Basidiobolus ranarum Eidam, Beiträge
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.545.1.3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6524945 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F34A59-1012-FFA7-FF51-FD43789F5C33 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Basidiobolus ranarum Eidam, Beiträge |
| status |
|
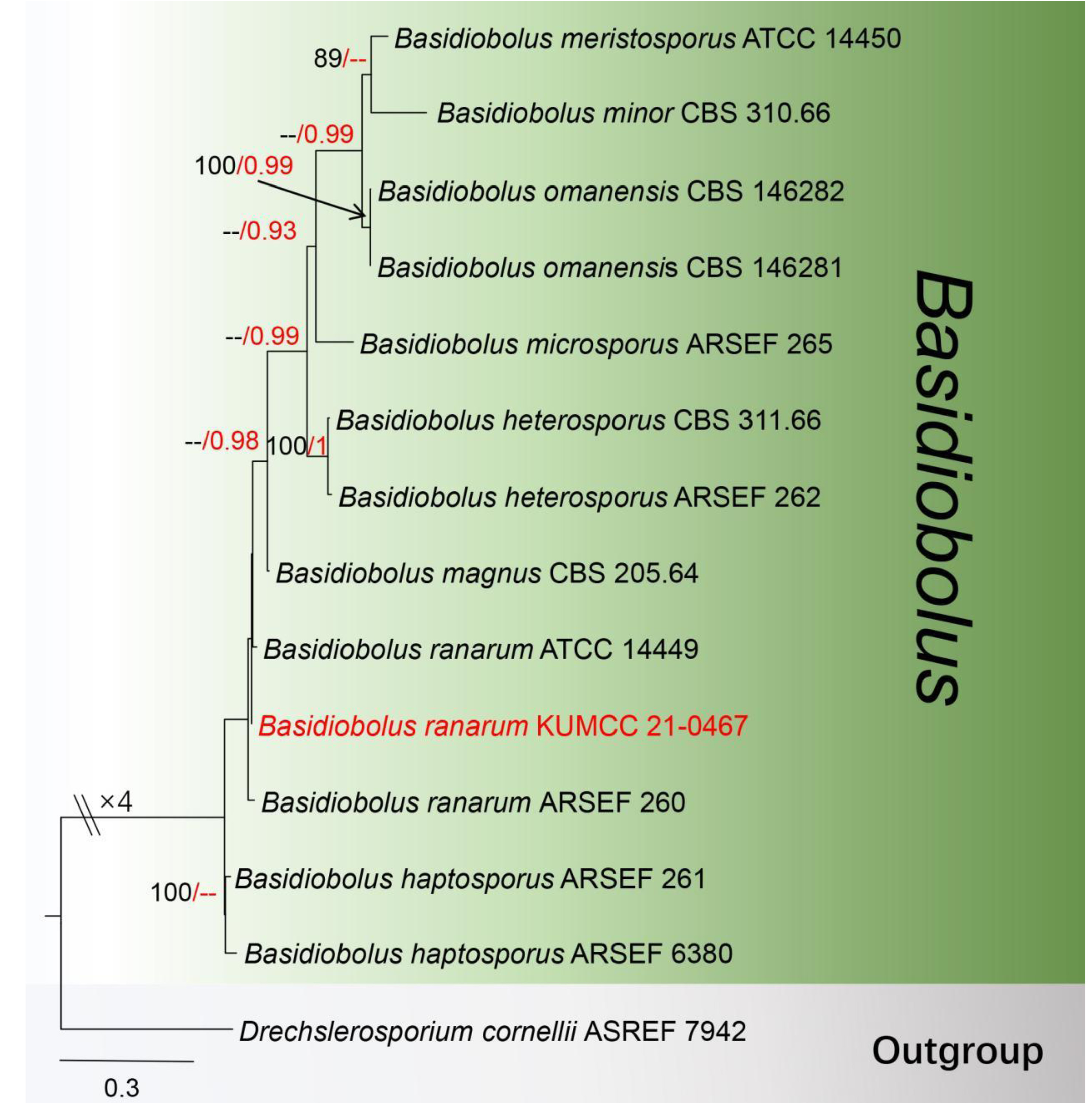
Basidiobolus ranarum Eidam, Beiträge View in CoL zur Biologie der Pflanzen 4: 194 (1886) ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 )
Index Fungorum number: IF224388
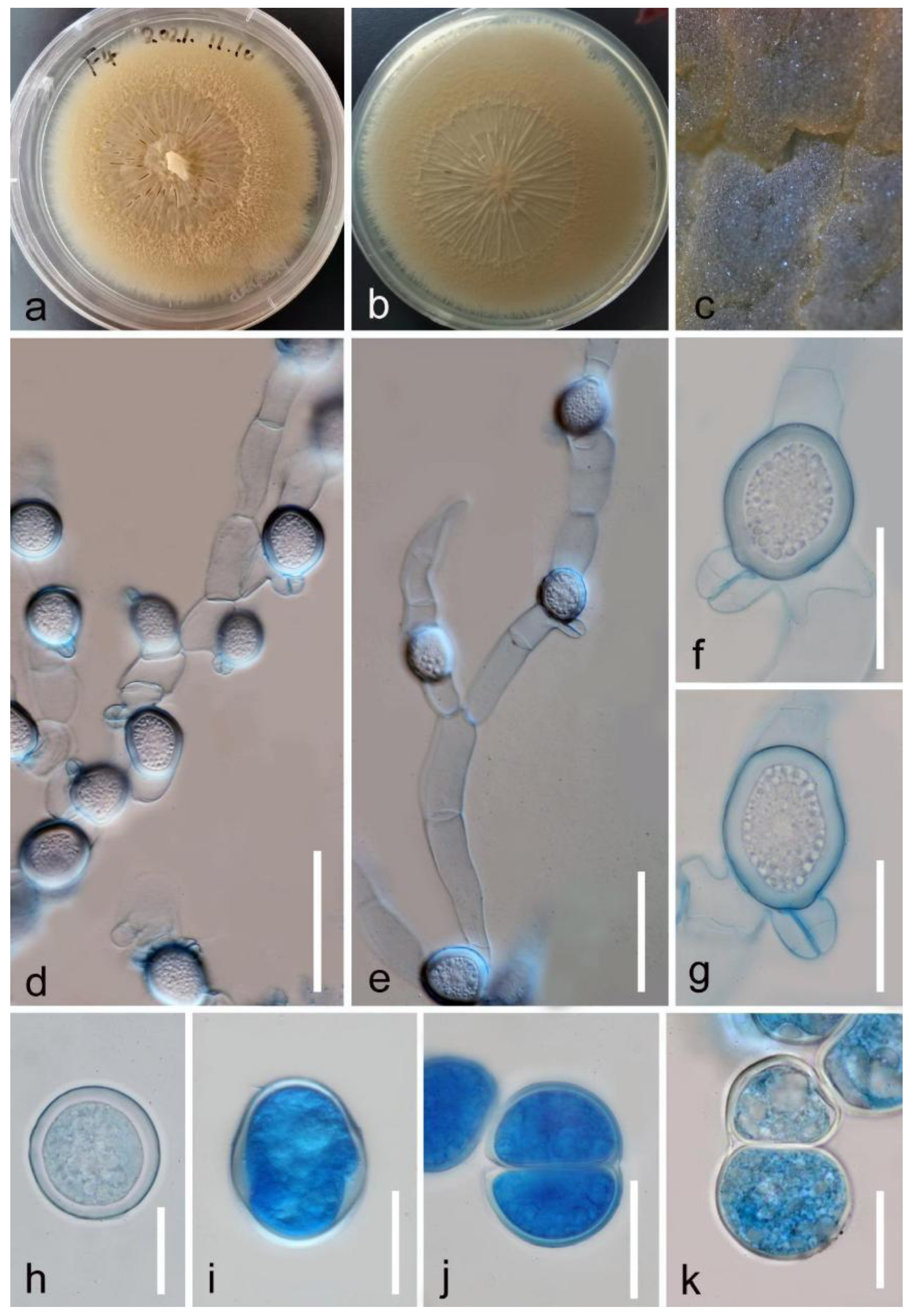
Saprobic or pathogenic on dead house gecko. Mycelium 10–20 μm wide (x̅ = 16 μm, n = 20), hyaline, septate, branched, tubular, sightly constriction at the septum, soon forming zygospores, the zygospores are (sexual spores) characterized by globose to subglobose 25–40 × 25–35 μm (x̅ = 34 × 31 μm, n = 20), wrapped in mycelium, with smooth and thick wall, 1–3.5 μm (x̅= 2.5 μm, n = 20) thickness, and wall layer thinner with the maturity, attaching a prominent conjugation beaks 10–15 μm wide, 8–11 high ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 : f, g), hyaline (the microscopic features observed with cotton blue), verruculose to granulate in cellular inner, some zygospores form meristospores by cleavage of the cytoplasm ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 : i–k).
