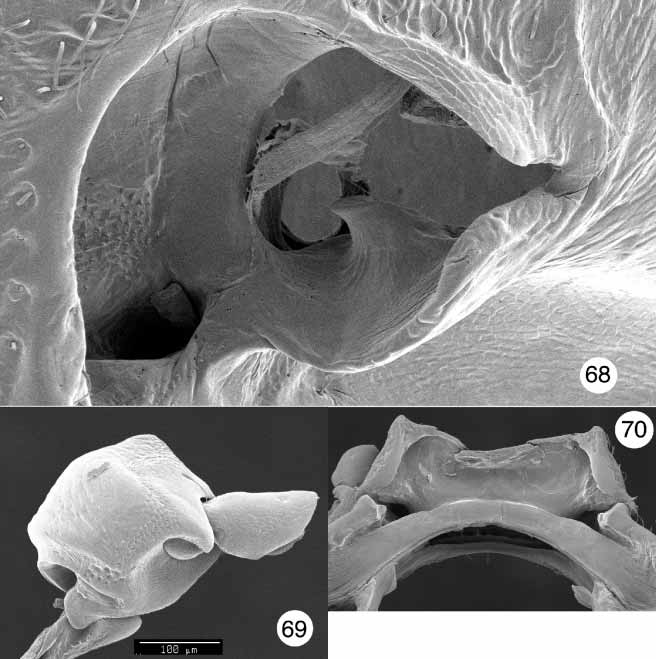
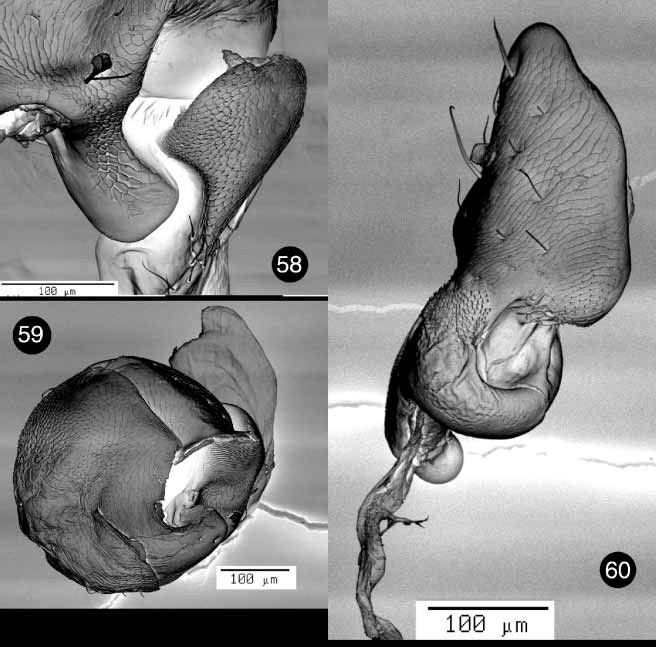
PRONOTUM: Denticles present on basal margin ( Figs. 54 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 63 View FIGURES 61 – 67 , 74 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 83); basal margin convex and truncate mesally, anteriad of mesoscutellum ( Figs. 53 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 64 View FIGURES 61 – 67 , 73 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 82); pronotal punctures distinct all over or absent, strongly pronounced on all margins. HYPOMERON: Hypomeral projection cylindrical ( Figs. 54 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 63 View FIGURES 61 – 67 , 74 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 83); hypomeron without apparent punctures ( Figs. 50 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 61 View FIGURES 61 – 67 , 71 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 81). PROSTERNUM: Intercoxal prosternal process truncate or bimodal; intercoxal prosternal process with caudal Mshaped rim ( Figs. 54 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 70 View FIGURES 68 – 70 , 74 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 83); prosternal opening wide, when viewed caudally ( Figs. 54 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 70 View FIGURES 68 – 70 , 74 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 83); posterior margin of intercoxal prosternal process concave, never projecting beyond hypomeron ( Figs. 50 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 61 View FIGURES 61 – 67 , 71 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 81); anterior margin of prosternum uniformly concave, with a medial flange, or with two submedial flanges ( Figs. 50 View FIGURES 50 – 55 , 61 View FIGURES 61 – 67 , 71 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 81); intercoxal width greater than width of coxal cavity. TROCHANTER: With a single dorsoproximal end ( Figs. 60 View FIGURES 58 – 60 , 84).
Stegnocephala: Pronotal punctures absent ( Figs. 71 View FIGURES 71 – 77 , 81). Intercoxal prosternal process truncate (Fig. 81); anterior margin of prosternum with a medial flange ( Fig. 71 View FIGURES 71 – 77 ), or two submedial flanges (Fig. 81).
Lexiphanes: Pronotal punctures distinct throughout ( Fig. 64 View FIGURES 61 – 67 ). Intercoxal prosternal process bimodal with small lateral projections ( Fig. 62 View FIGURES 61 – 67 ); anterior margin of prosternum uniformly concave ( Fig. 61 View FIGURES 61 – 67 ).
Heptarthrius: Pronotal punctures absent ( Fig. 53 View FIGURES 50 – 55 ). Intercoxal prosternal process bimodal ( Fig. 51 View FIGURES 50 – 55 ); anterior margin of prosternum uniformly concave ( Fig. 50 View FIGURES 50 – 55 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Cryptocephalinae |
|
Tribe |
Cryptocephalini |