Bayerotrochus delicatus, Zhang, Suping, Zhang, Shuqian & Wei, Peng, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4161.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:826751C7-1E6B-4E5E-A158-7E282217CCA7 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5691275 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E9B249-FD48-FFAA-AAC8-FC5FFFC3FEF3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bayerotrochus delicatus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bayerotrochus delicatus View in CoL sp. nov.
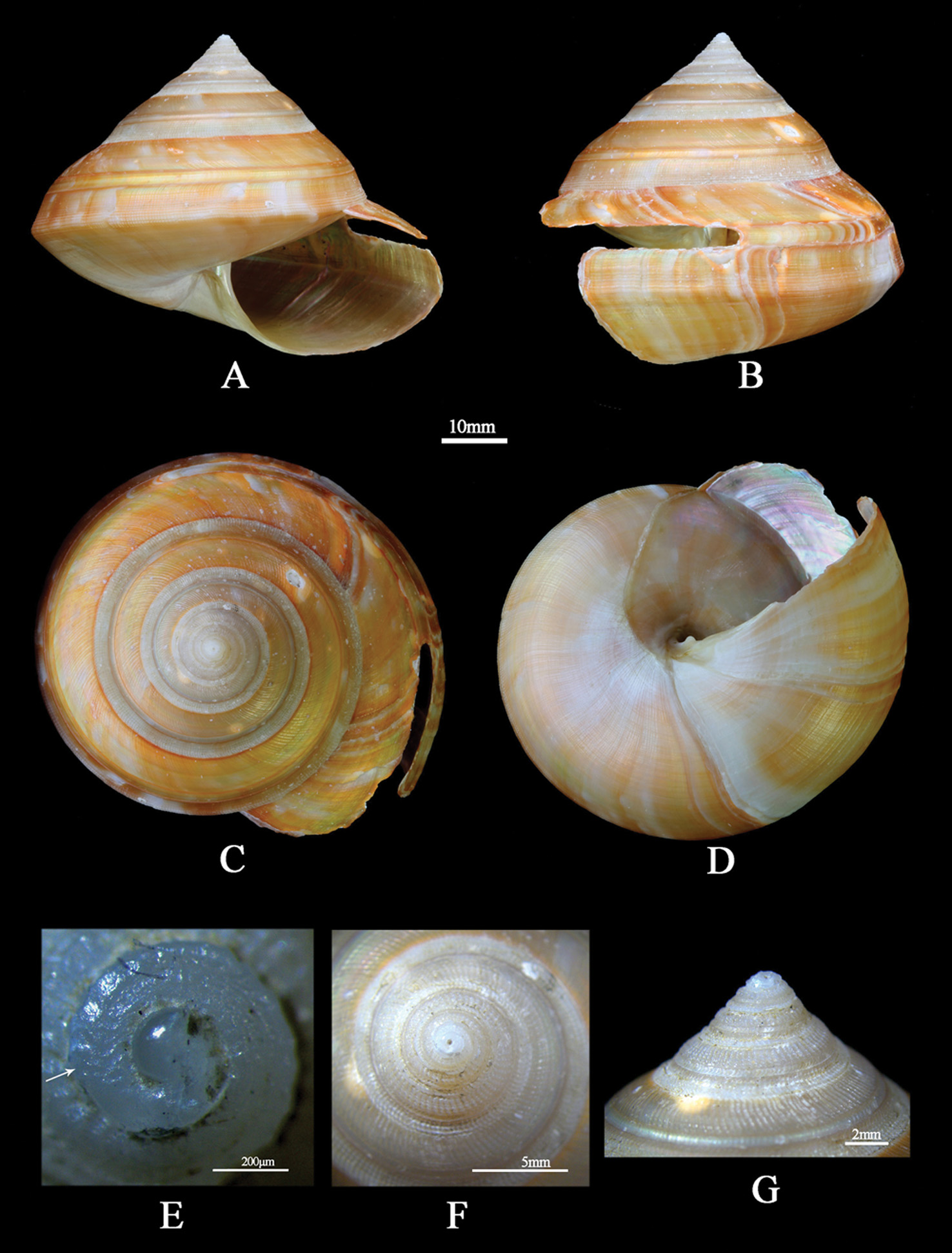
( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2A–C View FIGURE 2. A – C , 3 View FIGURE 3 , 4 View FIGURE 4 )
Type Material. Holotype: RN: MBM283051, CN: Y30109 View Materials ; height: 47.8 mm, maximum width: 62.1 mm, maximum basal diameter: 62.1mm, depth of slit along upper margin: 30.1 mm, depth of slit along lower margin: 24.2 mm; 8°51′N, 137°47′E, 255.3 m deep, hard bottom, December 22, 2014. Paratype: RN: MBM283052, CN: 30001; height: 45.4 mm, maximum width: 59.6 mm, depth of slit along upper margin: 29.1mm, depth of slit along lower margin: 23.0 mm; 8°51′N, 137°47′E, 289 m deep, hard bottom, December 12, 2014.
