Spartimas hainanensis, Zhang, Ting-Ting & Yang, Ding, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.196683 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6195591 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F54011-FF8B-237B-FF76-FD67FBBBFB02 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Spartimas hainanensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Spartimas hainanensis View in CoL sp. nov.
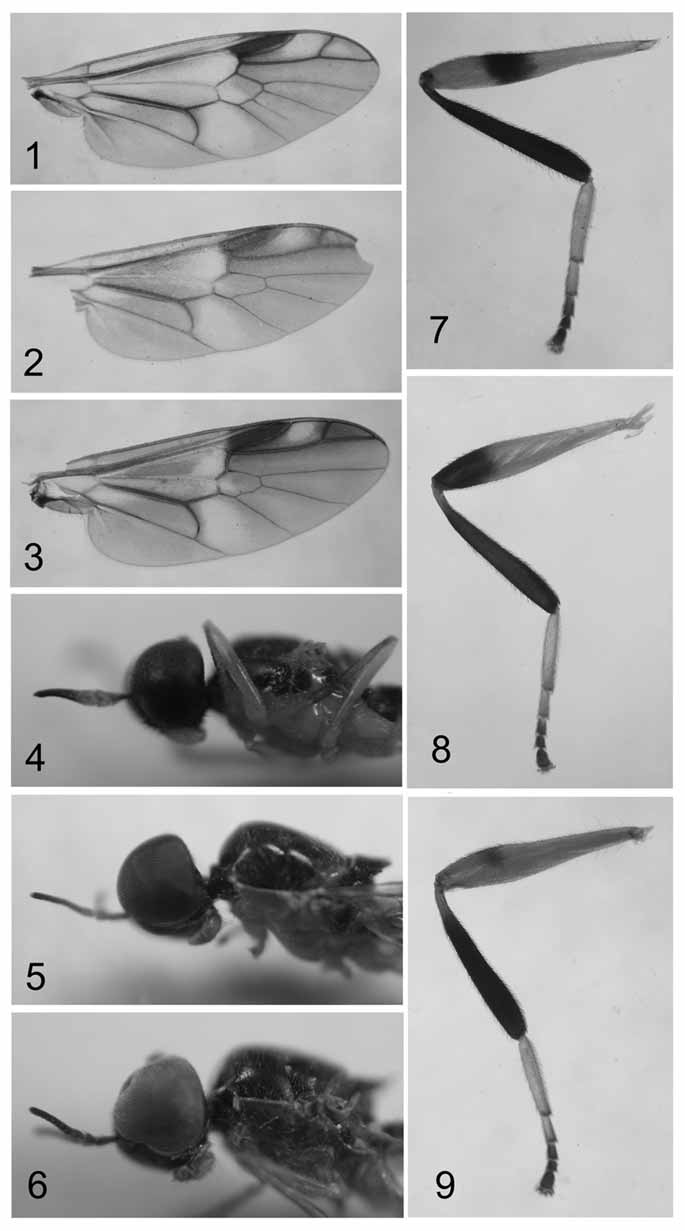
( Figs. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 3 , 6, 9, 14–17 View FIGURES 14 – 17 )
Diagnosis. Scutellum with 4 brownish yellow spines in male and with 6 pale yellow spines, lateral pair of them much smaller than others in female; pleura wholly yellow; subapical portion of hind femur with a narrow yellowish brown ring which is not connected on ventral surface; M3 absent. Abdomen with a pair of quadrate yellow spots on tergite 4 in female. Gonocoxal apodeme short, barely reaching beyond anterior margin of genital capsule; posteromedian portion of gonocoxites with a flattened process; dorsal bridge of gonocoxites with straight anterior margin; phallic with two slender and short lobes.
Description. Male. Body length 6.5–7.5 mm, wing length 5.0– 5.5 mm.
Head ( Fig. 6) black, more or less shining metallic purple. Eye red brown and bare, contiguous at frons, upper facets conspicuously larger than lower ones. Ocellar tubercle large; ocelli brownish yellow. Hairs on head pale yellow; face along eye margin pale grey pollinose. Antenna yellow, but base of scape dark brown, flagellomeres 2–8 pale brown to dark brown, pale pilose, outer surface of scape and pedicel dark brown haired and tip of flagellomere 8 with 2–3 short hairs; first flagellomere as long as flagellomeres 2+3, flagellomeres 2–7 subequal in length, last flagellomere as long as flagellomeres 6+7; antennal ratio 1.0: 0.8–0.9: 3.9–4.4. Proboscis yellow with pale yellow hairs. Palpus yellow except segment 1 being brownish yellow to brown; hairs pale yellow. Head 1.1–1.3 times higher than long; eye width 0.9 times distance from anterior ocellus to antennal insertion, 3.1–3.4 times frons width just above antenna and 1.0–1.4 times face width at lowest point from direct view; frons width just above antenna 6.0–10.0 times that at anterior ocellus and 0.3–0.4 times face width at lowest point from a direct frontal view; distance from anterior ocellus to antennal insertion 0.8-0.9 distance between antennal insertion to ridge-like posterior margin of mouth opening behind proboscis.
