STYLOCHIDAE Stimpson, 1857
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930500081997 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E6427790-6DB4-4633-AD85-7A5FB041FF2D |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EB1969-0302-FFE6-B6A4-E184CF1DFC59 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
STYLOCHIDAE Stimpson, 1857 |
| status |
|
Family STYLOCHIDAE Stimpson, 1857 View in CoL
Diagnosis (emend. nov.)
Stylochoidea , most with great dorsal resemblance, namely a basic colour with irregularly reticulated darker spots or streaks. Tentacles lie rather forwards. Ruffled pharynx usually highly folded, more or less centrally orientated in the body. Male copulatory apparatus directed backwards, prostatic vesicle with long-fingered extensions having polyglandular outlets or having tubes each with a central, monoglandular duct; prostatic glands extravesicular. Gonopores in the second body half.
Remarks
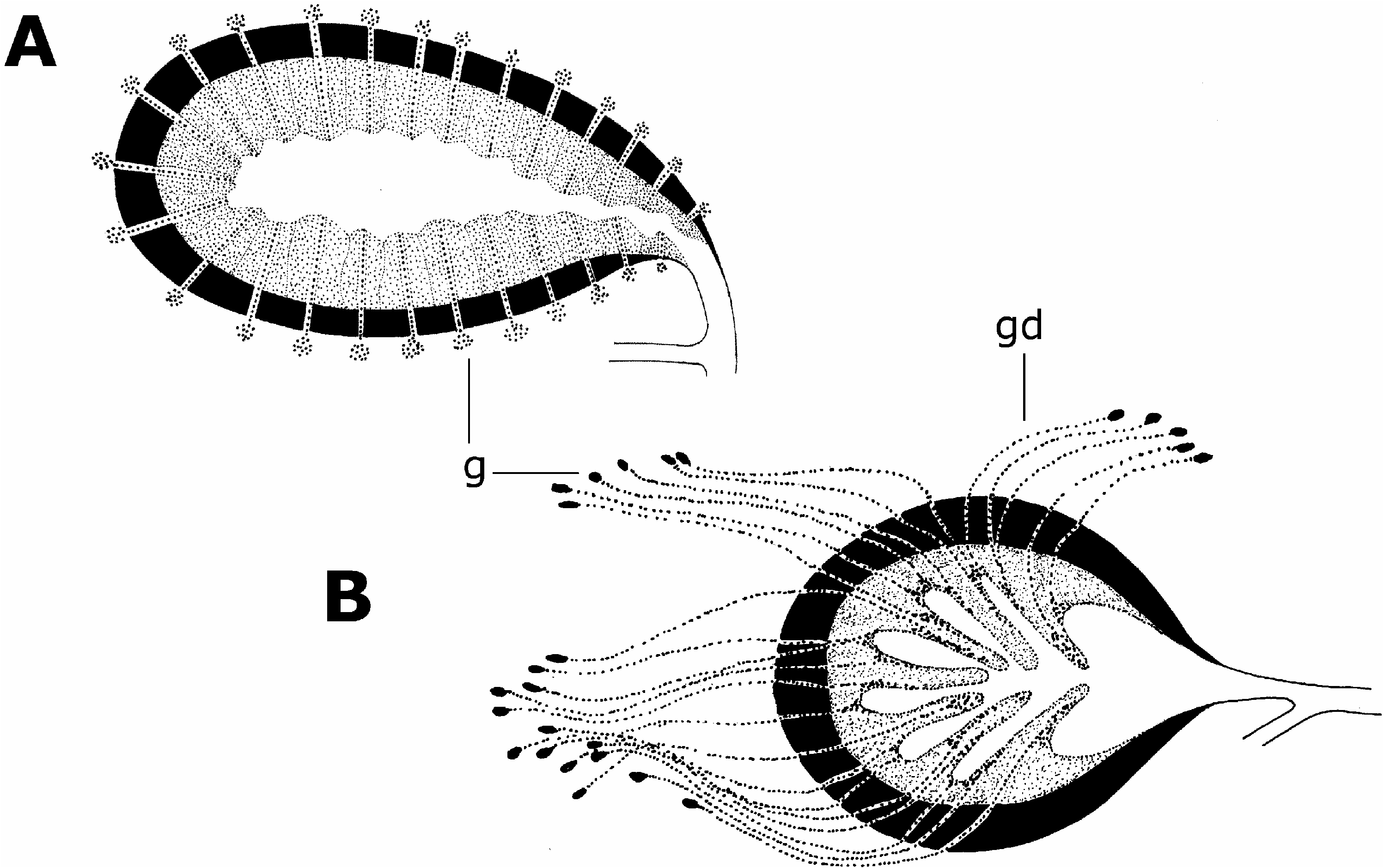
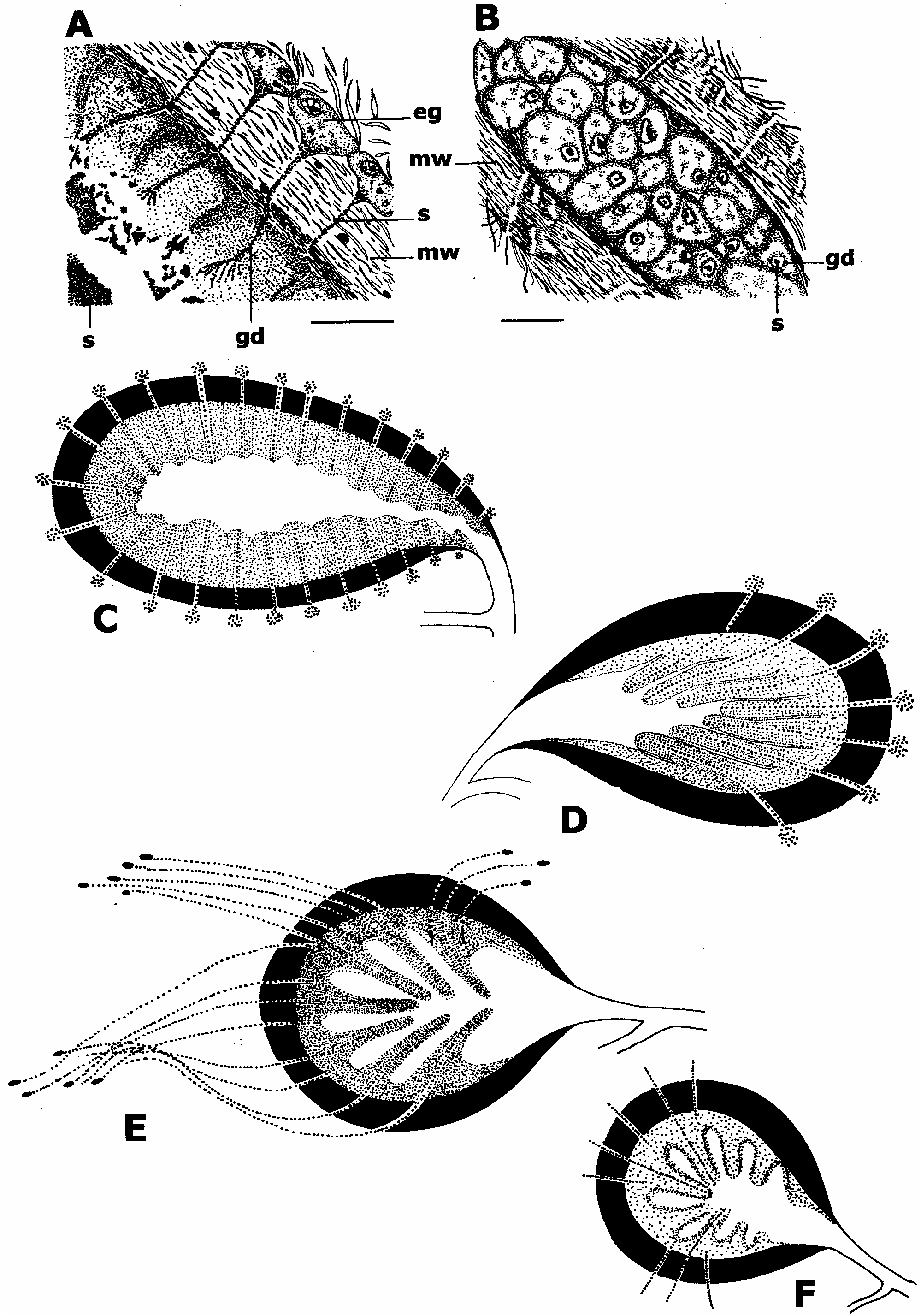
The species of the family Stylochidae are characterized by two different types of prostatic vesicle regarding the inner glandular lining and the appropriate extra-vesicular glands, namely the polyglandular type and the monoglandular type.
The monoglandular type ( Figures 1A View Figure 1 , 3D View Figure 3 ) represents a roundish to elongate prostatic vesicle surrounded by a strong muscular wall. The interior lining consists of either long, finger-like tubes ( Figure 3D View Figure 3 ), arising from the proximal half of the vesicle or of short tubes radially arranged around the inner muscular wall ( Figure 1A View Figure 1 ). Each tube has a central duct with single opening at the distal tip of the tube. The central duct is connected to a single extra-vesicular gland, therefore the number of extra-vesicular glands and inner tubes is identical. The extra-vesicular glands have small and rounded cell-bodies lying immediately on the external surface of the muscular wall.
The polyglandular type ( Figure 1B View Figure 1 ) consists of a mostly roundish to oval vesicle with few, long, finger-like extensions of the proximal lining of the prostatic vesicle. The finger-like extensions are directed distad more or less horizontally. The whole interior glandular lining of the prostatic vesicle is supplied by glandular ducts of extra-vesicular glands which cross the well-developed muscular wall of the prostatic vesicle. The glandular cell-bodies of the extra-vesicular glands are localized more or less distant in the parenchyma surrounding the male apparatus. The number of finger-like extensions is considerately fewer than the number of extra-vesicular glands.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.