Distribution and habitat. Yap Seamount, near Palau, Western Pacific, where the specimens were collected at depth of 255.3–289 m on hard bottom.
Etymology. The name of new species refers to its delicate sculpture.
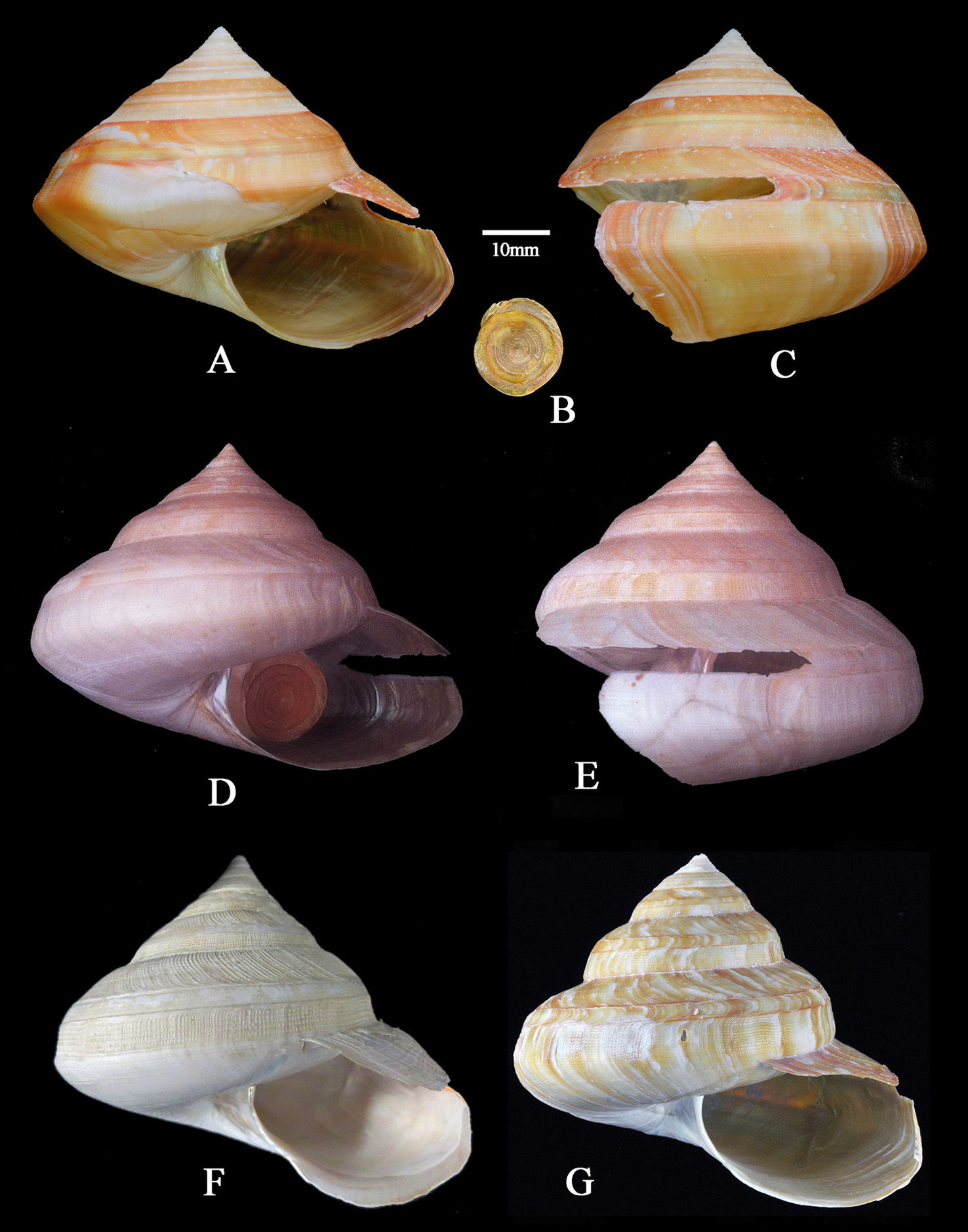
Description Shell ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 ; 2A–C). Shell small sized for genus (height up to 47.8 mm, width up to 62.1 mm), depressed trochoid in shape, thin and fragile; consisting of 8.25 whorls. Apical angle of first four whorls 83°; mean spire angle 95°. Protoconch slightly eroded, of about one glassy, non-sculptured whorl, protoconch/teleoconch discontinuity distinct.
