Cyrea carla Canepari and Gordon, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5171097 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0011FDFF-35F5-4B7E-B952-7FD2B29D538B |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F8C140-FFA0-9429-FF4E-FF04FDFEF9C2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Cyrea carla Canepari and Gordon |
| status |
sp. nov. |
92. Cyrea carla Canepari and Gordon , new species
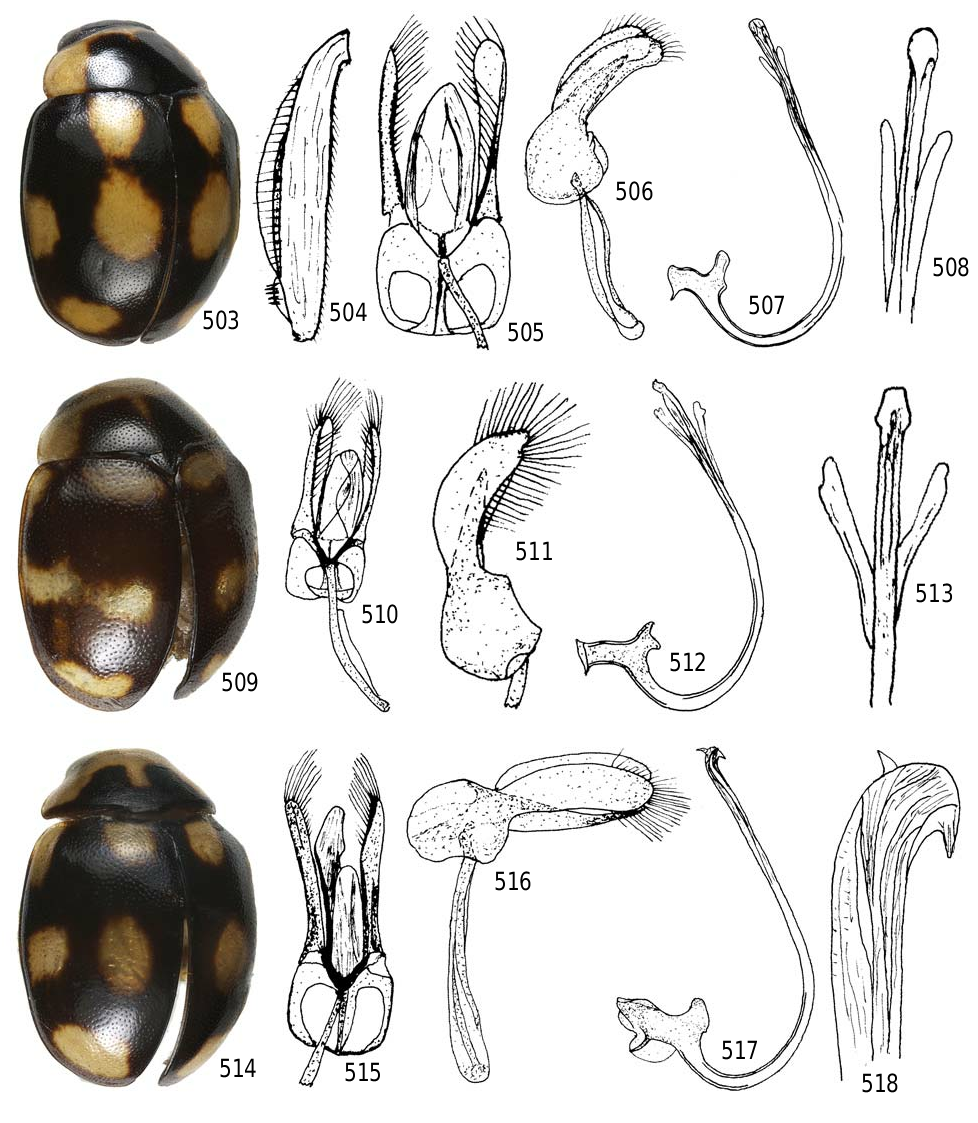
Description. Male holotype. Length 1.6 mm, width 1.2 mm; body oval, convex. Dorsal surface with head weakly alutaceous, shiny, pronotum and elytron smooth, shiny. Color yellow except pronotum with basomedian dark brown macula extended 2/3 distance to pronotal apex, apex of macula briefly, narrowly indented with yellow medially; elytron dark brown with 4 (actually 5 because median lateral and discal spots connected) small yellow spots, humeral spot narrowly triangular, scutellar spot transversely oval, median lateral spot projected inward and narrowly connected to transverse discal spot, forming a narrow, irregular transverse vitta, apical spot transversely oval with anterior border emarginate ( Fig. 509 View Figures 503-518 ); ventral surface with head, prosternum, meso- and metaventrites dark brown, metafemur brown; abdomen with ventrites yellowish brown medially, slightly paler laterally. Head punctures small, separated by about diameter or less, each puncture as large as an eye facet; pronotal punctures larger than head punctures, separated by 1 to 2 times a diameter, elytral punctures larger than on pronotum, separated by a diameter or less; metaventral punctures absent medially, as large as elytral punctures and nearly contiguous laterally. Clypeus weakly emarginate apically, lateral angle rounded, surface with sparse, long pubescence. Eye canthus about 6 eye facets long, angled forward, apically rounded, yellow. Pronotum narrowed from base to apex, basal and anterior angles abrupt, lateral margin rounded, basal margin without trace of bordering line medially. Epipleuron narrow, weakly grooved, not descending externally, deeply emarginate for reception of femoral apices. Protibia with slight oblique angle, basal tooth absent, sponda slightly extended beyond angle. Carinae on prosternal process narrowly separated at apex, convergent toward base, joined at basal 1/4 of prosternum, connected to prosternal base by short carina. Metaventrite without setal tuft. Basal abdominal ventrite without setal tuft. Abdomen with postcoxal line on basal abdominal ventrite rounded throughout, extended forward at apex, ventrite with short, dense pubescence and coarse, sparse punctures; ventrites 2-6 pubescent throughout, punctures fine, dense; 5th ventrite not depressed in median 1/3, apex shallowly emarginate; 6th ventrite depressed at apex, apex shallowly emarginate. Apical tergite finely, densely punctured, apex emarginate. Genitalia with basal lobe short, less than 3/4 as long as paramere, slightly asymmetrical, sides weakly convergent in basal 5/6, curved to rounded apex in apical 1/6; paramere Psc, about same width throughout ( Fig. 510, 511 View Figures 503-518 ); sipho robust, strongly curved in basal 2/3, with visible alae in apical 1/5, basal capsule with inner arm short, narrow, apex bifid, outer arm slightly curved, about as wide as and longer than inner arm, with accessory piece, basal border shallowly emarginate ( Fig. 512, 513 View Figures 503-518 ).
Female. Unknown.
Variation. Unknown.
Type material. Holotype male; N. Venezuela: Estado Aragua, P. Nac. Henri Pittier, Maracay/Occumare km 36, La Trilla, 300m. alt., FOG 3.26. iii.1990, Deciduous forest , Talisia sp., J.G. Davies ( BMNH).
Geographical distribution. Venezuela.
Remarks. Cyrea carla is a comparatively tiny species, only 1.6 mm long, distinguished externally by an elytral color pattern having a narrow, irregular transverse vitta composed of connected median lateral spot and discal spot ( Fig. 509 View Figures 503-518 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.