Culture characteristics: The pure culture was obtained from slimy tissue of gecko’s swollen forelimb, colonies circular, fast-growing on PDA at the room temperature, reaching around 40 mm diameter after two weeks, with an irritating odor, yellowish-brown to creamy grey, waxy, radially striated with barren crack at the centre, visible sparse mycelium tips at the margin, abundant global to subglobose zygospores (conidia) pave on folded surface; reverse sunken at the centre, yellowish to pale outwardly, without pigments produced from PDA.
Substratum: Fish ( Nickerson & Hutchison 1971); Amphibians (frogs, toads) ( Coremans-Pelseneer 1973); house gecko faeces ( Hemiolactylus sp.) ( Claussen & Schmidt 2019); wall gecko ( Hemiolactylus sp.) ( Gugnani & Okafor 1980); bat ( Chaturvedi et al. 1984); child/adult, human ( Khan et al. 2001, Yusuf et al. 2003); dead Asian House Gecko ( Hemiolactylus sp.) (this study).
Distribution: Arkansas and Missouri, American ( Nickerson & Hutchison 1971); Kinshasa, Zaire (Coremans-Pelseneer 1973); Nsukka, Nigeria ( Gugnani & Okafor 1980); India ( Chaturvedi et al. 1984, Khan et al. 2001); Jizan, Saudi Arabia ( Yusuf et al. 2003); KwaZulu-Natal ( South Africa) ( Claussen & Schmidt 2019), Yunnan, China (this study)
Material examined: China, Yunnan Province, on dead Asian House Gecko, Peter E. Mortimer, F-4 (Herb. KUN-HKAS 122654), living culture, KUMCC 21-0467. Genebank numbers: ITS: OM 670164 View Materials , LSU: OM 670161 View Materials , mtSSU: OM 692370 View Materials .
Notes: Our isolate KUMCC 21-0467 shares similar characteristics with Basidiobolus magnus and B. ranarum in having globose to subglobose, smooth, thick-walled zygospore 20–60 μm in diameter, wrapped in mycelium, with a conjugation beak ( Eidam 1886, Davis et al. 1994). The BLASTn results show the ITS gene region highly overlaps with B. magnus (ARSEF 1139) at 99.3% (668/673 bp, 0 gap), at 99% (664/672 bp, 0 gap) similarity with B. ranarum ( ARSEF 260), and the LSU region indicates 99.8 % similarity (1010/1012bp, 0 gap) with B. ranarum ( ARSEF 8303) and B. magnus ( CBS 205.64). In addition, 667 bp of the mtSSU region was 100% similar to B. ranarum (AFTOL-ID 301); unfortunately, we were unable to amplify the rpb2 (7F/11aR) gene of our strain KUMCC 21-0467, The phylogenetic trees based on ITS, LSU, rpb2 and mtSSU show our isolate clusters with B. ranarum ( ARSEF 260 and ATCC 14449) ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Basidiobolus ranarum has also been found on frogs in Canada, and many infected cases in humans all over the world have been reported ( Gugnani 1999, Al-Hatmi et al. 2021). As morphological characteristics examined largely overlap with B. ranarum , also supported by the phylogenetic evidences, our isolate is identified as Basidiobolus ranarum with a new country record for China; however, B. ranarum has previously been reported on wall gecko and house gecko faeces ( Hemidactylus spp. ) ( Gugnani & Okafor 1980, Gugnani 1999, Claussen & Schmidt 2019).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Basidiobolus ranarum Eidam, Beiträge
| Yang, Erfu, Tibpromma, Saowaluck, Dai, Dongqin, Promputtha, Itthayakorn, Mortimer, Peter E. & Karunarathna, Samantha C. 2022 |
Basidiobolus ranarum Eidam, Beiträge
| Eidam 1886: 194 |