Selenops micropalpus Muma, 1953
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2020.1844914 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EBB43509-9E17-4F75-920A-BE332F014705 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E97817-FF8E-1D70-FE1F-FE54FF65FB5F |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Selenops micropalpus Muma, 1953 |
| status |
|
Selenops micropalpus Muma, 1953 View in CoL
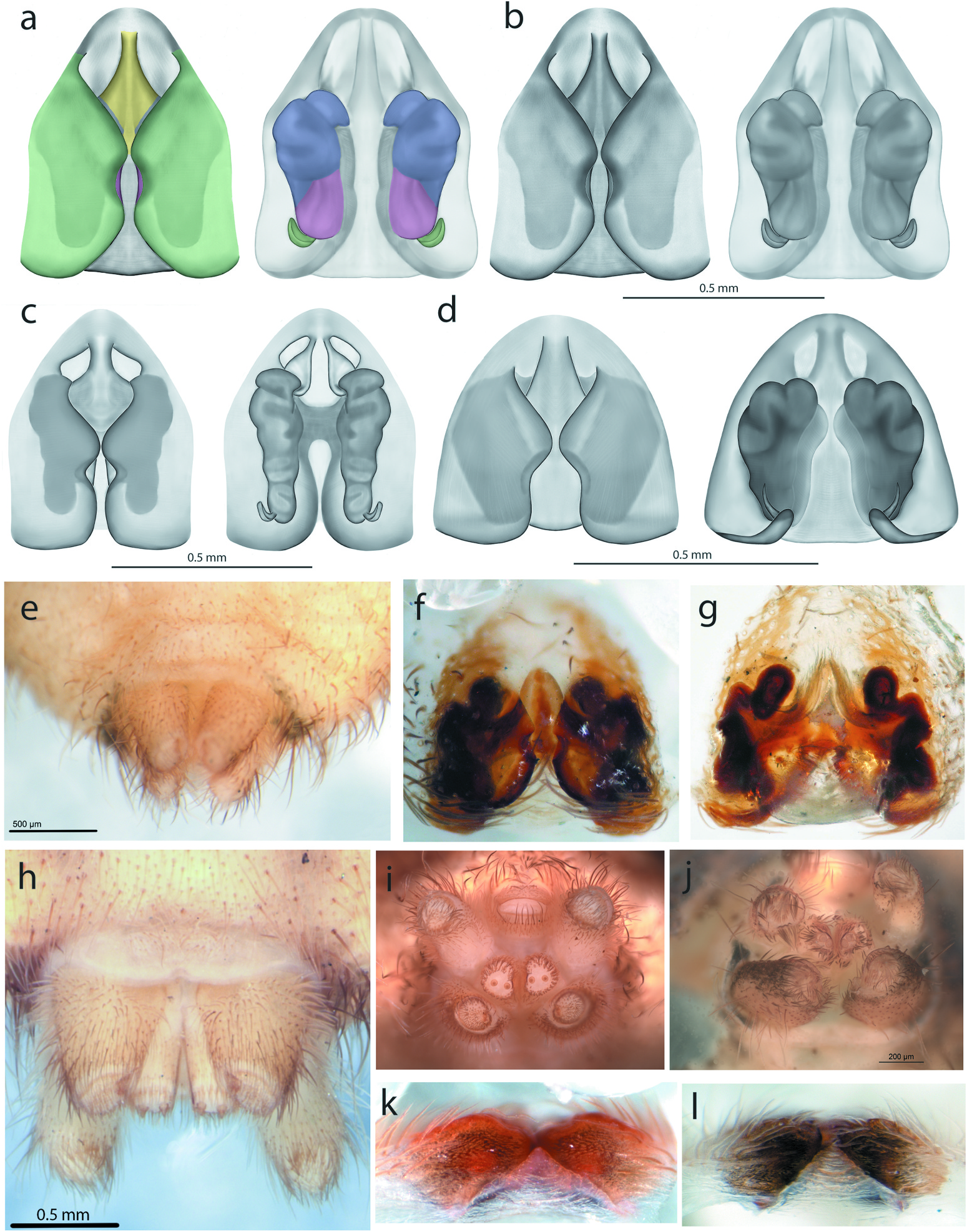
( Figures 1 View Figure 1 (f), 2(s–v), 3(e), 5(f), 6(c, j–k) and 7(d))
Selenops micropalpus Muma, 1953: 39 View in CoL , Figs 66–68 (♂ holotype and ♀ paratype from Laudat , Dominica, in AMNH, examined).
Selenops micropalpus Crews, 2011: 27 View in CoL , Figs 17–20, 180.
Diagnosis. Females of S. micropalpus differ from females of S. ducke and S. curruganja sp. nov. by the epigynal plate being longer than wide ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (c–d, f–g)). Females of this species differ from females of S. banksi by being grey in life and brown when preserved, whereas S. banksi is green in life and yellow-orange when preserved ( Figures 1 View Figure 1 (a–d, f) and 2(a–i, s–v)). Additionally, the copulatory ducts of S. micropalpus turn multiple times, in contrast to the copulatory ducts of S. banksi ( Figure 6 View Figure 6 (a–c)).
Males of S. micropalpus can be separated from males of S. ducke by the palpal tibia being longer than the cymbium, and the embolus and embolic process are completely separate, whereas in S. ducke , the palpal tibia is of similar size to the cymbium, and the embolus and embolic process are connected by a weakly sclerotised area ( Figures 3 View Figure 3 (e–h) and 5(d–f)). S. micropalpus can be separated from males of S. banksi by having fewer, more dispersed chemosensory setae on the tip of the cymbium and by the embolar process and embolus originating from the sides of the embolar base, gradually nearing one another distally ( Figures 3 View Figure 3 (a–d, e) and 5(a–c, f)).
See Crews et al. (2008) and Crews (2011) for full descriptions and natural history information.
Distribution. Southern Lesser Antilles: Dominica, Martinique, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines. For detailed locality data, see Crews (2011) and Crews (2018).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Selenops micropalpus Muma, 1953
| Crews, Sarah C., Galvis, William & Esposito, Lauren A. 2021 |
Selenops micropalpus
| Crews SC 2011: 27 |
Selenops micropalpus
| Muma MH 1953: 39 |