Conicera, Meigen, Meigen, 1830
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5380.5.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:ACB1AD75-CC1F-424C-81BD-D6DC77330F30 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10280206 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F087C5-FFDC-E73A-FF35-2CEEF7BCAAAF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Conicera |
| status |
|
Key to species View in CoL View at ENA ( ♂)
1. Vein Rs with basisetula ( Fig. 30D View FIGURES 30 )....................................................................... 17
Vein Rs without basisetula.............................................................................. 2
2. Posterior face of mid femur with sense-organ ( Figs. 24D View FIGURES 24 , 27D View FIGURES 27 )................................................. 3
Posterior face of mid femur without sense-organ............................................................. 7
3. Sense-organ of mid femur including a rounded pit (or groove) and a apical process................................. 4
Sense-organ of mid femur only with a groove, but without a apical process........................................ 6
4. Sense-organ composed of a long groove and a long apical process ( Fig. 24D View FIGURES 24 )...................... C. formosensis Brues
Sense-organ with a rounded pit and a short apical process..................................................... 5
5. Sensory pit large, its diameter more than 1/2 width of mid femur ( Fig. 26D View FIGURES 26 ); the aspect ratio of first flagellomere is 3:1.......................................................................................... C. tibialis Schmitz
Sensory pit small, its diameter less than 1/2 width of mid femur ( Fig. 25D View FIGURES 25 ); the aspect ratio of first flagellomere equaled to or less than 2:1.......................................................................... C. simili s (Haliday)
6. The naked area at the base of posterior face of mid femur extends to half length of mid femur; the sensory groove is short and broad ( Fig. 27D View FIGURES 27 ); basidorsal process of right surstylus long and finger-like ( Fig. 27C View FIGURES 27 ).................. C. kempi Brunetti
The naked area at the base of posterior face of mid femur extends to one third of mid femur; the sensory groove is long and narrow ( Fig. 28B View FIGURES 28 ), basidorsal process of right surstylus short, rectangular ( Figs. 28D, F View FIGURES 28 ).............. C. rectangularis Liu
7. The base part of left surstylus is equaled to or broader than the apical part........................................ 8
The base part of left surstylus is significantly contracted and narrower than the apical part........................... 11
8. Left surstylus with a long, band-shaped basiprocess; posterior edge of left and right surstyli with 7–8 teeth respectively.... 9
Left surstylus without a long band-shaped basiprocess; posterior edge of left and right Surstyli only with1–4 teeth respectively......................................................................................... 10
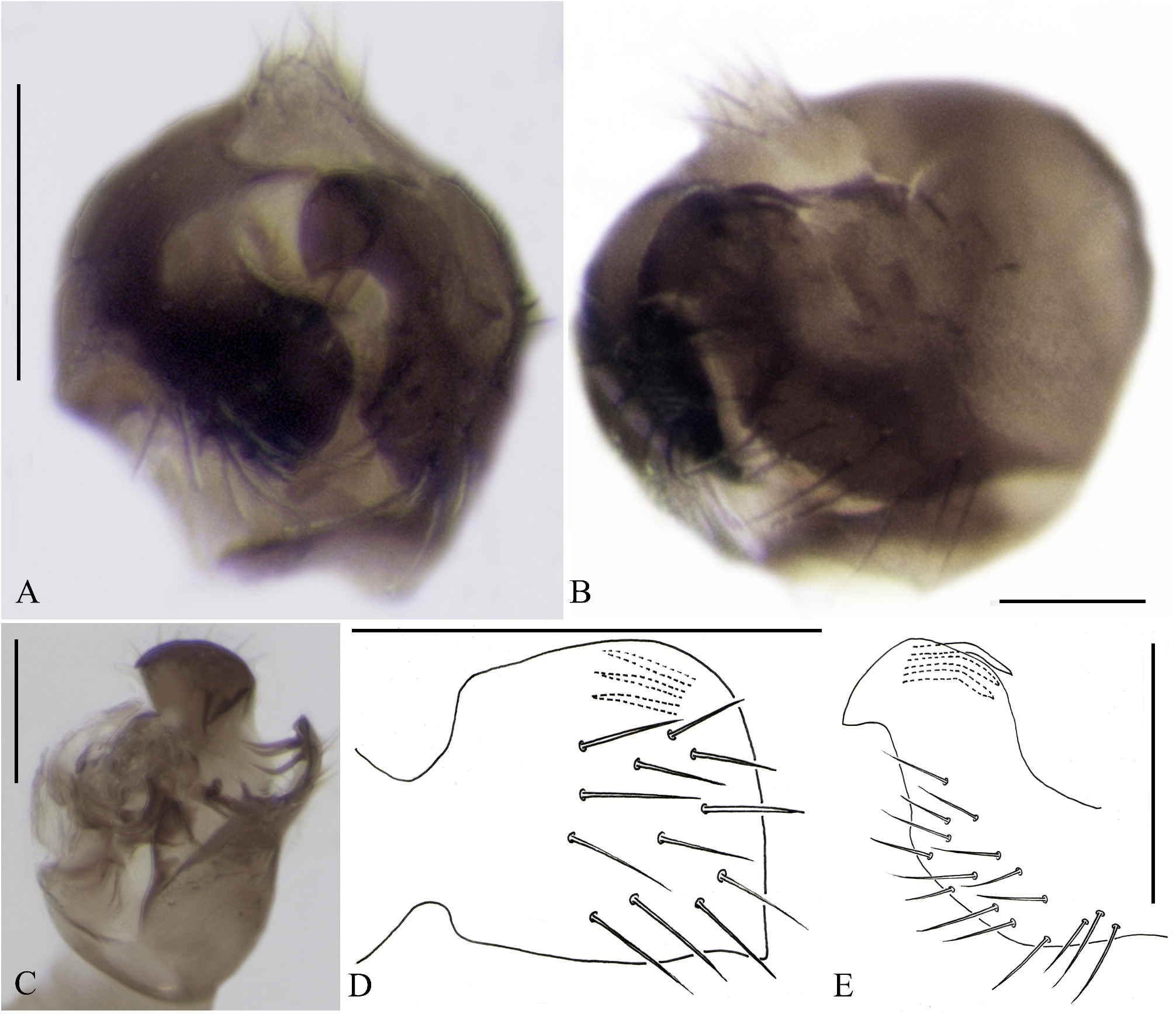
9. Both anterior and posterior edges of surstylus are similar length, so the surstylus looks square ( Figs. 4B–E View FIGURES 4 ).... C. ulrichi Liu