Thoracic pronotum, scutum and scutellum black, more or less shining metallic purple, pale grey pollinose; postpronotal callus blackish to yellowish brown and postalar callus yellow to brownish yellow; scutellum with 4 brownish yellow spines; pleura wholly yellow. Hairs on thorax pale yellow; anepisternum (except anterior and posterior parts), anepimeron and meron bare. Legs ( Fig. 9) yellow, but fore femur and mid tarsomeres 4–5 brownish yellow, fore tibia and tarsus (except ventral surface), hind tibia (except basal part) and hind tarsomeres 3–5 brown, subapical portion of hind femur with a narrow yellowish brown ring which not connected on ventral surface, hind tarsomeres 1–2 pale yellow, mid and hind tarsomeres 3–5 brown. Hairs on legs pale yellow, but fore and mid femora, tibiae and tarsi with brown hairs which become thick on the ventral surface, subapical portion of hind femur, apical margin of hind tarsomere 2 and tarsomeres 3–5 with brown hairs. Wing ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 3 ) tinged with brown but basal part, middle part of cell r2+3 (except lower margin), apical part of cell bm, basal part of cell dm and cell cua1 (except apical part) nearly hyaline; stigma distinctly brown; veins pale brown to brown; evenly set with microtrichia except wing base (excluding alula), basal portion of cell cu p bare. Halter yellow.
Abdomen 5.0–5.6 times longer than wide, nearly parallel-sided; brown (sometimes tergites 1–4 yellowish brown), with brown short hairs being longer, erect and yellow on sides of dorsum; sternites 1–4 pale yellow with yellow hairs. Male genitalia ( Figs 14–17 View FIGURES 14 – 17 ): Epandrium narrow with anterior margin deeply concave; dorsal bridge of gonocoxites with straight anterior margin; posteromedian portion of gonocoxites with a flattened process; gonocoxal apodeme long; gonostylus wide, apical part obliquely truncated and bifurcate, with dorsal lobe small and sharp; phallic complex with two lobes, much slender and shorter than in S. apiciniger sp. nov.
Female. Like male except as follows.
Body length 6.5–7.5 mm, wing length 5.0– 5.5 mm.
Eye widely separated, facets uniform. Frons nearly parallel-sided. Ocellar tubercle not as large and distinct as in male; ocelli brownish yellow. Antennal ratio 1.0: 0.6–0.9: 3.9–4.3. Proboscis yellow with pale brown hairs. Palpus yellow except segment 1 being yellowish brown. Head 1.3 times higher than long; eye width 0.7–0.8 times distance from anterior ocellus to antenna insertion, 1.1–1.3 times frons width just above antenna and 0.7–0.9 times face width at lowest point from direct view; frons width just above antenna 1.0–1.1 times that at anterior ocellus and 0.7 times face width at lowest point from a direct frontal view; distance from anterior ocellus to antennal insertion 0.8-0.9 distance between antennal insertion to ridge-like posterior margin of mouth opening behind proboscis.
Thoracic postpronotal callus and postalar callus yellow but anterior part of postpronotal callus and posterior part of postalar callus yellowish brown; scutellum with 6 pale yellow spines of which lateral pair much smaller than others; pleura wholly yellow. Hairs on thorax pale yellow; anepisternum (except anterior and posterior parts), posterior part of anepimeron, posteroventral part of katepisternum and meron bare. Legs yellow, but fore tarsus, mid and hind tarsomeres 3–5 yellowish brown, subapical portion of hind femur with a narrow yellowish brown ring which is not connected on the ventral surface, hind tibia brown (except basal part being yellowish brown), hind tarsomeres 1–2 pale yellow. Hairs on legs yellow, but fore and mid tibiae and tarsi with yellowish brown hairs which become thick on ventral surface, hind tibia with yellowish brown hairs, apical margin of hind tarsomeres 1–2 and tarsomeres 3–5 with brown hairs.
Abdomen nearly arc-sided, segment 4 widest; yellowish brown, tergite 4 with a pair of quadrate yellow spots, with brown short hairs being longer, erect and yellow on sides of dorsum; sternites 1–4 pale yellow with yellow hairs. Cercus yellow.
Type material. Holotype male, CHINA: Hainan, Yingge Ridge, Yinggezui, 19°00΄N, 109°22΄E, 17. IV. 2009, Shan Huo. Paratypes: 1 male, CHINA: Hainan, Wuzhi Mountain, 18°52΄N; 109°40΄E, 16. V. 2007, Jie Zeng; 2 males, CHINA: Hainan, Jianfeng Ridge, Mingfeng vale, 18°45΄N, 109°50΄E, 25. IV. 2009, Shan Huo; 2 females, CHINA: Hainan, Yingge Ridge, 19°00΄N, 109°22΄E, 23. V. 2007, Liqiong Weng.
Distribution. China (Hainan).
Remarks. The new species is somewhat similar to S. ornatipes Enderlein , but it can be separated by the narrow yellowish brown ring on the hind femur, the wholly yellow pleura and absence of vein M3. In S. ornatipes , the ring of the hind femur is distinctly brown and wider; anepisternum is posteriorly largely blackish (except the upper border), the anterodorsal part of the anepimeron and the meron are blackish; vein M3 is present ( Yang & Nagatomi 1992). It is more similar to S. apiciniger sp. nov., but in S. apiciniger sp. nov., the apical 1/3 of the hind femur is black; posteromedian portion of the gonocoxites has an obtusely rounded process; dorsal bridge of the gonocoxites has the V-shaped anterior margin; phallic complex is thick and long.
Etymology. The species is named after the type locality, Hainan Island.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |