Capniidae (Lee & Baumann, 2011)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3812.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7847D731-9F66-4856-A79F-9435FED25B1D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5116356 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F99336-FF0E-FFE3-1BE4-59F1D5A3F9AE |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Capniidae |
| status |
|
Capniidae View in CoL terminalia
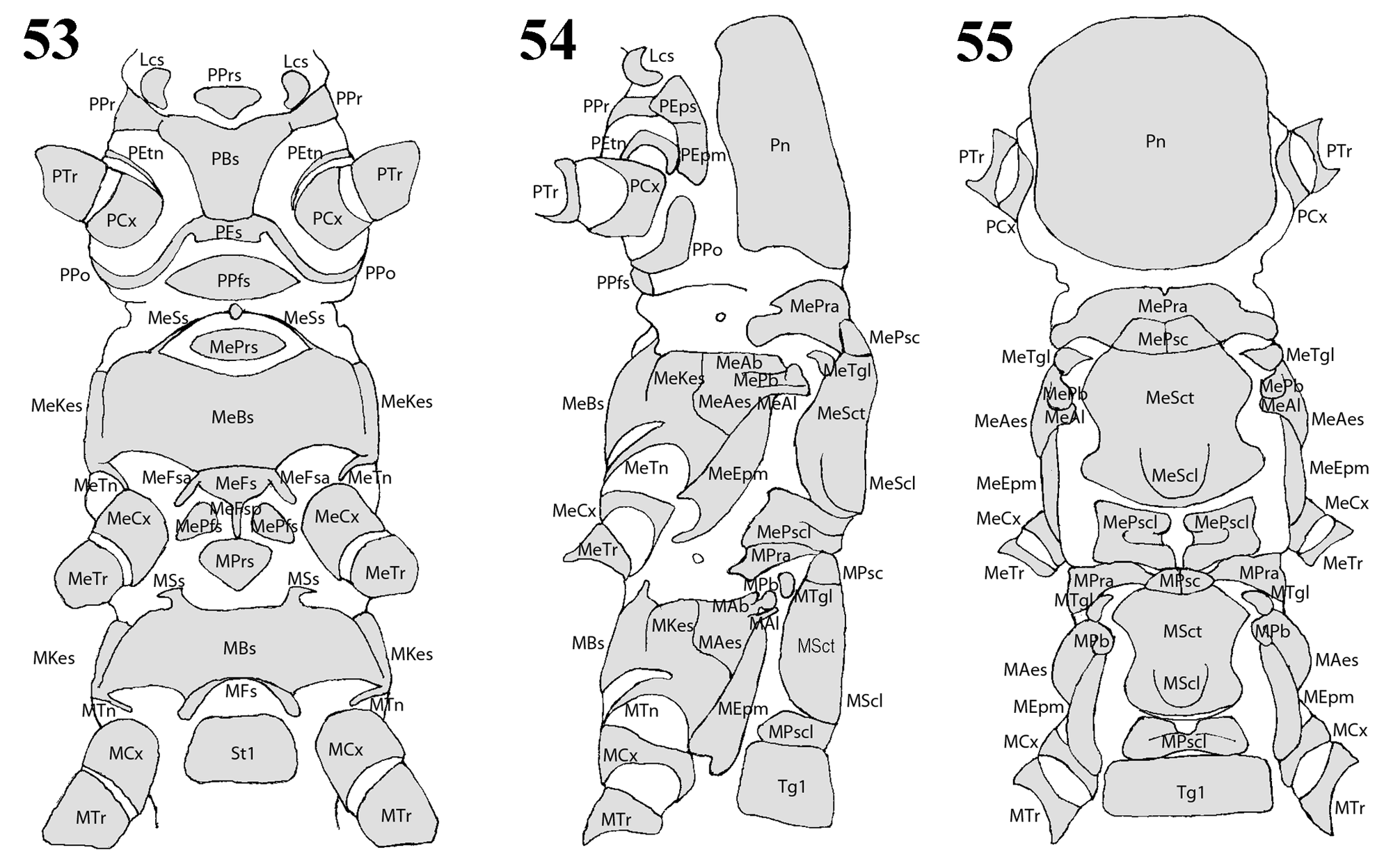
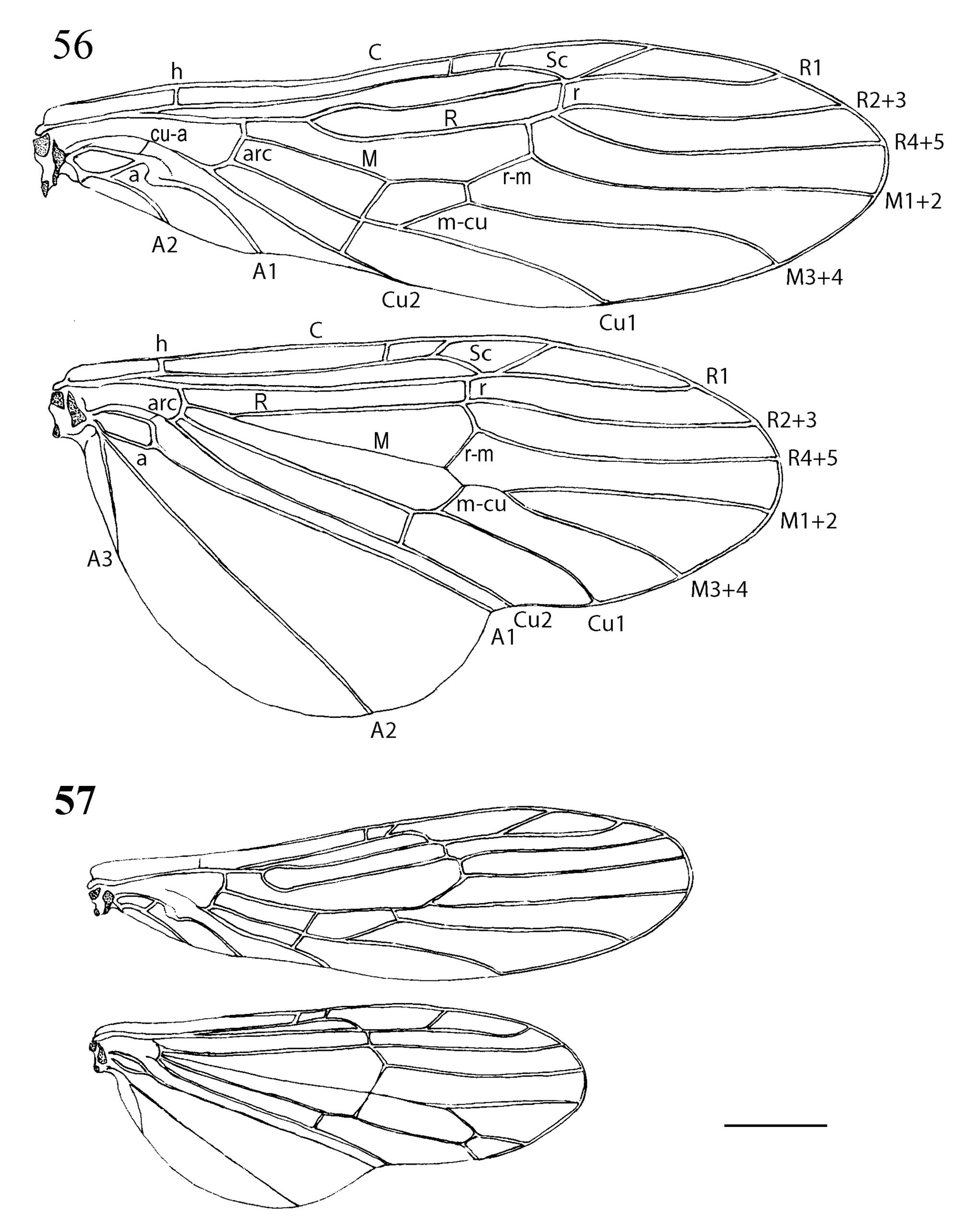
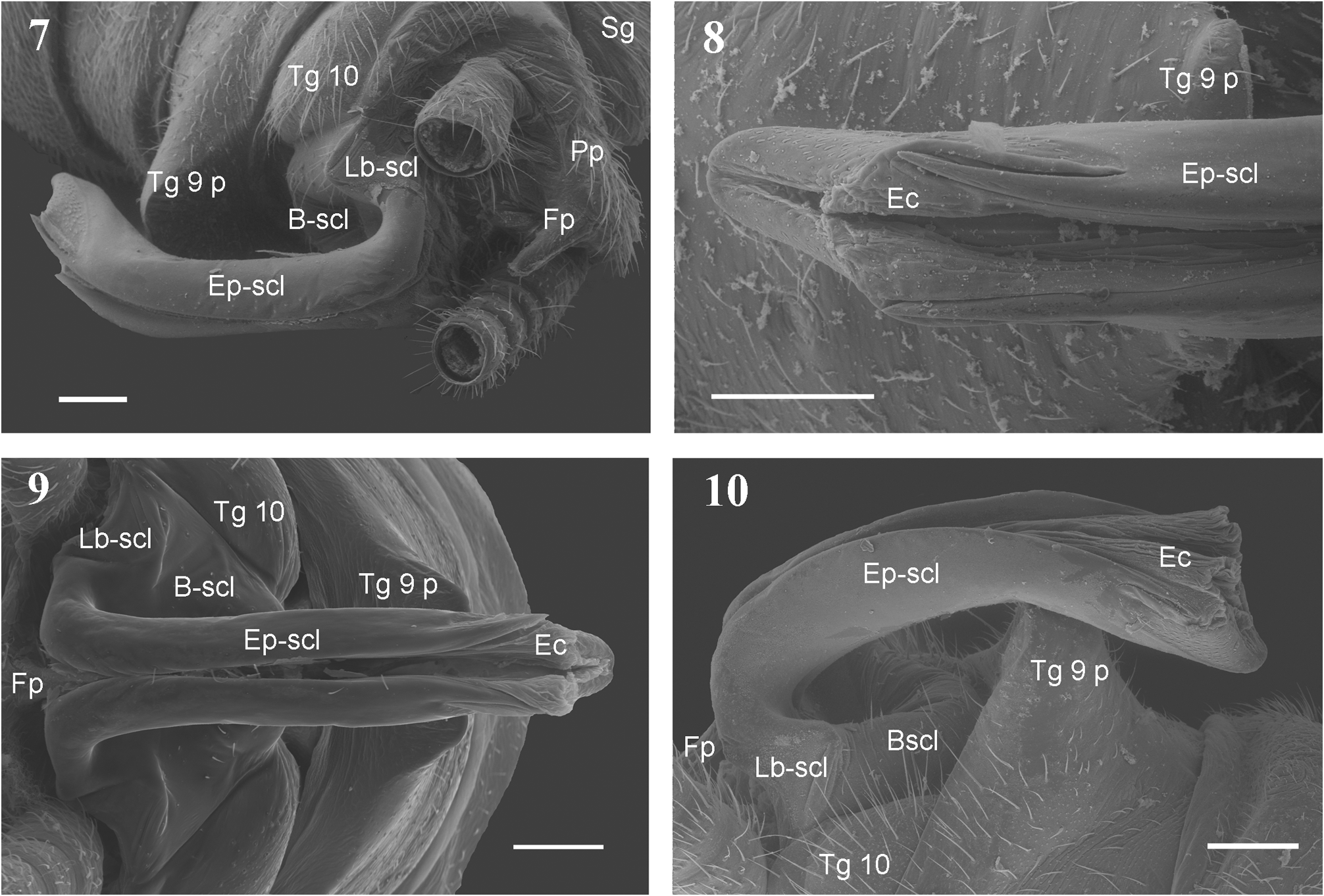
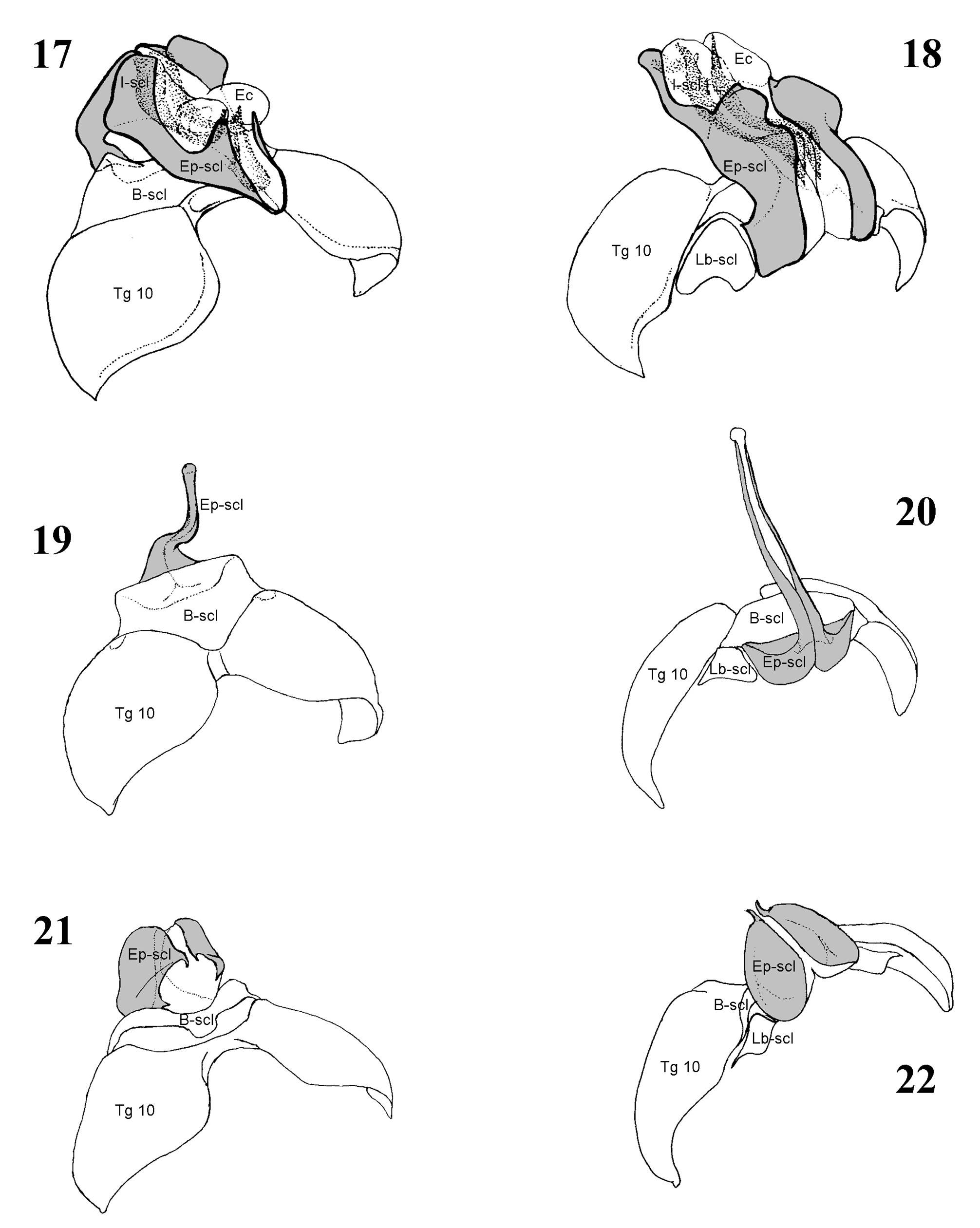
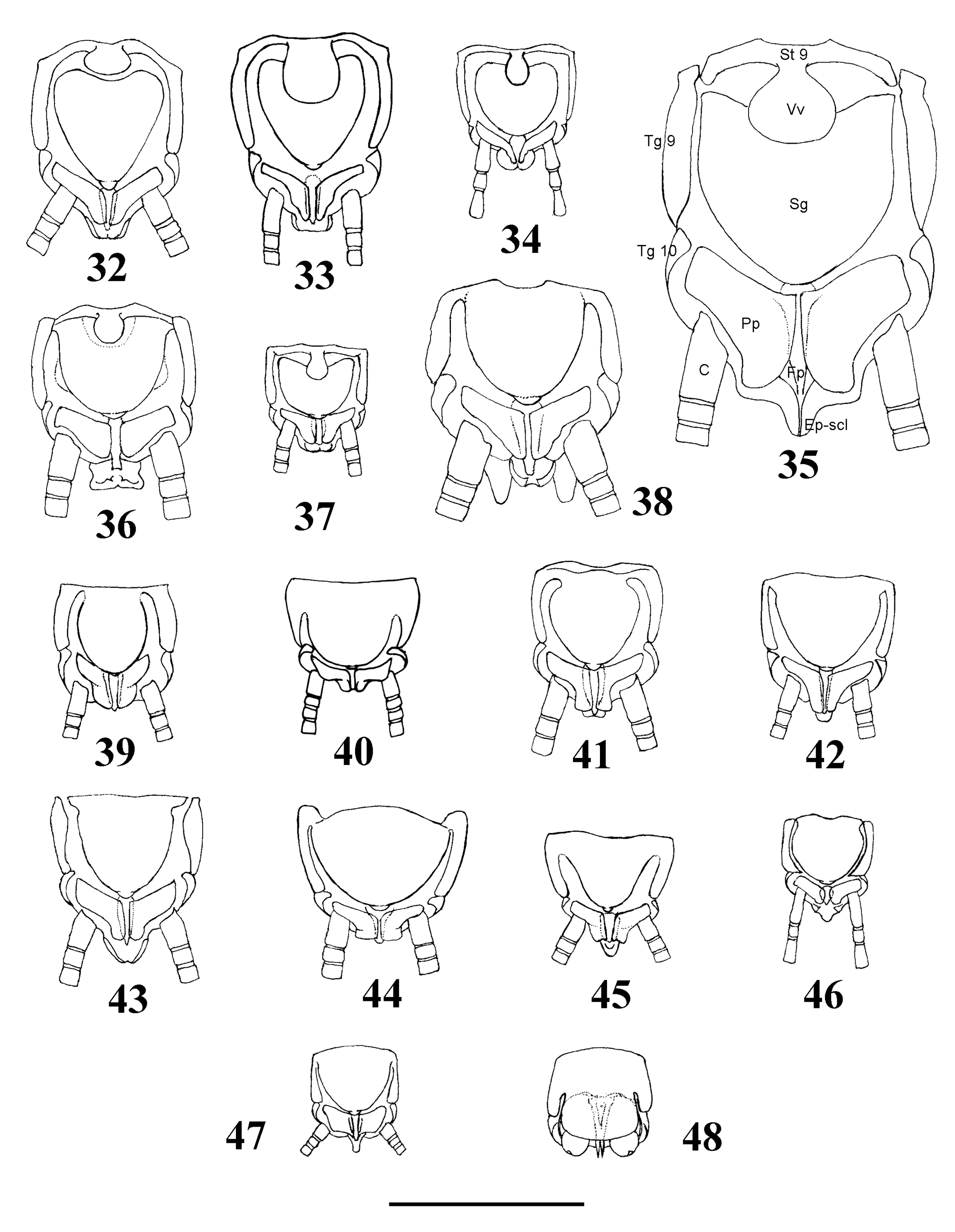
In addition to wing venation and thoracic sclerites ( Figs. 53–57 View TABLE 1 View FIGURES 53–55 View FIGURES 56–57 , Tables 1–2 View TABLE 1 View TABLE 2 ), the systematics of adult Capniidae is based mainly on the terminalia ( Figs. 1–48 View FIGURES 1–6 View FIGURES 7–10 View FIGURES 11–16 View FIGURES 17–22 View FIGURES 23–31 View FIGURES 32–48 , Tables 3–5 View TABLE 3 View TABLE 4 View TABLE 5 ). This study discusses the structure of the male epiproct, paraprocts, and the fusion plate. These structures are directly involved in mating. The general form and associated structures are illustrated in Figs. 1–31 View FIGURES 1–6 View FIGURES 7–10 View FIGURES 11–16 View FIGURES 17–22 View FIGURES 23–31 . These figures are shown to support new generic diagnoses that are presented. A ventral view of the male terminalia is depicted for all genera examined ( Figs. 32–48 View FIGURES 32–48 ). Terminology and comments are given below:
Basal sclerite (B-scl): The basal portion of the epiproct that can be divided or fused with the main and the laterobasal sclerites (Ep-scl, Lb-scl). It can be vestigial or lacking; its size is usually typical for the genera ( Figs. 1–2, 5–6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 11–22 View FIGURES 11–16 View FIGURES 17–22 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 ). In some genera the B-scl is developed into the Lower limb (Ll) of the epiproct, see below.
Laterobasal sclerite (Lb-scl): One of two lateral sclerites of the epiproct that are positioned caudally to the Bscl and laterobasally to the Ep-scl (see below). It can be divided or fused with both of those sclerites. The size is also typical for the genera ( Figs. 1–6 View FIGURES 1–6 , 17–22 View FIGURES 17–22 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 ).
Main epiproct sclerite (Ep-scl): The main sclerite of the epiproct, sometimes called the upper limb of the epiproct ( Nelson & Baumann 1987). It is open apically, usually divided in its dorsal portion, and can be divided or entire in its ventral and lateral portion; its ventral connection and lateral division are typical for the genera, as are the presence or absence of setae on its basocaudal portion ( Figs. 1–22 View FIGURES 1–6 View FIGURES 7–10 View FIGURES 11–16 View FIGURES 17–22 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 ).
Lower limb (Ll): An epiproctal sclerite is developed from the B-scl ( Figs. 3–6 View FIGURES 1–6 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 ). It is large in Utacapnia Gaufin, 1970 and Capnura Banks, 1900 , where the B-scl is completely formed into the Ll and the original sclerite is vestigial or lacking. In Allocapnia Claassen, 1928 , a small Ll is present on the B-scl but not divided. However, the epiproctal portion previously termed Ll in this genus, is in fact the highly separated lower part of the longitudinally divided Ep-scl. A vestigial Ll also present on the vestigial B-scl fused with the Ep-scl in genus Capnia s.s. and in C. s.l. vidua Klapálek 1904 ( Figs. 3–6 View FIGURES 1–6 ).
Inner sclerite (I-scl): An epiproctal sclerite that is present in some genera, surrounded by the Ep-scl. It is not connected to the Ep-scl but to the membranes forming the epiproct’s inner funnel that fix the Fp and lead the sperm into the apical opening of the epiproct ( Figs. 1–4 View FIGURES 1–6 , 11–18 View FIGURES 11–16 View FIGURES 17–22 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 ).