Anterior edge of surstylus longer than posterior edge, so the surstylus looks rhombic ( Figs.3B–E View FIGURES 3 ) C. gracilis Michailovskaya
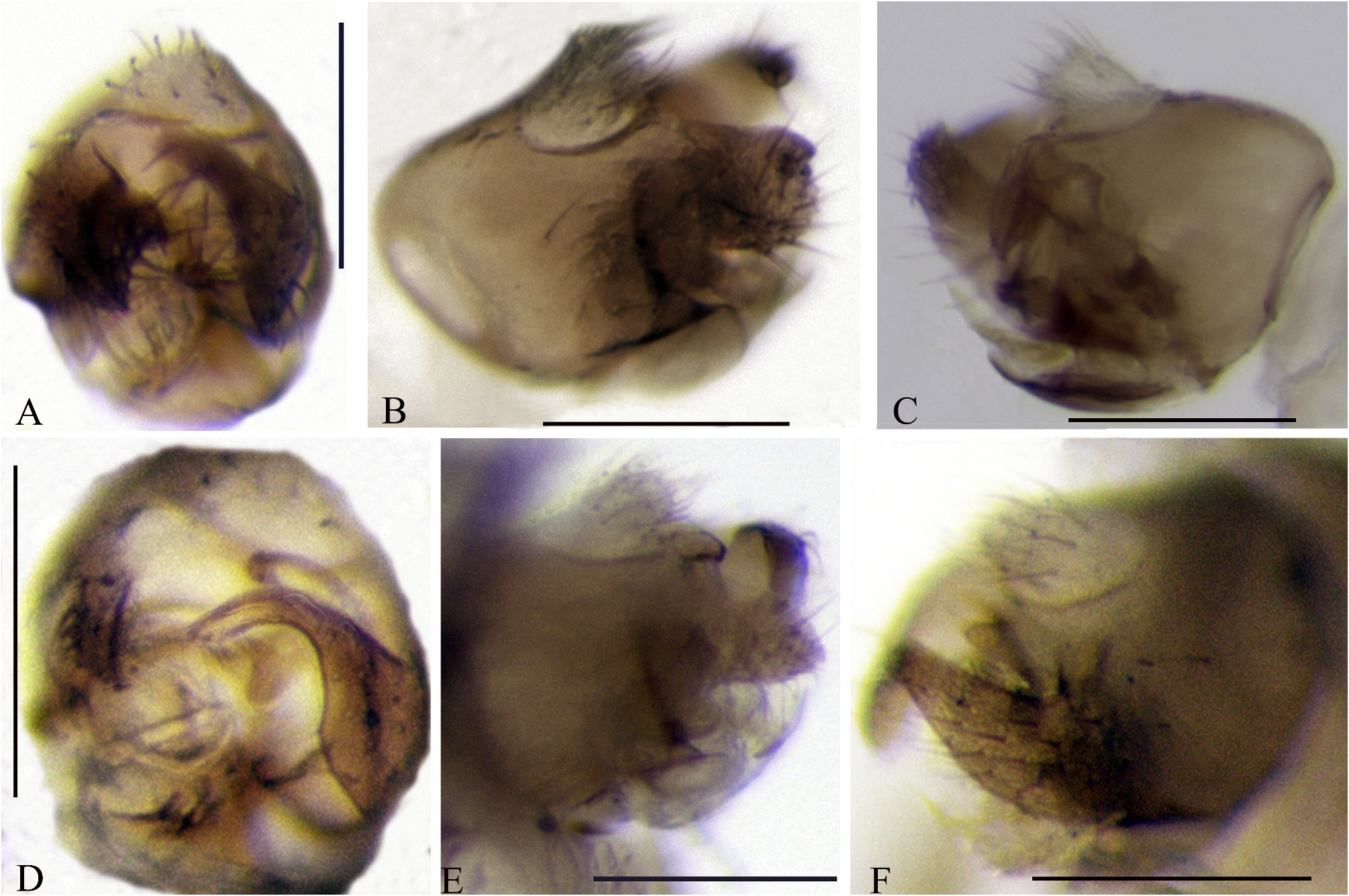
10. Apex of surstyli pointed ( Figs. 1D–G View FIGURES 1 ); fine veins whitish gray( Fig. 29A View FIGURES 29 )........................... C. dauci (Meigen)
Apex of surstyli blunt ( Figs. 2B–E View FIGURES 2 ); wing with light-brown fine veins ( Fig. 29C View FIGURES 29 ).................. C. obtusifinis sp. nov.
11. Both surstyli with concave, petal-like apical edge ( Figs. 5B–E View FIGURE 5 ).................................. C. petalina sp. nov.
Surstyli without this features........................................................................... 12
12. Right surstylus long, slender, base part broader than the apex; left surstylus short.................................. 13
Right surstylus various shapes, base part narrower than the apex............................................... 15
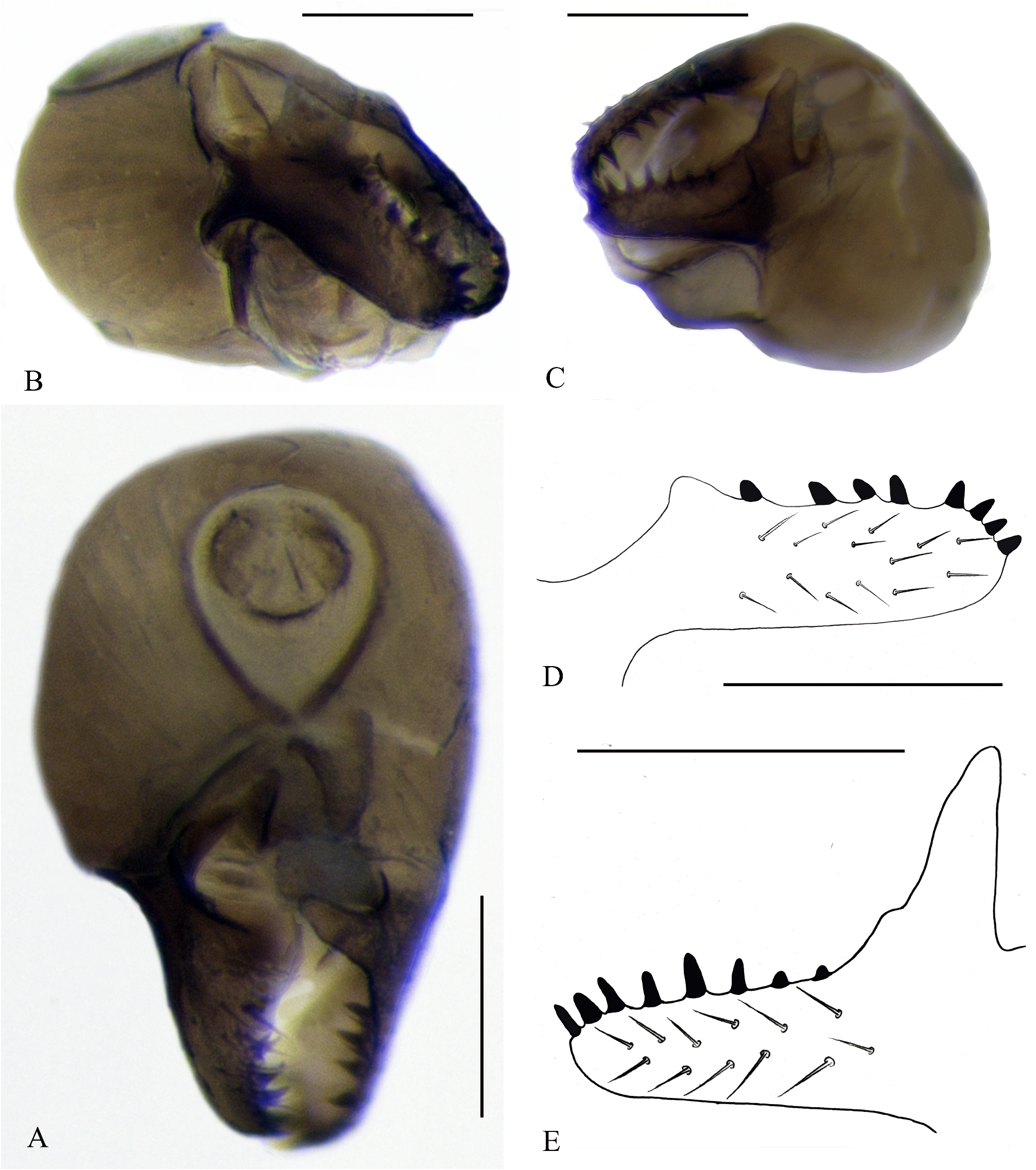
13. Right surstylus parallel-sided, and the apex beak-shaped, with 3 long, thick, curved inner teeth ( Figs. 9A–C, E View FIGURES 9 ).................................................................................................. C. spinifer a Liu
Right surstylus thin and lanceolate, and the apex not beak-shaped.............................................. 14
14. The apex of right surstylus suddenly becomes thinner, without inner teeth ( Fig. 10D View FIGURES 10 ).................. C. longilobusa Liu
The apex of right surstylus gradually tapered, with 3 inner teeth ( Fig. 10A View FIGURES 10 ).................. C. pacifica Michailovskaya