Teleoconch of 7 flattened to slightly convex whorls, sculptured with spiral cords crossed by axial ribs that well developed on the first four teleoconch whorls, forming squarish, rectangular interspaces with pronounced beads where they intersect; of the spiral cords, the suprasutural one on second and third whorl is more developed than others. From fifth whorl on, spiral cords become obsolete above selenizone; below selenizone, sculpture consists of axial ribs crossed by 8–10 spiral cords; of these, the three cords near the suture are separated by narrower spaces than that between others. Selenizone bordered by two raised lines, sculptured with close-set, backward-curving incremental lines, and spiral traces. Shell profile straight. Shell surface lustrous orange mottled with iridescence, axial orange flammules exclusively present on shell surface near the aperture.
Aperture ovate in shape, inner surface iridescent. Slit short, 30.1 mm along upper margin; 24.2 mm along lower margin. Umbilicus closed. Basal disk slightly convex, with numerous faint growth lines and spiral threads.
Operculum brown, sub-circular in shape, with central nucleus.
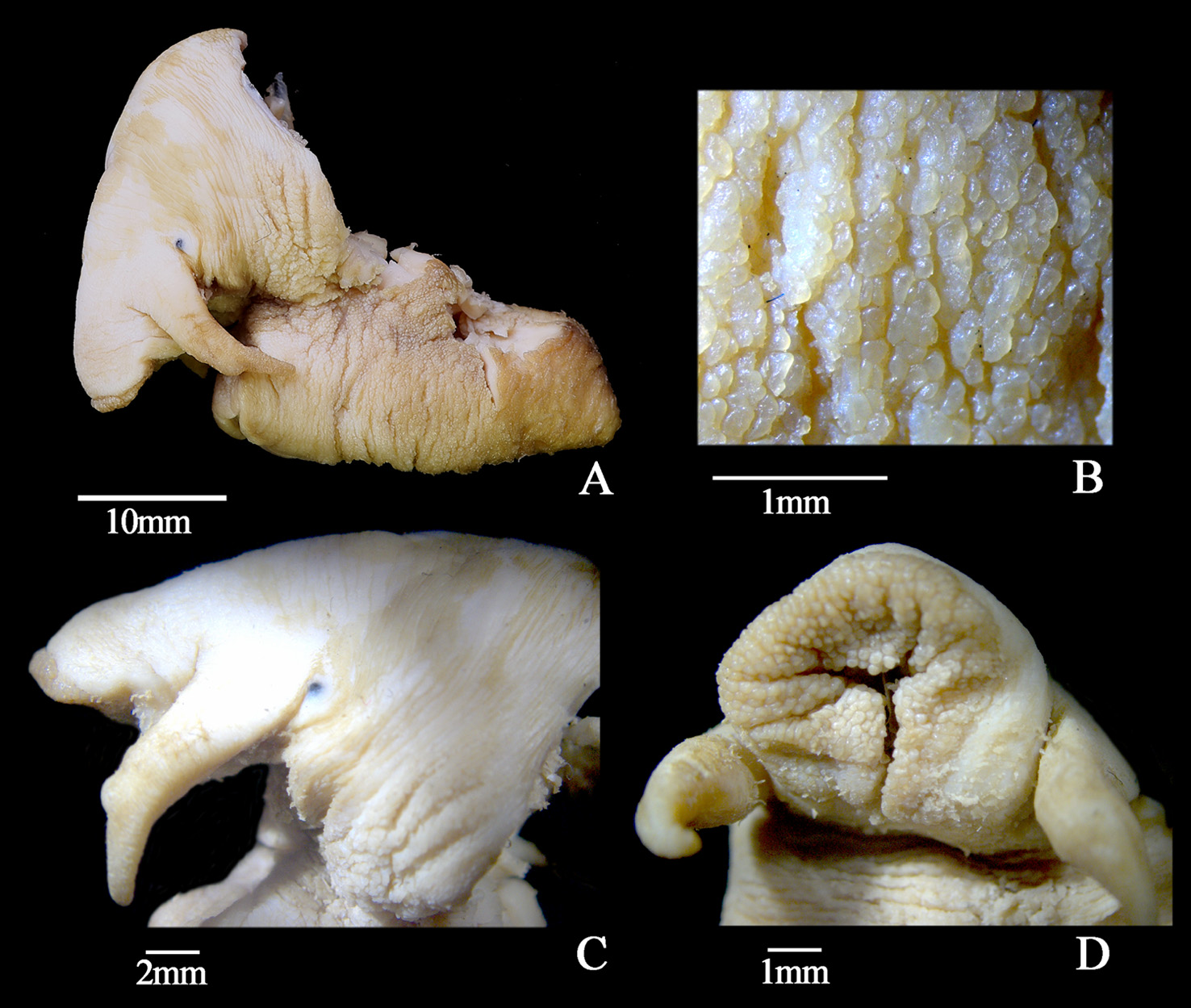
Radula ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ): Radular formula: R + 3 + 23 + (ca. 30) +(ca. 65) + 9, composing 5 distinct groups of teeth on either side of the single rachidian, referred to as inner laterals, outer laterals, sickle teeth, filament-tipped teeth and paddle-shaped teeth. Right side of each row skewed anteriorly. Rachidian with broad shaft and acute tip. Inner laterals subequal in size, with truncate tip. Outer laterals at first decreasing and then increasing in size, very short.
Sickle teeth very long and slender, firstly increasing and then decreasing in size; inner sickle teeth simple, outer ones with two hooks near the distal end. Filament-tipped teeth and paddle-shaped teeth equal in size, respectively.
Head-foot ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ). The head off-white in colour mottled with beige patches. Snout cylindrical, the ventral surface of the snout flattened and equipped by numerous papillae. Mouth trilobate. Tentacles long, tapering; left tentacle with a papilla-like structure on one-third from distal end. Eyes black, situated on eye lobe that is separated from tentacle. Foot short and narrow, trapezoidal in shape, with beaded lateral surfaces. The lower part of the head and the lateral surface of foot mottled with pale to dark tan.
Remarks. Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. is characterised by its small sized, depressed shell with delicate sculpture, its straight shell profile, a mean spire angle of 95°, the teleoconch whorls being lustrous orange mottled with iridescence, its wide slit, and the ratio of the slit length to circumference of the body whorl being around 1/6.6. These characters distinguish Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. from other congeners.
Bayerotrochus tangaroana ( Bouchet & Metivier, 1982) (see fig. 2F) resembles Bayerotrochus delicatus View in CoL sp. nov. in general sculpture pattern. From the new species, however, Bayerotrochus tangaroana differs in having convex whorls with impressed suture, in having a rounded rather than an angular periphery of the body whorl, in having a much coarser sculpture, a more circular aperture with expanded and reflected basal lip, and a different colour pattern.
Bayerotrochus delicatus View in CoL sp. nov. is smiliar to juvenile specimens of Bayerotrochus westralis ( Whitehead, 1987) View in CoL in general shell shape (ratio of diameter to number of whorls is around 8), but can be distinguished from Bayerotrochus westralis View in CoL (see figs. 2D, E) in having a different colour pattern and sculpture pattern. The shell of the new species is coloured with lustrous orange that is mottled with iridescence, axial orange flammules exclusively occur near the aperture, and the shell surface is sculptured with spiral cords crossed by axial ribs forming squarish, rectangular interspaces with pronounced beads on first four teleoconch whorls, and spiral cords lacking above selenizone from the fourth whorl on. These characters not present in Bayerotrochus westralis ( Whitehead, 1987) View in CoL .