Eversible crest (Ec): An eversible, membranous portion of the epiproct on its dorsoapical part, connected to the Ep-scl. Its absence or presence is typical for the genera, although it is difficult to recognize in its contorted state ( Figs. 1–4 View FIGURES 1–6 , 8–10 View FIGURES 7–10 , 17–18 View FIGURES 17–22 , Table 3 View TABLE 3 ).
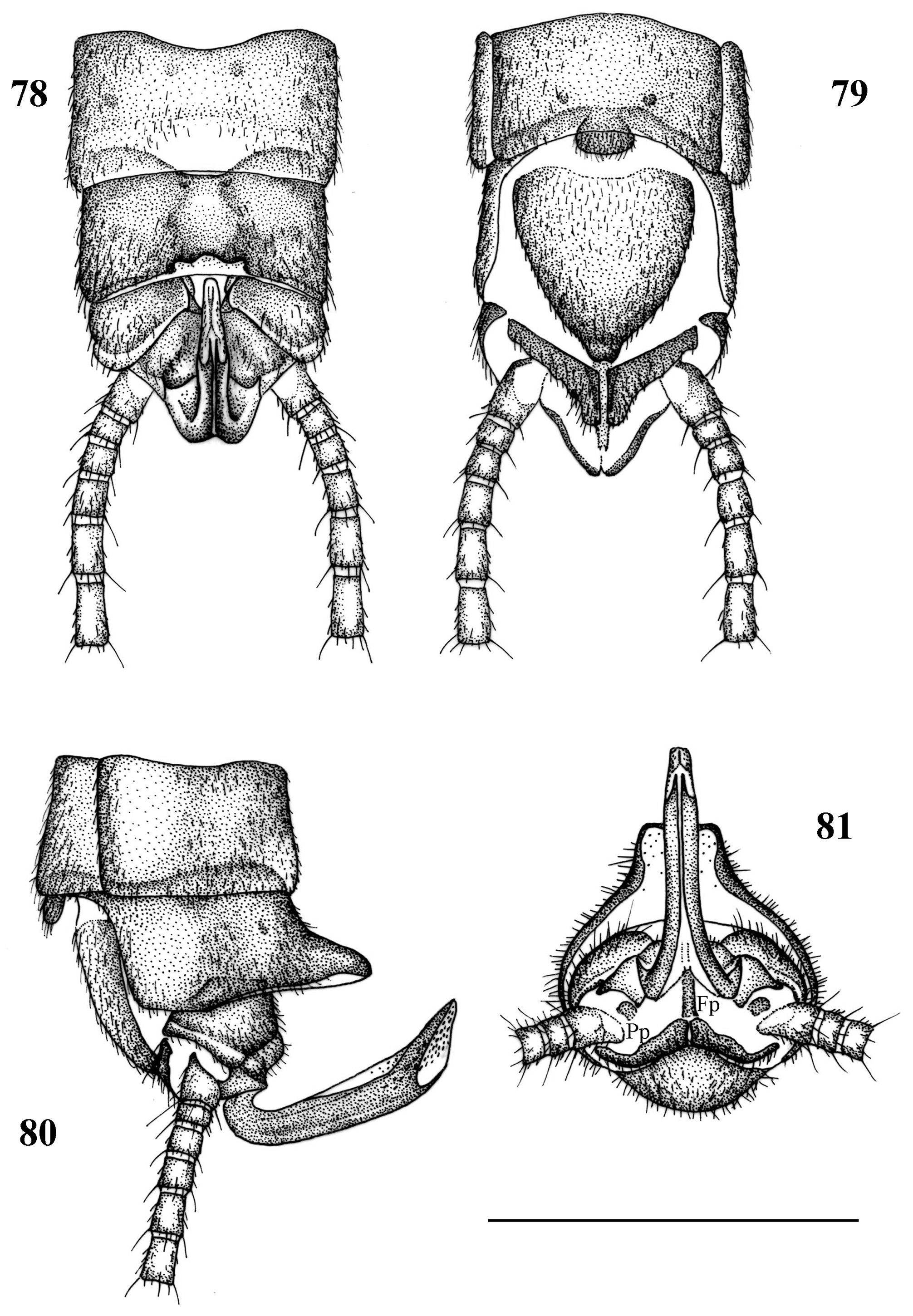
Fusion plate (Fp): As described by Klapálek (1896), this organ leads the sperm into the epiproct, and it is more or less fused with the paraprocts ( Fig. 7, 9 View FIGURES 7–10 ). In this study we note the relative length and width of the organ, and its division or fusion with a small basal sclerite, called the Retractoral plate (Rp) by Hanson (1946) ( Figs. 23–31 View FIGURES 23–31 , 81 View FIGURES 78–81 , Table 4 View TABLE 4 ).
Paraprocts (Pp): The relative length and width of the apical part are typical for the genera, and it is usually related to the dimensions of the Fp ( Figs. 32–48 View FIGURES 32–48 , 81 View FIGURES 78–81 , Table 4 View TABLE 4 ).
Subgenital plate (Sg): In males, its fusion or division with Sternite 9 (St 9) and through this to Tergite 9 (Tg 9) is typical for the genera. If a ventral vesicle is present, the Sg is always separated from the St 9 that is restricted to a well sclerotized arch connecting ventrobasal corners of Tg 9; the vesicle is located on this arch-like St 9, and not on the Sg ( Figs. 32–48 View FIGURES 32–48 , Table 4 View TABLE 4 ).
.
TABLE 3. Male epiproct of valid extant Capniidae genera. — in case of two character states the first one refers to the type species; for abbreviations of parts see Figs. 1-22.
| B-scl size, /Ep-scl | Lb-scl size, /Ep-scl | Ep-scl ventral connection | Ep-scl laterally | Ep-scl caudal setae | I-scl | Ec | Ll | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allocapnia | medium or large, fused | large, divided | entire | longitudinally divided | present | lacking | absent | present |
| Apteroperla | lacking? | large?, divided? | ? | entire | absent? | long, bifid? | present | absent |
| Arsapnia | lacking or vestigial | large, fused | entire | apically divided | present | lacking | absent | absent |
| Baikaloperla | lacking? | large, divided? | ? | longitudinally divided? | absent? | ? | absent? | absent? |
| Bolschecapnia | large, divided | small, divided | basal & apical or apical | apically or longitudinally divided | absent | long, divided hook or tube | present | absent |
| Capnia s.s. | vestigial | large, divided | entire | longitudinally divided | present | small, curved stick | present | vestigial |
| Capniella | lacking? | large, divided? | ? | longitudinally divided | present | ? | absent? | present? |
| Capnioneura | lacking | large, divided | entire | entire | absent | lacking | absent | absent |
| Capnopsis | small, divided | small, fused | apical | entire | present | long, erect stick | absent | absent |
| Capnura | lacking | large, divided | entire | entire | vestigial or present | lacking | absent | present |
| Eocapnia | large?, divided? | small?, fused? | ? | entire | absent? | ? | absent? | absent |
| Eucapnopsis | small, divided | small, divided | full divided | entire | absent | lacking | absent | absent |
| Isocapnia | large, divided | small, divided | entire | entire | absent | lacking | absent | absent |
| Mesocapnia | small, fused or divided | small, fused | entire | entire | present | lacking | absent | absent |
| Nemocapnia | large, divided | small, divided | entire | entire | absent | lacking | absent | absent |
| Paracapnia | vestigial or large, divided | large, hardly divided | entire | entire | absent | lacking | present | absent |
| Takagripopteryx Utacapnia | large, divided? lacking | small, fused? medium, fused | basal & tip? entire | entire? entire | absent? present | lacking? lacking | absent? absent | absent present |
| Zwicknia | large, divided | small, divided | basal & tip | apically divided | absent | long, open tube | present | absent |
TABLE 4. Male terminalia (besides epiproct) of valid extant Capniidae genera. — in case of two character states the first or the non-parenthesised one refers to the type species; for abbreviations of parts see Figs.7-10, 23, 35, 81.
| Sg/Tg 9 | Vesicle | Cercal | Pp apical | Fp length & | Fp/Rp | Tg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| segments | part | width | processes | ||||
| Allocapnia | fused | absent | many | long, | medium, wide | divided | Tg (7-) 8 |
| tapering | |||||||
| Apteroperla | fused | absent | many | short | short, wide | divided | Tg (6-7-) 8 |
| Arsapnia | fused | absent | many | long, wide | long, narrow | divided | Tg 7 |
| Baikaloperla | divided? | absent | many | long, wide | ? | ? | Tg 7-8 |
| Bolschecapnia | divided | present | many | long, | long, narrow | divided | absent |
| narrow | or T 9 | ||||||
| Capnia s.s. | fused | absent | many | long, wide | long, medium | fused | Tg 7 |
| Capniella | hardly | absent | many | long, | ? | ? | Tg 6-7 (-8) |
| separated | wide? | ||||||
| Capnioneura | fused | absent | one | needle- | long, narrow | fused | absent |
| like | |||||||
| Capnopsis | fused | absent | few | short, | medium, wide | divided | absent |
| wide | |||||||
| Capnura | divided | absent | many | medium, | long, narrow | divided | Tg 7 (6-8) |
| tapering | |||||||
| Eocapnia | fused | absent | many | long, | medium, wide | fused | Tg (7) 8 |
| wide? | |||||||
| Eucapnopsis | divided | present | few | medium, | long, medium | fused | absent |
| tapering | |||||||
| Isocapnia | divided | present | many | long, wide | long, very | divided | absent |
| narrow | or Tg 9 | ||||||
| Mesocapnia | fused | absent | many | long, | long, medium | divided | absent |
| narrow | |||||||
| Nemocapnia | hardly | absent | few | short, | medium, wide | fused | Tg 9 |
| separated | narrow | ||||||
| Paracapnia | fused | absent | many | long, | short or | divided | absent |
| narrow | medium, wide | ||||||
| Takagripopteryx | fused | absent | many | medium, | short, wide | fused | Tg 8 (-9) |
| tapering? | |||||||
| Utacapnia | fused | absent | many | long, wide | long, wide | divided | absent |
| Zwicknia | divided | present | many | short, | long, narrow | divided | Tg 9 |
| wide |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.