15. Fore femur with a brownish spot ( Fig. 6A View FIGURES 6 ); left surstylus short, extending downwards, pointed apically, with a basidorsal and a adjacent small processes ( Figs. 6D, F View FIGURES 6 )............................................... C. maculifemoris sp. nov.
Fore femur without a brownish spot...................................................................... 16
16. Right surstylus is split into a rectangular upper branch and a crescent lower branch ( Figs. 7C, E View FIGURES 7 ); left surstylus large and oval ( Figs. 7B, D View FIGURES 7 )........................................................................... C. forcipis sp. nov.
Right surstylus trapezoid ( Figs. 8C, E View FIGURES 8 ); left surstylus enlarged apically, anchor-shaped ( Figs. 8B, D View FIGURES 8 )...................................................................................................... C. ancoraria sp. nov.
17. Left and right surstyli similar in shape, triangular or long banded.............................................. 18
Left and right surstyli very different...................................................................... 22
18. Both surstyli are long banded........................................................................... 19
Both left and right surstyli are nearly triangular............................................................ 20
19. Right surstylus with basidorsal process ( Figs. 11C, E View FIGURES 11 ); left surstylus straight ( Figs. 11B, D View FIGURES 11 )............ C. angusta sp. nov.
Right surstylus lacking basidorsal process ( Figs. 12C, E View FIGURES 12 ); left surstylus S-form curved ( Figs. 12B, D View FIGURES 12 )... C. tortuosa sp. nov.
20. Dorsal edge of left surstylus shorter than ventral edge; left and right surstyli symmetrical inversely ( Figs. 14B–E View FIGURES 14 ).............................................................................................. C. convallis sp. nov.
Dorsal edge of left surstylus equaled to ventral edge......................................................... 21
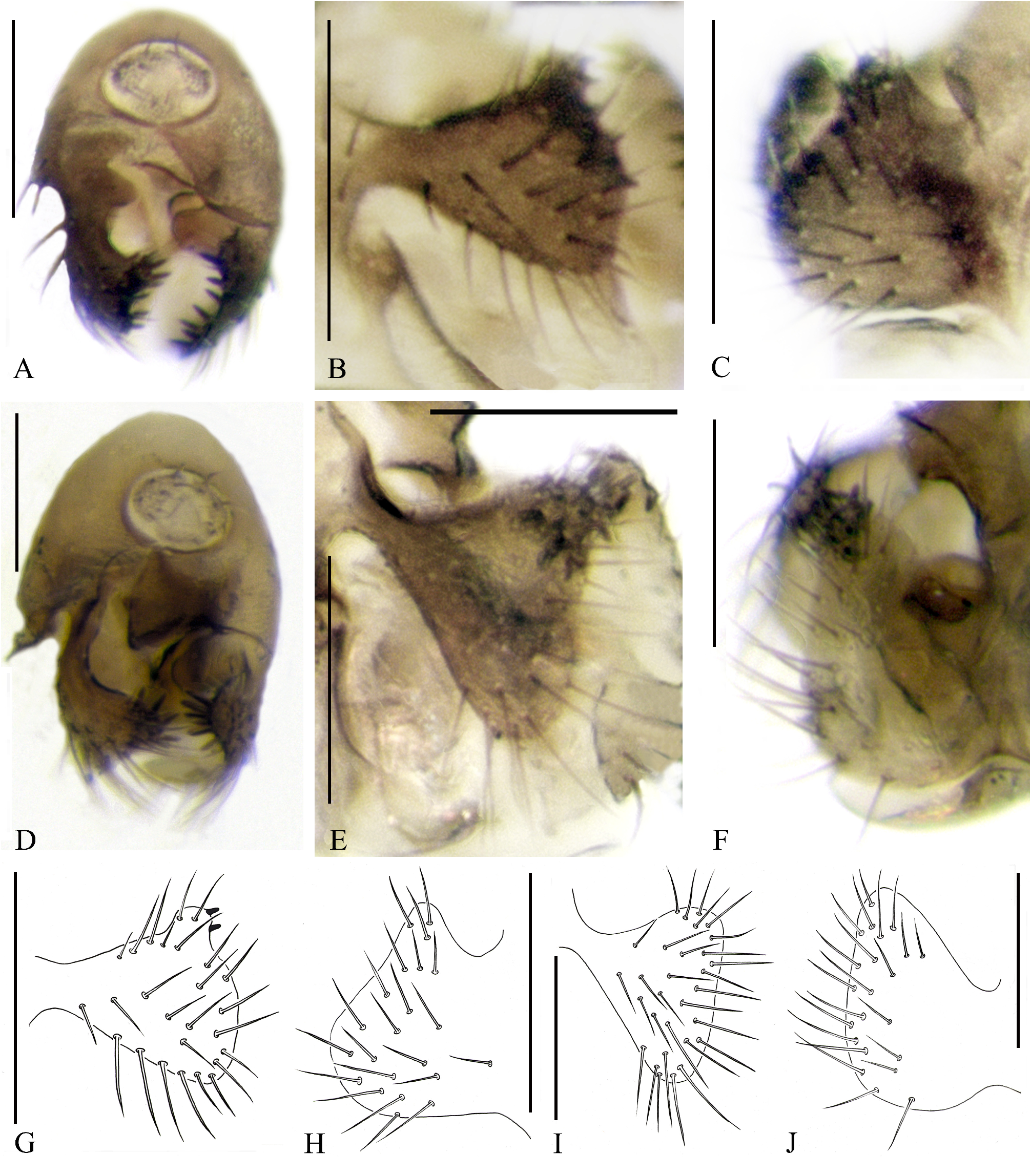
21. Left surstylus with a short dorso-apical process, on which there are about 10 inner teeth ( Figs. 15B, G View FIGURES 15 ); the dorso-apical corner of right surstylus pointed, with about 8 inner teeth ( Figs. 15C, H View FIGURES 15 ).............................. C. chayuensis sp. nov.
Left surstylus without dorso-apical process and with 4–6 inner teeth ( Figs. 15E, I View FIGURES 15 ); right surstylus with 6–8 inner teeth ( Figs. 15F, J View FIGURES 15 )............................................................................ C. triangularis sp. nov.
22. Right surstylus with a basidorsal process ( Figs. 23F, H View FIGURES 23 )...................................................... 28
Right surstylus without a basidorsal process............................................................... 23
23. Right surstylus oval or near square; inner teeth spread on the inner surface....................................... 24
Right surstylus trapezoidal or palm; inner teeth are mostly distributed on the edge................................. 25
24. Left surstylus oval, without a basidorsal process; with 16 inner teeth ( Figs. 13B, E View FIGURES 13 )............... C. dentisparsa sp. nov.
Left surstylus kidney-shaped, with a basidorsal process and a depression at the Apex; scattered with 1–5 inner teeth ( Fig. 19B View FIGURES 19 )..................................................................... C. quadrata Mostovski et Disney
25. Left surstylus axe-shaped ( Figs. 17A, D View FIGURES 17 )................................................. C. securiclata sp. nov.
Left surstylus without this feature....................................................................... 26
26. Right surstylus large, palmar-shaped, and lacking inner teeth ( Figs. 18B, E View FIGURES 18 )........................ C. palmata sp. nov.
Right surstylus small, with teeth........................................................................ 27
27. The apical edge of right surstylus wavy, with short setulae on surface ( Figs. 16A, C, E View FIGURES 16 )............ C. margiflucta sp. nov.
The apical edge of right surstylus slightly concaved; with long setulae on surface ( Figs. 19F, H View FIGURES 19 )......... C. longicilia Liu
28. Basidorsal process of right surstylus membranous.......................................................... 29
Basidorsal process of right surstylus sclerotized............................................................ 30
29. Left surstylus with a broad edge on basidorsal part ( Figs. 20G, I View FIGURES 20 ); right surstylus with 2 small blunt basiprocess ( Figs. 20H, J View FIGURES 20 ).................................................................................. C. marginata sp. nov.
Left surstylus only with a small basiprocess ( Figs. 20B, D View FIGURES 20 ); right surstylus with 2 pointed basiprocess ( Figs. 20C, E View FIGURES 20 )............................................................................................. C. reniformis Liu
30. Frons without lower fronto-orbital setae; basidorsal process of left surstylus with inner teeth ( Figs. 21B, D View FIGURES 21 )................................................................................................ C. denticulata sp. nov.
Frons with lower fronto-orbital setae; basidorsal process of left surstylus without inner teeth......................... 31
31. The base of left surstylus not contracted ( Figs. 21F, I, K View FIGURES 21 ); the inner teeth of the left and right surstyli thin and not sclerotized (same color with other setulae) ( Fig. 21H View FIGURES 21 )............................................. C. microspinulosa sp. nov.
The base of left surstylus contracted; the inner teeth of the left and right surstyli thick and sclerotized (darker than other setulae)............................................................................................ 32
32. Terminalia Large ( Fig. 22A View FIGURES 22 ), length 0.40–0.44 mm; right surstylus with 14–18 inner teeth arranged in two rows ( Figs. 22C, H View FIGURES 22 )............................................................................. C. grandicaudata sp. nov. Terminalia small, length less than 0.35 mm; right surstylus with less than 10 inner teeth............................ 33
33. Posterior edge of right surstylus with 7 inner teeth, the undermost one is pointed ( Figs. 22D, F, J View FIGURES 22 ); terminalia 0.31–0.33 mm................................................................................. C. schnittmanni Schmitz
Posterior edge of right surstylus with 8–9 inner teeth, which all of them similar................................... 34
34. Basidorsal process of right surstylus short, inner teeth robust and blunt ( Figs. 23A, C View FIGURES 23 ); terminalia 0.31–0.33 mm........................................................................................... C. obtusidentis sp. nov.
Basidorsal process of right surstylus long, inner teeth slender and pointed ( Figs. 23D, F, H View FIGURES 23 ); terminalia 0.31–0.33 mm...................................................................................... C. digitalis Liu et Zhang
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.