Bayerotrochus delicatus View in CoL sp. nov. resembles Bayerotrochus philpoppei Anseeuw, Poppe & Goto, 2006 View in CoL in shell size, but can be differentiated from it in having a different apical profile, flattened rather than much more convex teleoconch whorls, a much broader slit (3.90 mm vs. 2.35 mm) and a different ratio of slit length to circumference of the body whorl (1/ 6.6 in the new species vs. 1/ 6.3 in Bayerotrochus philpoppei View in CoL ).
Bayerotrochus delicatus View in CoL sp. nov. is also similar to Bayerotrochus boucheti ( Anseeuw & Poppe, 2001) View in CoL in general shape. However, Bayerotrochus boucheti View in CoL differs from the new species in having much larger shell, a different mean spire angle, a gradate rather than a straight shell profile, and a different ratio of slit length to circumference of the body whorl (1/ 5.7 in Bayerotrochus boucheti View in CoL vs. 1/ 6.6 in the new species).
Some sculpture pattern on parts of teleoconch indicate the new species maybe related to Bayerotrochus teramachii ( Kuroda, 1955) View in CoL , but the new species clearly differs it in having much weaker spiral threads on basal disc surface, different color pattern and different radula formula (R+3+23+ca.30+ca.65+ 9 in new species vs. R+3+18+12+33 + 8 in Bayerotrochus teramachii View in CoL ) (see Anseeuw & Goto 1996: 157; Kuramochi et al. 1996: 113, photos 8–10). In addition, Bayerotrochus delicatus View in CoL sp. nov. can be separated from Bayerotrochus teramachii View in CoL by molecular features (see blow)
It is worth mentioning that two pleurotomariid specimens collected from Palau Island were identified as Bayerotrochus africanus teramachii by Okutani & Kurata (1998). Recently, Harasewych (personal communication) also collected a Bayerotrochus teramachii -like specimen from Palau that appears to belong to the same species as Okutani & Kurata’s specimens according to shell size, shape and general sculpture (see Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2. A – C G). Molecular data show that the COI sequence of Harasewych’s specimen from Palau is different from that of Bayerotrochus teramachii ( Kuroda, 1955) (see below). Thus, the Harasewych’s specimen together with Okutani & Kurata’s specimens perhaps represent an undescribed species. These specimens seem to be the geographically closest species to Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. However, the mean K2P genetic distance between Harasewych’s specimen and Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. shows that they belong to distinct species (see below). Morphologically, Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. differs from these specimens in having smaller shell with straight profile and a much more delicate shell sculpture.
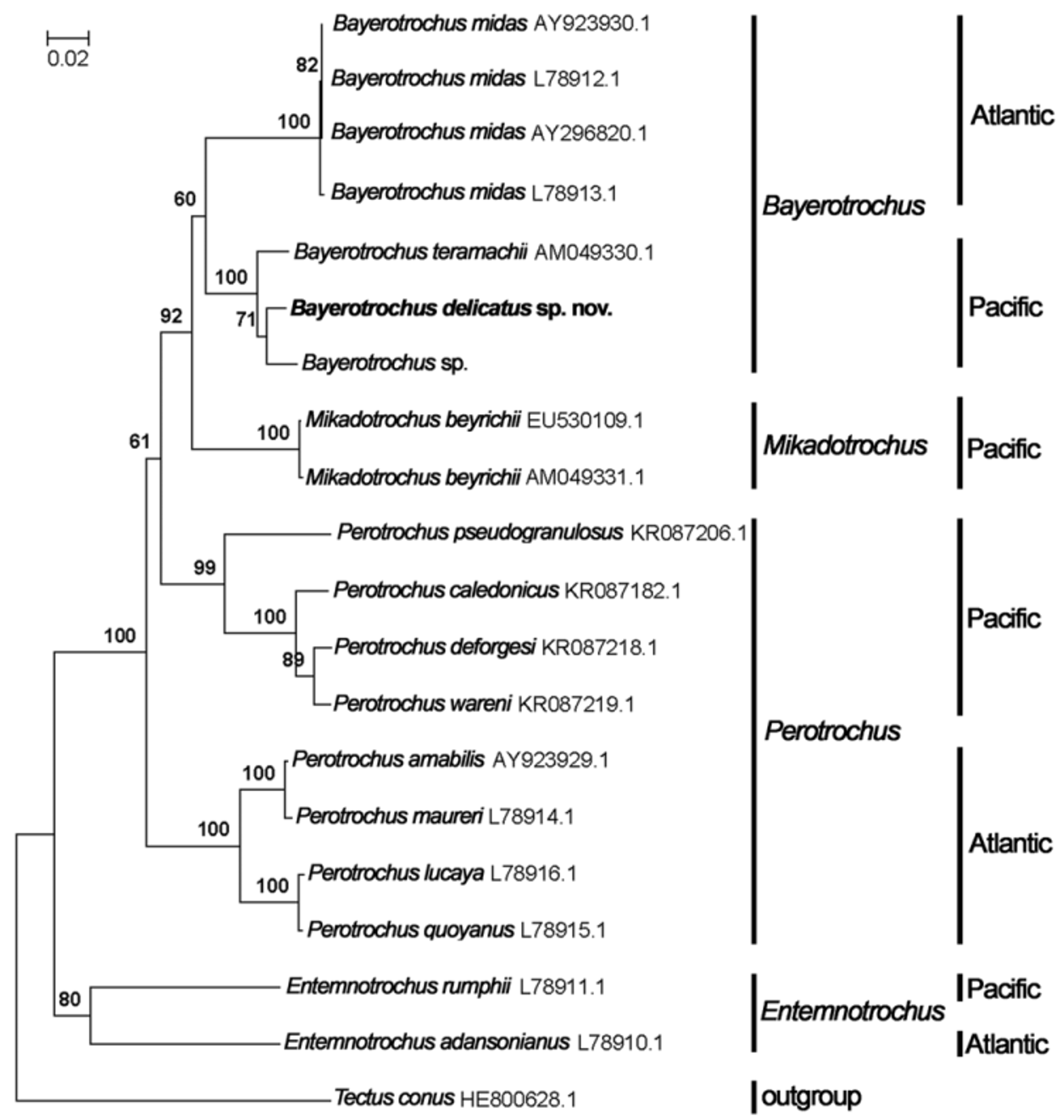
Molecular analyses. One sequence type was obtained for the COI region in Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. The length of the COI sequence of Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. is 636 bp. The Neighbor-joining (NJ) tree ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ) was reconstructed using available COI sequences from this study and GenBank. The alignment of COI had a total 480 bp. The NJ tree shows that the new species falls into the genus Bayerotrochus in which Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. together with Bayerotrochus sp. form a sister group of Bayerotrochus teramachii . The mean K2P genetic distance between Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. and Bayerotrochus teramachii is 3.0%; between Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. and Bayerotrochus sp. is 2.3 %; and that between Bayerotrochus teramachii and Bayerotrochus sp. is 3.2%. Although the K2P genetic distance among Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov., Bayerotrochus teramachii and Bayerotrochus sp. is much less than those distances between Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. and other pleurotomariids (9.1%–23.6%). However, considering the intraspecific conservation of COI sequence in pleurotomariid species (intraspecific distance <1%), the distance is sufficient to warrant a separation of Bayerotrochus delicatus sp. nov. from Bayerotrochus teramachii and Bayerotrochus sp. Anseeuw et al. (2015) pointed out that the four Perotrochus species from New Caledonia are not convergent with those Perotrochus species from Atlantic, which is confirmed by the present study.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Bayerotrochus delicatus
| Zhang, Suping, Zhang, Shuqian & Wei, Peng 2016 |
Bayerotrochus philpoppei
| Anseeuw, Poppe & Goto 2006 |
Bayerotrochus boucheti (
| Anseeuw & Poppe 2001 |
Bayerotrochus westralis (
| Whitehead 1987 |
Bayerotrochus westralis (
| Whitehead 1987 |
Bayerotrochus westralis
| Whitehead 1987 |
Bayerotrochus tangaroana (
| Bouchet & Metivier 1982 |
Bayerotrochus tangaroana
| Bouchet & Metivier 1982 |
Bayerotrochus teramachii (
| Kuroda 1955 |